Abstract
Abstract 2701
The First-Line Indolent Trial (FIT) demonstrated that administration of a single infusion of 90Y-RIT to follicular lymphoma grade 1 or 2 patients with CR or PR after induction chemotherapy could significantly prolong remissions over no further therapy. Only 13% of patients in that trial received rituximab with their first-line chemotherapy and maintenance rituximab was not administered [JCO 2008;26(32):5156–63]. We report a phase II study of safety and efficacy of 90Y-RIT following R-CHOP chemotherapy in patients with high-risk advanced stage FL. Maintenance rituximab is given every 3 months post 90Y-RIT, for 24 months. The protocol accrues up to 33 evaluable patients. First-time novel insights into the biologic and immunologic effects of this combination regimen are presented.
The primary endpoint of our study is the final complete response (CR) rate, defined according to the Cheson criteria and measured 3 months after day 1 of the 90Y-RIT therapy. The CR rate among similar risk advanced stage FL patients after R-CHOP is known to be about 20% [Blood 2005;106(12):3725–32]. The current study is designed to detect a significantly greater response rate of 40% with a p value of 0.05 and a power of 80%.
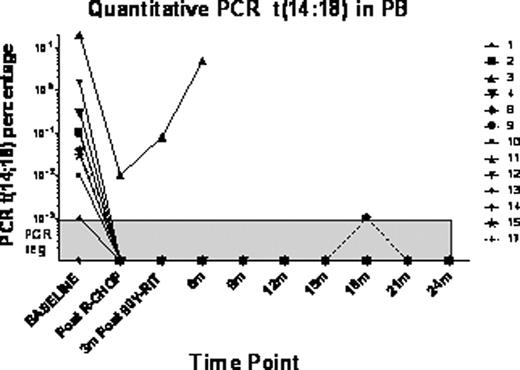
Secondary outcomes included molecular remission and immunologic effects. Since molecular remission is associated with prolonged survival [Blood 105(9): 3428–3433], we analyzed quantitative PCR for up to two years post 90Y-RIT therapy on a subset of patients with baseline PCR detectable t(14:18) lymphoma.
In patients who had PCR detectable t(14;18), quantitative real-time PCR was performed on blood and available bone marrow, at baseline, post 6xR-CHOP and Q 3 months post 90Y-RIT treatment for 24 months. The sensitivity of our PCR assay was 1 in 105 cells. Flow cytometry for % B cell clonality was performed at the same time points. T and B cell counts, Ig levels and vaccine serology have been recorded pre and post treatment. Genotyping of FCGR3A polymorphism was performed.
24 pts have been enrolled with a median age of 54 yrs, 79% stage 4, 63% high FLIPI, 38%, intermediate FLIPI. 10 of 19 [53%] patients had a complete response (CR/CRu) to R-CHOP and the remaining 9 showed partial response (PR). One patient died due to sepsis prior to 90Y-RIT. 5 Patients with a partial response post R-CHOP converted to CRu post 90Y-RIT resulting in 14 of 18 (77%) patients who achieved CR/Cru. One patient progressed 6 m post 90Y-RIT, another relapsed at 12 months. One pt developed a secondary malignancy by 9 m. There were no SAEs attributable to the 90Y-RIT treatment.
16 of 24 (67%) had PCR detectable t(14:18) translocations. Quantitative PCR measurements were concordant with flow cytometry. 18 have been evaluated post 90Y-RIT. 12/13 (92%) of these pts became PCR negative in blood. Post 90Y-RIT, one pt relapsed and showed increase in PCR levels. All remaining pts with PCR markers are PCR negative in blood as far as 24 m post 90Y-RIT.
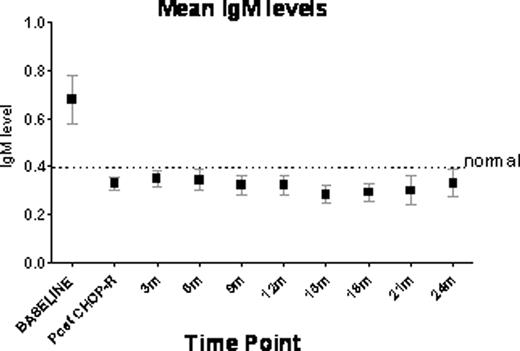
CD3+T cell counts remained normal, but CD19+B cells fell below the 1% detection level by flow cytometry during the two yrs of maintenance therapy post 90Y-RIT. 16 patients have been followed for more than 6 m and 8 pts for 18–24 m with no significant increases in the CD19+ B cell numbers. Interestingly, mean IgG levels remained close to normal, but mean IgM levels fell below normal. Memory immune responses to measles and mumps were maintained post chemo-radiotherapy. Antibody titres to Rubella did not change significantly post 90Y-RIT.
We found effective eradication of follicular lymphoma from the blood and bone marrow of the high risk lymphoma pts with first line treatment of 6xRCHOP and all but one of our evaluable patients (92 %) achieved molecular remission in blood post 90Y-RIT. Molecular remission was sustained with maintenance rituximab after 90Y-RIT up to 2 years. Longer follow-up will be necessary to determine the precise response duration. Our molecular response results compare favourably with those of the FIT trial. [JCO 2009;27(34):6094–00].
In our trial, IgG levels remain close to normal indicating that memory B cells are intact and this was consistent with no significant change in titres to common previously vaccinated pathogens such as rubella. A reduction in IgM levels indicating potential functional consequences in mounting primary humoral responses was documented.
Off Label Use: Zevalin in first line follicular lymphoma.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal