Abstract
Abstract 734
Severe hemophilia A is an X-linked congenital bleeding disorder occurring in 1:5,000 male births. Among neonates with severe hemophilia A, failure to recognize hemophilia and associated bleeding may result in severe blood loss anemia from circumcision, central nervous system (CNS) bleeding during the birth process or with head trauma and associated neurologic sequelae, and unrecognized joint bleeding that, when recurrent, increases the risk of joint damage which may lead to chronic disability. In at least one-third of cases, the disease arises as a spontaneous mutation: yet, even among the two-thirds with a family history, most carriers do not undergo carrier testing or prenatal diagnosis, leaving only a minority in whom cord blood screening is performed. About half of newborns with severe hemophilia A have a factor VIII (F.VIII) intron 22 inversion mutation, readily detected by PCR screening. We, therefore, sought to determine the effects of newborn screening by F.VIII intron 22 inversion PCR on early diagnosis in children with severe hemophilia A, specifically, on prevention of early life bleeding and associated cost, morbidity, and quality of life.
We constructed a decision tree model to evaluate the cost effectiveness of newborn F.VIII intron 22 screening for severe hemophilia A. We assumed all newborn males were tested as part of screening, and that treatment modifies the likelihood of bleeding but not bleeding associated morbidity. Rates of major and minor CNS, joint, and procedural/surgical bleeding, including circumcision, morbidity and mortality, cost, and quality of life utilities were obtained from the literature. We assumed the cost of intron 22 PCR testing to be $3.00 per newborn male, that test results were available within 2 days of screening, and that clotting factor was infused prior to procedures and at the first sign of joint bleeding or head trauma. The probability of severe bleeding requiring hospitalization or red blood cell transfusion was estimated to be 5% or less in children with severe hemophilia A. The cost of F.VIII concentrate was based on the average wholesale price, and transfusion and hospitalization costs were based on local data. Outcomes included medical costs for each bleeding event, effectiveness measured as quality-adjusted-life-years (QALY), and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) over the first two years of life. Sensitivity analysis was used to test the robustness of analysis results.
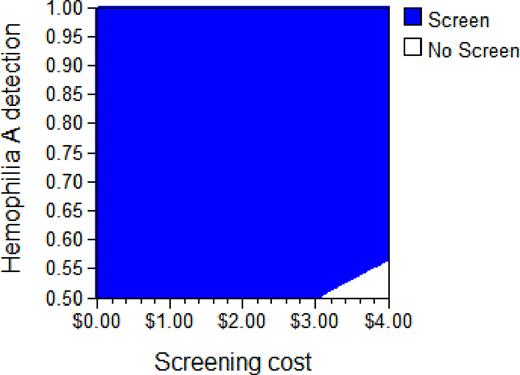
Compared to no screening, screening for hemophilia had an ICER of $96,918/QALY, a value considered economically reasonable. Results were sensitive to variation of screening cost and overall detection of hemophilia A by PCR screening (base case 50%). Effects of varying both these parameters in a two-way sensitivity analysis are shown in the Figure. Using a $100,000 per QALY cost-effectiveness criterion over the depicted ranges for both parameters, screening was favored if screening cost ≤$3 or if ≥56% of all newborns with hemophilia A were detected by screening.
It is cost effective to perform factor VIII intron 22 PCR screening to identify severe hemophilia A in newborn males in order to prevent bleeding morbidity, if the cost of the test does not exceed $3.00.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal