Abstract
Abstract 4416
EspP (E. coli secreted serine protease, large plasmid encoded) is an extracellular serine protease produced by enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) O157:H7. Brunder et al. (Mol Microbiol 1997, 24:767–78) have shown that EspP cleaves, amongst other proteins, human coagulation factor V, and the authors hypothesized that it may contribute to the mucosal hemorrhage in patients with EHEC infection. We have since shown that EspP also cleaves factor VIII. Since the mechanism by which EHEC induces diarrhea-associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (D+HUS) has not been fully elucidated, and EspP has been cited as a putative virulence factor in D+HUS, we investigated the role of EspP in primary and secondary hemostasis in the pathogenesis of D+HUS.
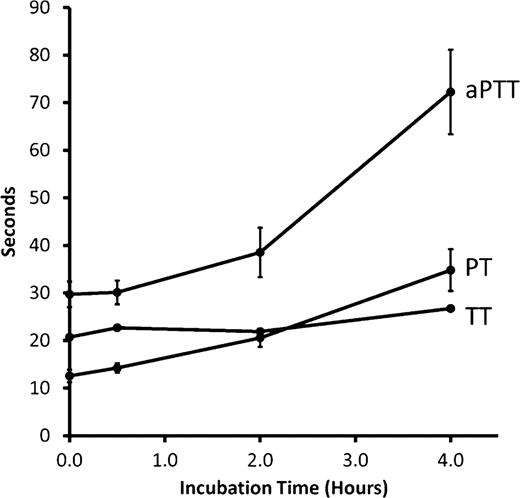
Wild type EspP (EspPwt) and EspPS263A, where the serine at the active site was mutated to an alanine thereby abolishing its proteolytic activity, were expressed in the non-pathogenic E. coli host BL21(DE3) and purified by hydrophobic interaction and size-exclusion chromatography. EspPwt at 1.0 mg/mL was incubated for 0.5, 2.0 and 4.0 hours ex vivo with citrated plasma from 6 healthy adults. EspPS263A, bovine serum albumin (BSA) and phosphate buffer saline-glycerol (PBS-G) served as negative controls. PT, aPTT and TT were found to be significantly prolonged and activity of factors V, VII, VIII and XII were reduced in a time- and concentration-dependent manner (Figures 1 and Figure 2). When citrated plasma was incubated with 1 mg/mL EspPwt at 37°C for 4 hours, PT was prolonged by 23.2 +/− 3.8 s, aPTT by 41.6 +/− 8.3 s and TT by 6.1 +/− 0.6 s, relative to the negative controls. Factor V activity decreased by 0.82 +/− 0.14 U/mL, factor VII by 0.72 +/− 0.28 U/mL, factor VIII by 0.69 +/− 0.31 U/mL and factor XII by 0.36 +/− 0.09 U/mL, relative to the negative controls. Prothrombin activity was significantly reduced (0.16 +/− 0.08 U/mL) compared to all negative controls but remained above 0.75 U/mL. Factors IX, × and XI activity, and fibrinogen concentration were not significantly different from the controls. To determine whether any cellular components in whole blood contribute to EspP's effect on the coagulation cascade, the experiment was repeated using citrated whole blood in place of plasma during the incubation phase. Plasma was then recovered and analyzed. Similar results were observed.
The results suggest that EspP has proteolytic activity against specific coagulation factors at least in an ex vivo setting. In patients with EHEC infection, EspP may contribute to the hemorrhagic diarrhea by impairing the coagulation cascade. Further studies are needed to determine whether EspP is able to induce coagulopathy in vivo and if so, whether induction of such a coagulopathic state may favour the entry of Shiga toxin into systemic circulation in patients with D+HUS.
EspP reduces coagulation factor activity in a time-dependent manner.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal