Abstract
Abstract 1981
Immune reconstitution after HCT is important for curbing infections and malignancy. ATG has been increasingly used to prevent graft-vs-host disease (GVHD), however, its impact on immune reconstitution has not been well studied. Here we studied (1) immune reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT, (2) compared it to non-ATG-conditioned HCT, and (3) determined factors influencing the immune reconstitution.
Immune subset cell counts were determined on day 28, 56, 84, 180, 365 and 730 post transplant in 125 recipients of allogeneic filgrastim-mobilized blood stem cells who received ATG (Thymoglobulin, 4.5 mg/kg) during conditioning. The subset counts were also determined in 47 non-ATG-conditioned patients (otherwise similarly treated). Subset counts (in blood) and ATG levels (in serum) were quantified by flow cytometry. Mann-Whitney rank sum test was used to compare subset counts (1) in ATG-conditioned patients vs donors, (2) in ATG-conditioned patients vs non-ATG-conditioned patients, and (3) between subgroups of ATG-conditioned patients; Spearman rank correlation test was used to determine associations between subset counts and ordinal variables like ATG levels.
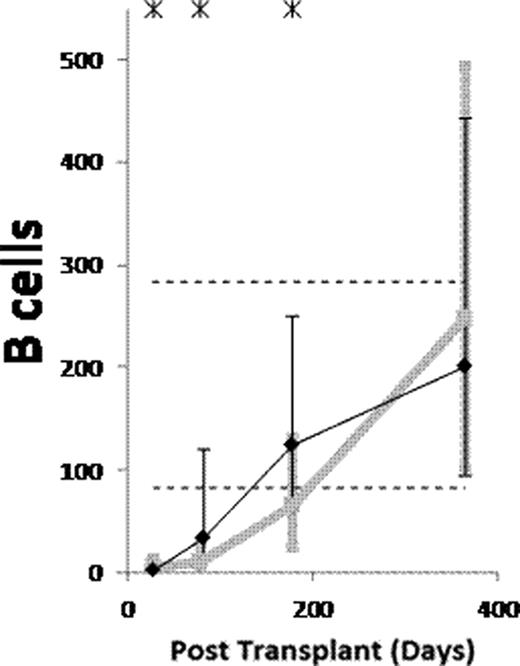
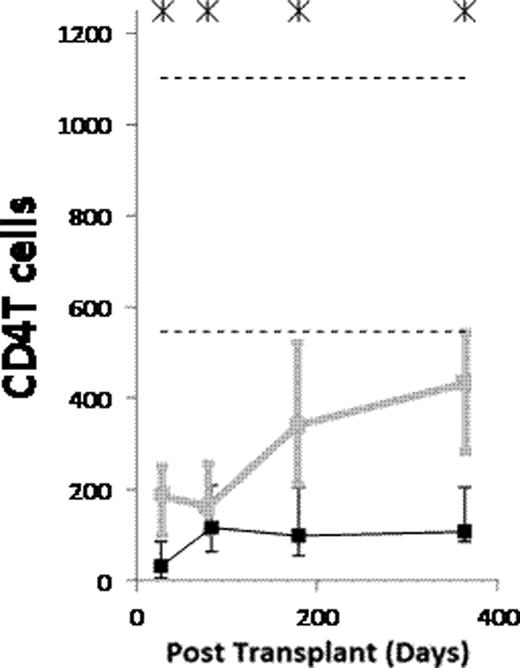
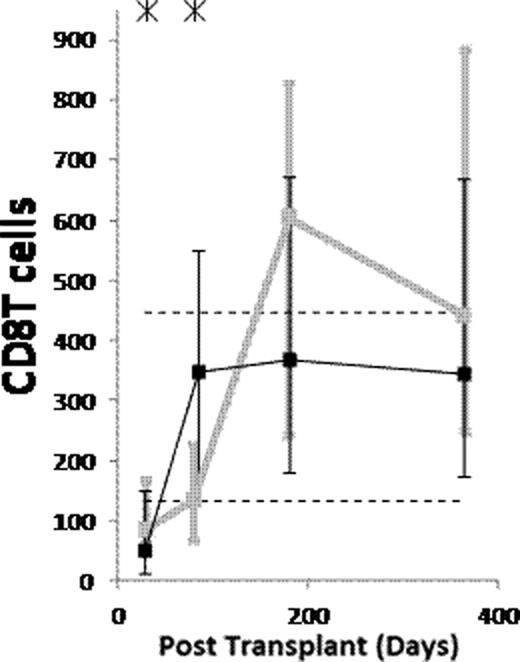
(1) After ATG-conditioned HCT, the counts of the following subsets normalized (became not significantly lower than in donors) by day 28: NK cells, monocytes, myeloid dendritic cells (MDCs), and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDCs). The counts of the following subsets normalized by day 84: memory/effector CD8 T cells, and CD4−CD8− T cells. The counts of naïve B cells normalized by day 180. The counts of the following subsets have not normalized by day 365 or 730: memory B cells (both isotype switched and unswitched), both naïve and memory/effector CD4 T cells, naïve CD8 T cells, CD4+CD8+ T cells, and invariant NKT (iNKT) cells. (2) Compared to non-ATG-conditioned HCT, counts of B cells, CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells were significantly lower after ATG-conditioned HCT on day 28. Thereafter, recovery of both naïve and memory B cells and memory/effector CD8 T cells was significantly faster in ATG-conditioned patients, leading to higher total B and higher total CD8 T cell counts on day 84 (Figure). On the contrary, recovery of naïve CD8 T cells and both naïve and memory/effector CD4 T cells was significantly slower, the latter leading to low total CD4 T cell counts throughout the first year (Figure). (3) Reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT was influenced by (a) the number of cells of the same subset transferred with the graft in case of increased memory B cells, naïve CD4 T cells, naïve CD8 T cells, iNKT cells and MDCs, (b) age of recipient in case of decreased naïve CD4 T cells and naïve CD8 T cells, (c) cytomegalovirus (CMV) serostatus of recipient in case of increased memory/effector T cells, (d) GVHD in case of increased naïve B cells, and (e) day 7 or 28 ATG levels in case of decreased T cell subsets.
(1) Reconstitution after ATG conditioned HCT is very fast for NK cells, monocytes, MDCs and PDCs, fast for memory/effector CD8 T cells and CD4−CD8− T cells, slow for naïve B cells, and very slow for memory B cells, both naïve and memory/effector CD4 T cells, naïve CD8 T cells, CD4+CD8+ T cells and iNKT cells. (2) Compared to no ATG, the patients conditioned with ATG have lower counts of B and T cells on day 28. Thereafter, the ATG-conditioned patients have faster recovery of both naïve and memory B cells and memory/effector CD8 T cells, and slower recovery of both naïve and memory/effector CD4 T cells and naïve CD8 T cells. (3) Similar to what has been described for non-ATG-conditioned HCT, reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT is influenced by the number of the immune cells transferred with the graft, recipient age, recipient CMV serostatus and GVHD. Moreover, the reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT is influenced by ATG clearance.
Counts of B cells, CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells per μL of blood in patients conditioned with (Black) and without (grey) ATG. Asterisks denote p<0.05. Dashed lines denote 10th and 90th percentiles for donors.
Counts of B cells, CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells per μL of blood in patients conditioned with (Black) and without (grey) ATG. Asterisks denote p<0.05. Dashed lines denote 10th and 90th percentiles for donors.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal