Abstract
Abstract 2527
In contrast to most translocations affecting the MLL gene, the t(9;11) is not associated with a markedly poor prognosis. Several studies revealed a very favorable outcome in the pediatric patient group. In adult AML, the t(9;11) has also been associated with superior survival, at least compared to other 11q23 abnormalities. Therefore, 11q23 rearrangements in adult AML are now often dichotomized into t(9;11) and non-t(9;11), with the former being included in the intermediate-risk group and the latter in the adverse-risk group. The proposed European Leukemia Net (ELN) cytogenetic reporting criteria reflect this division. We investigated whether the outcome of AML patients treated with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) with t(9;11) remains significantly different from the rest of the adverse-risk cytogenetic group.
Conventional cytogenetics and FISH data from diagnostic bone marrow of 110 adult AML patients treated with HSCT was reviewed and patients classified according to the recommendations of the European Leukemia Net and included 32 with favorable risk, 60 in the intermediate-risk group, and 18 in the adverse-risk group. FISH confirmed MLL rearrangement in cases with apparent 11q23 abnormalities. We compared outcome of patients with t(9;11) to the group of patients with adverse-risk cytogenetics that included all MLL-positive non-t(9;11) among other cytogenetic abnormalities classified adverse-risk. Our study included 62 (56%) patients treated in first remission (CR1), while most non-CR1 AML patients were treated with HSCT in CR2. Patients were between 14 and 57 years, with median age of 25 years.
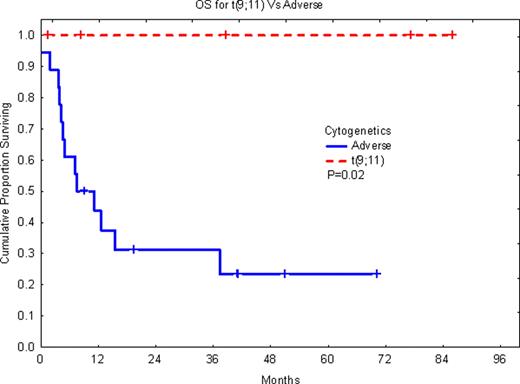
Of the 110 AML patients, 9 (8%) had MLL gene rearrangement. Of these patients only 5 (4.5% of all patients) had t(9;11). When all patients with MLL rearrangement were considered, there was no significant difference between this group and the patients with adverse-risk cytogenetics in overall survival (OS) or event-free survival (EFS). In contrast, when only patients with the t(9;11) were considered, the t(9;11) patients had significantly longer OS (P=0.02) and EFS (P=0.03) as compared with patients with adverse cytogenetics including all non-t(9;11) MLL-rearranged cases. The outcome of MLL-positive non-t(9;11) patients was similar to the group with adverse-risk cytogenetics. MLL rearrangements in the non-t(9;11) group included t(4;11)(q21;q23), t(6;11)(q27;q23) and a variant t(6;11;7)(q27;q23;q11.2), as well as t(11;17)(q23;q25). The survival for patients with t(9;11) remained significantly longer even when only patients treated with HSCT in first remission were considered, although numbers were small. All five patients with t(9;11) were treated with HSCT in CR1.
The data supports the conclusion that MLL-positive t(9;11) AML patients should be classified differently from the rest of the MLL-rearranged cases and should be considered as part of the intermediate-risk group. This classification separating the t(9;11) cases from the rest of the MLL-positive cases should be maintained even when patients are treated with allogeneic HSCT.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal