Abstract
Abstract 4988
Increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) has been described in multiple myeloma (MM) patients, particularly when exposed to immunomodulatory drugs. Epidemiological studies have showed that monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) patients also have an increased risk of VTE compared with normal subjects. Acquired activated protein C resistance (APC-R) is an independent risk factor for VTE in hematologic malignancies.
We reviewed the records of patients with MM and MGUS for APC resistance by PREFAKIT APC-R test. We excluded from the analysis patients with a documented Factor V Leiden mutation. The PREFAKIT APC-R is a plasma-based functional clotting assay based on the ratio of patient clotting time with and without APC which is standardized and reported as normalized ratio (normalized to results obtained on pooled normal plasma which is performed on each run).
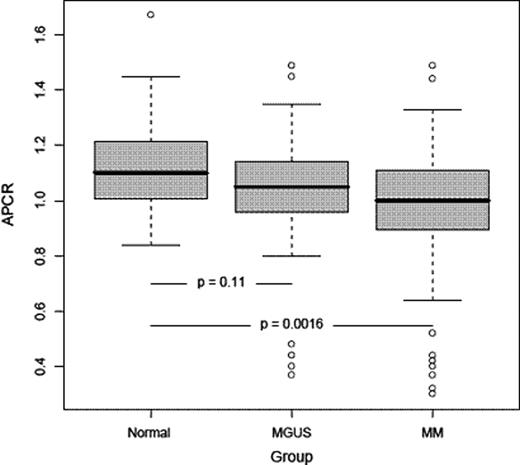
APC-R results from 33 MGUS and 75 MM patients were compared with 39 normal subjects. The median APC-R for MM, MGUS and normal subjects were 1, 1.05 and 1.1 respectively. MM patients compared to normal subjects, had significantly lower APC-R (P = 0.0016). No significant difference was observed between MGUS and normal subjects (P= 0.11) (Figure 1). Baseline characteristics from the three groups were similar in terms of age, sex, and performance status.
APC-R measured as continuous variable shows a statistically significant decrement in patients with paraproteinemias compared to normal subject and correlates to the underline hypercoagulability observed in patients with MGUS and MM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal