Abstract
Abstract 1845
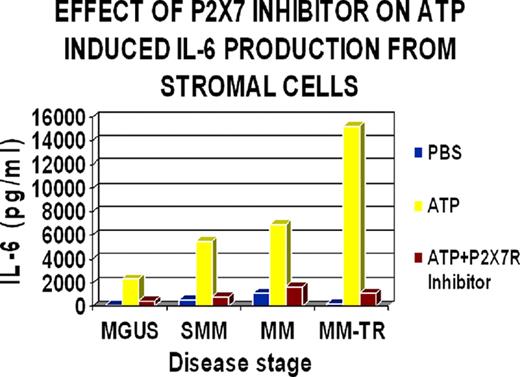
Inflammation is a driving factor in the pathogenesis of many cancers including multiple myeloma (MM). The active role that cytokines play, IL-1β in particular, during the early stages of MM has been extensively characterized. Myeloma is a plasma cell tumor whose early stages are characterized by cytokine dependent growth, predominantly driven by IL-6. We have demonstrated that IL-1β is a key inducer of IL-6 expressed by bone marrow stromal cells in a paracrine fashion during the progression of multiple myeloma from smoldering myeloma (SMM) to active disease (Mayo Clinic Proc 84:114 (Feb. 2009)). Elevated ATP levels have been documented in vivo in tumor micro-environments and is a potential contributing factor to IL-1β induced inflammation. The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) is an ATP-gated ion channel expressed by cells of the hematopoetic lineage that has been shown to play a critical role in IL-1b processing and secretion. We investigated the role this receptor may have in the release of IL-1β in the bone marrow microenvironment using bone marrow samples from both chemotherapy treated and untreated patients.
Myeloma cell lines were evaluated by RT-PCR for the expression of P2X7R mRNA. Expression was detected and confirmed by sequencing in ANBL-6, MM1.S, U266, RPMI-8226 and KAS-6/1 and was comparable to U937, a previously characterized P2X7R positive cell line. A newly derived plasmacytoma cell line, PCYT3, showed very low levels of message expression. The ability of ATP, the P2X7R agonist, to trigger the processing and release of IL-1β by activation of the P2X7 channel was studied using KAS-Pro, a myeloma cell line stably transfected with a pro- IL-1β gene. IL-1β, measured by ELISA, was released in a dose dependent fashion in response to increasing amounts of ATP ranging from.6mM to 5mM. Four P2X7R specific antagonists were tested for their effect on ATP stimulated IL- 1β release from KAS-Pro; all 4 compounds demonstrated inhibition in a dose dependent manner with varying degrees of potency correlating with P2X7R inhibition.
These results confirm the activity of functional P2X7 receptors on myeloma cell lines and in fresh patient samples and suggest a role for the use of P2X7 receptor antagonists in the therapy of myeloma, particularly in patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Hromockyj:Pfizer Corporation: Employment. Meyer:Pfizer Corporation: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal