Abstract
Abstract 3574
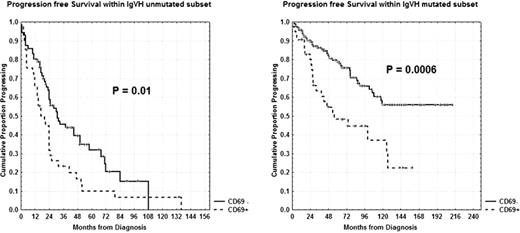
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) is a very heterogeneous disease with some patients experiencing rapid disease progression and others living for years without requiring treatment and therefore it is mandatory to find new prognostic markers. CD69 overexpression which resembles B cells at an earlier and greater state of activation (Damle, 2002 and 2007) and induces increased proliferation and survival of leukemic B-lymphocytes, may reflect an aggressive and progressive clinical outcome. The primary endpoints of our research were: 1) to determine progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) upon CD69 in univariate analysis; 2) to correlate CD69 with other clinical or biological prognostic factors such as age, Rai stages, lymphocyte doubling time, beta-2 microglobulin, CD38, CD49d, ZAP-70, cytogenetics by FISH and IgVH status and finally, 3) to confirm CD69 as an independent prognostic factor. We investigated 417 patients (pts), median age 66 years (range 33–89), 239 males and 178 females. With regard to modified Rai stages, 127 pts had a low stage, 272 an intermediate stage and 18 a high stage. CD69 was determined by multicolor flow cytometry, fixing the cut-off value at 30%. CD69+ pts were 111/417 (26.6%). CD69 <30% was significantly associated with low Rai stage (111/127; P<0.0001), lymphocyte doubling time >12 months (260/337; P=0.0006), beta-2 microglobulin <2.2 mg/dl (176/218; P=0.0005) and soluble CD23 <70 U/ml (199/245; P<0.0001). Significant associations were found between CD69 <30% and ZAP-70 <20% (189/243; P=0.01) or CD49d <30% (135/171; P=0.007). There were significant correlations between CD69 <30% and IgVH mutated status (323 total cases, 169/211; P=0.001). On the other hand, no significant correlation was found with FISH cytogenetics (337 studied cases). With regard to clinical outcome, interestingly, 79 (71%) of 111 of the CD69+ patients had received chemotherapy at the time of analysis (P<0.00001). Moreover, both shorter PFS and OS were observed in CD69+ patients (5% vs 40% at 16 years, P<0.0001 and 26% vs 76% at 20 years, P<0.0001). To further explore the prognostic impact of CD69, we investigated its expression within unmutated (112 pts) and mutated (211 pts) IgVH subsets. As a matter of fact, pts with CD69 <30% showed longer PFS and OS both within the unmutated subgroup (32% vs 10% at 5 years, P=0.01 [Figure] and 77% vs 38% at 12 years, P=0.04) and within the mutated subgroup (56% vs 22% at 12 years, P=0.0006 [Figure] and 94% vs 70% at 16 years, P=0.05). In multivariate analysis of PFS, FISH cytogenetics (P=0.00005), ZAP-70 (P=0.0001), CD69 (P=0.002), Rai stages (P=0.001) and IgVH status (P=0.004) were independent prognostic factors. With regard to OS, age > or <60 years (P=0.001), CD69 (P=0.004), ZAP-70 (P=0.01) and CD38 (P=0.03) were identified as significant. Noteworthy, here, we demonstrated that CD69 is able to improve the historical prognostic ability of the IgVH mutational status. Since the IgVH mutated subset represents a large and heterogeneous population with a variable progression, CD69 may better define prognosis within this subgroup. Therefore, CD69, determined by flow cytometry, should be considered a novel important prognostic parameter in B-CLL and has to be necessarily added in a new scoring prognostic system. In fact, its easy and rapid laboratory determination allows us to identify early progressive pts in order to take timely therapeutic decisions.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal