Abstract
Abstract 1694
Clonal evolution (CE) and variant Philadelphia (Ph) chromosomal translocations (vPh) are seen in <10% of newly diagnosed CML patients. While the vPh is thought to have no prognostic significance, CE maybe associated with an inferior outcome compared to the presence of a single standard Ph for patients treated with imatinib (IM). This study aims to evaluate the prognostic significance of vPh and clonal evolution in a cohort of CML chronic phase (CP) and accelerated phase (AP) patients treated with IM.
From June 1999 to December 2008, 247 Ph+ CML CP and AP patients treated with IM (300–600 mg daily) were analyzed. Patients having had a prior allogeneic stem cell transplant were excluded. Patients were categorized into 4 groups according to karyotype at diagnosis: Group 1 (CP with CE only, n=28); Group 2 (AP, n=31); Group 3 (CP with vPh, n=20); Group 4 (CP with standard Ph, n=168). Cytogenetic response, treatment failure, event free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated for each group and multivariate analysis was performed to determine potential variables predictive of response and survival.
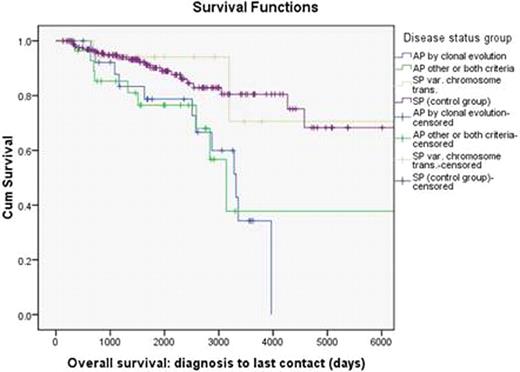
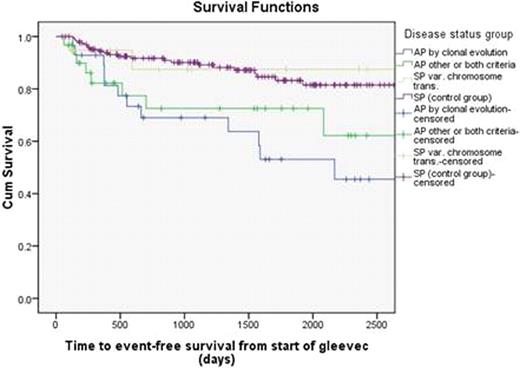
Groups 1 and 2 had lower complete cytogenetic responses (CCR) to IM and higher rates of treatment failure compared to Group 4. (Table1). At a median follow up 4.2 years, Groups 1 and 2 had lower median OS and EFS compared to Groups 3 and 4 (Table1). The 5 year probabilities of OS and EFS were 79 % and 53 % (Group 1), 77 % and 73 % (Group 2), 94 % and 87 % (Group 3), and 90 % and 83 % (Group 4). (Figures 1 and 2).
Clinical characteristics and outcome between groups
| . | Grp 1 (CE) . | Grp 2 (AP) . | Grp 3 (vPh) . | Grp 4 (CP) . | Total . | P value . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 28 (11%) | 31 (13%) | 20 (8%) | 168 (68%) | 247 (100%) | – | |
| Median age (years) | 47.3 | 47.7 | 40.4 | 48.1 | 47.3 | – | |
| CCR | 15 (54%) | 17 (55%) | 11 (55%) | 129 (77%) | 172 (70%) | .01 | |
| Status last follow up | Alive | 16 (57%) | 21 (70%) | 18 (90%) | 146 (87%) | 201 (82%) | 0.001 |
| Death | 12 (43%) | 9 (30%) | 2 (10%) | 22 (13%) | 45 (18%) | ||
| Treatment failure | No event | 13 (46%) | 10 (36%) | 10 (53%) | 108 (65%) | 141 (58%) | 0.015 |
| Event | 15 (54%) | 18 (64%) | 9 (47%) | 59 (35%) | 101 (42%) | ||
| Median event free survival (months) | 72 | 96 | not reached | not reached | not reached | 0.001 | |
| Median overall survival (months) | 111 | 105 | not reached | not reached | not reached | 0.002 | |
| . | Grp 1 (CE) . | Grp 2 (AP) . | Grp 3 (vPh) . | Grp 4 (CP) . | Total . | P value . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 28 (11%) | 31 (13%) | 20 (8%) | 168 (68%) | 247 (100%) | – | |
| Median age (years) | 47.3 | 47.7 | 40.4 | 48.1 | 47.3 | – | |
| CCR | 15 (54%) | 17 (55%) | 11 (55%) | 129 (77%) | 172 (70%) | .01 | |
| Status last follow up | Alive | 16 (57%) | 21 (70%) | 18 (90%) | 146 (87%) | 201 (82%) | 0.001 |
| Death | 12 (43%) | 9 (30%) | 2 (10%) | 22 (13%) | 45 (18%) | ||
| Treatment failure | No event | 13 (46%) | 10 (36%) | 10 (53%) | 108 (65%) | 141 (58%) | 0.015 |
| Event | 15 (54%) | 18 (64%) | 9 (47%) | 59 (35%) | 101 (42%) | ||
| Median event free survival (months) | 72 | 96 | not reached | not reached | not reached | 0.001 | |
| Median overall survival (months) | 111 | 105 | not reached | not reached | not reached | 0.002 | |
CE = Clonal evolution, AP = Accelerated phase, vPh = variant Philadelphia chromosomal translocations, CCR = Complete cytogenetic response
In multivariate analysis, the only significant factors predictive of CCR were Sokal score (p=.01), CE at diagnosis (p=.03) and dose of IM (p=.03). When the analysis was restricted to EFS and OS, the presence of CE at diagnosis (p<0.0001), prior treatment before IM (p=0.04), the dose of IM (p=0.01) and the response to IM (p<0.0001) were the factors associated with significant EFS and the presence of CE at diagnosis (p=0.004), the dose of IM (p=0.05) and the response to IM (p<0.0001) were predictive of OS. The presence of a vPh had no effect on EFS and OS.
The presence of CE at diagnosis and/or features of AP in patients with CML treated with IM are associated with an inferior prognosis, but the presence of the vPh does not appear to have any prognostic significance. It remains to be determined whether the second generation TKI's can overcome the negative influence of CE on EFS and OS.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal