Abstract
Abstract 639
PNH is an acquired clonal hemolytic anemia associated with severe symptoms, life-threatening thrombosis, pulmonary hypertension (PH), chronic renal impairment (CRI) and bone marrow failure resulting in reduced quality of life (QoL) and survival (median: 10 – 15 years). Eculizumab is a monoclonal humanized antibody that inhibits terminal complement activity and thereby prevents intravascular hemolysis, reduces transfusions, improves QoL and protects against PH, CRI and thromboses. Eculizumab was approved for PNH in 2007 as a result of studies with short follow-up and with no information on it's impact on survival.
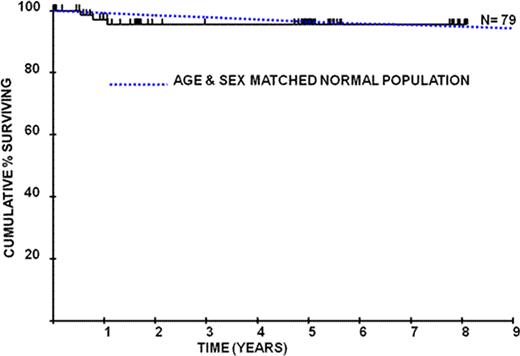
Kaplan-Meier survival plots depicting PNH patients on eculizumab compared to age and sex matched controls
Kaplan-Meier survival plots depicting PNH patients on eculizumab compared to age and sex matched controls
There were 34 thrombotic episodes in 21/79 patients (27%) prior to eculizumab and only 2 thromboses since. Importantly primary prophylaxis with warfarin has now been stopped in 21 patients (mean duration of 8.4 months (range: 1–25) and total of > 14 years) with no thromboses occurring. Seven patients had thrombosis within 12 months prior to starting eculizumab and they had no further thromboses on therapy. Therefore eculizumab is effective in preventing new, or evolution of pre-existing thrombosis, and appears to remove the need for primary prophylactic anticoagulation. We have not systematically stopped the anticoagulation of patients with a previous history of thrombosis. Patients had a mean of 19.9 units transfused (0-156) in the 12 months before eculizumab. Of the 64 patients on eculizumab for at least a year, 43 (67%) have been transfusion independent for >12 months. Twenty one patients still needing transfusions had a significant (P=0.028) reduction in their mean requirement of 24.6 (4-52) units in the 12 months before eculizumab compared to a mean of 14.6 (2-50) units in the last 12 months.
Eculizumab is well tolerated long-term (> 8 years of therapy) with continued improvement in PNH associated symptoms, reduction in transfusion requirements and a higher proportion of transfusion independent patients than previously seen. There is a significant reduction in the development of thromboembolism on eculizumab therapy and importantly we have been able to stop primary prophylaxis with warfarin in 21 patients without any thrombotic complications. We demonstrate for the first time that eculizumab has a major impact on survival in PNH so that survival is comparable to an age- and sex-matched control population.
Kelly:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Hill:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Richards:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Arnold:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Hillmen:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.

This icon denotes an abstract that is clinically relevant.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal