Abstract
Abstract 3110
High-dose therapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is standard therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL), although the optimal conditioning regimen remains uncertain. The three drug alkylating agent regimen, BuMelTt, has been established as our institutional regimen. We performed a retrospective review of outcomes obtained with BuMelTt compared to those achieved with other standard conditioning regimens.
133 patients with relapsed/refractory HL who underwent ASCT between January 1990 and December 2009 were analyzed. 62 patients received BuMelTt and 71 patients received other standard preparative regimens (Standard) consisting of CBV (44), CyVp16TBI (20), BEAM (4), CyTBI (2), and Mel (1). The median follow-up (range) was 4.3 years (0.01–14.24) in BuMelTt and 3.9 years (0.07–20.21) in Standard. The two groups (BuMelTt vs Standard) were balanced for gender (65% male vs 65% male), median age (29 vs 33), median number of prior regimens (2 vs 2), and pre-transplant disease status. Disease status was categorized as PR2/CR2 (48% vs 42%), primary induction failure sensitive (16% vs 17%), and Other which included PIF-refractory, 1st relapse refractory, and greater than 1st relapse (35% vs 41%).
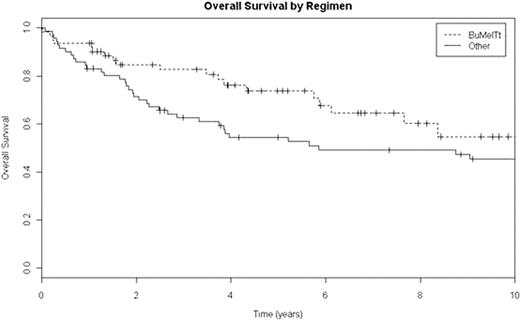
The 5 year overall survival (OS) was superior for patient who received BuMelTt conditioning (74% vs 54%, p = 0.03). There was also a trend for improved 5 year event free survival (EFS) for BuMelTt at 56% vs 39% for Standard (p=0.07). Other risk factors for outcome after ASCT were also analyzed and included disease status, more than 2 chemotherapy regimens before ASCT, Karnofsky score < 90% at ASCT, time from diagnosis to ASCT < 12 months, prior extranodal involvement, and age > 40 years. By univariate analysis, >2 chemotherapy regimens before ASCT (HR 1.7, p=0.05) and disease status of Other (HR 2.8, p<0.01) were predictive for lower OS. There was a trend for influence on OS for BuMelTt (HR 0.6, p=0.07) and PIF-sensitive (HR 1.9, p=0.09). By multivariate analysis, disease status of PIF-sensitive or Other predicted worse outcomes for OS (HR 2.4 & 2.9, p 0.03 & <0.01, respectively), and there was still a trend for benefit with BuMelTt (HR 0.6, p=0.09), although >2 chemotherapy regimens lost significance (p=0.22). For EFS, disease status of PIF-sensitive or Other were prognostic in univariate analysis (HR 2.1 or 2.3, p=0.02 or <0.01, respectively), and there was a trend for improved EFS with BuMelTt (HR 0.66, p=0.08). In multivariate analysis, disease status of PIF-sensitive or Other remained prognostic (p=0.03 & 0.004, respectively), while BuMelTt was not significant (p=0.27).
There was no significant difference in 100 day non-relapse related mortality for BuMelTt vs Standard conditioning (5% vs 3%, p=0.88). More patients developed NCI CTCAE grade 3/4 mucositis with BuMelTt than Standard (89% vs 61%, p<0.01), but fewer patients had bacteremia with BuMelTt than Standard (7% vs 23%, p=0.02). There was no difference in duration of hospitalization, episodes of febrile neutropenia, incidence of veno-occlusive disease, time to neutrophil engraftment, or time to platelet engraftment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal