Abstract
Abstract 1640
The introduction of radioimmunotherapy (RIT) into clinical practice for the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL) occurred at a time at which many patients did not have prior exposure to rituximab. Clinical trials in the relapsed/refractory setting, as well as consolidation in the upfront setting have included a small number of patients that had been previously treated with rituximab or a rituximab containing treatment regimen. We evaluated the effect of prior rituximab therapy on the efficacy of RIT.
The prospective lymphoma database was queried for all patients having received a single dose of yttrium-90 ibritumomab tiuxetan for relapsed/refractory FL which had previously been treated with systemic therapy (patients receiving only prior external beam radiation therapy were excluded). The database includes all consecutive adult patients diagnosed with lymphoma seen at Mayo Clinic Rochester. The diagnosis of follicular lymphoma was as by WHO classification and centrally reviewed. Patients with evidence of histologic transformation to diffuse large B cell lymphoma prior to RIT were excluded. Time to treatment failure (TTF) was defined as the time from RIT to next anti-lymphoma therapy.
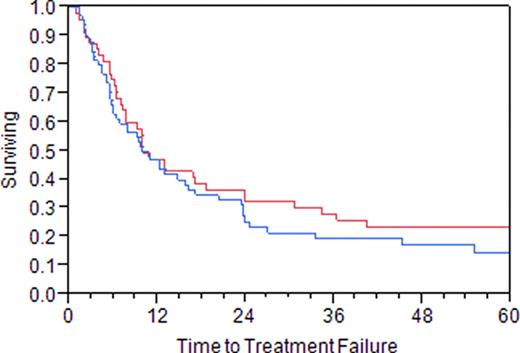
111 patients were identified. 57 (51%) were male. Median age at time of RIT was 58 (19–88). Median time from diagnosis to RIT was 35 (6–281) months in patients having received prior treatment with rituximab and 47 (12–272) months in those who had not (p=0.19). 63 (57%) of patients received prior treatment with rituximab or rituximab containing chemotherapy. Median number of prior therapies was 2 (1–10), which was not different between the rituximab treated or untreated groups [2(1–6) vs 2(1–10) p=0.12]. Median TTF was 10.0 months in the patients having received prior rituximab and 10.1 months in those that had not (p=0.29). Figure 1. The median overall survival from RIT was not reached, but appeared similar (Kaplan-Meier estimate 125 months without prior rituximab exposure vs 95 months with prior rituximab exposure; p=0.33).
Time to treatment failure (Prior treatment with rituximab = blue; No prior treatment rituximab = red)
Time to treatment failure (Prior treatment with rituximab = blue; No prior treatment rituximab = red)
Prior rituximab exposure does not seem to adversely impact the time to treatment failure or overall survival in those patients treated with RIT. While the data leading to the approval of RIT were accrued prior to the routine clinical use of rituximab, our data demonstrate similar clinical benefit of RIT in patients with prior exposure to rituximab or rituximab containing therapy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal