Abstract
Abstract 3716
Rituximab monotherapy as initial treatment for low-grade B-cell lymphomas produces responses in approximately 70% of patients with one third achieving a complete response, and progression-free survival (PFS) of approximately 2 years. Maintenance rituximab appears to prolong initial remissions after rituximab alone. Current dosing for rituximab is largely empiric, so we sought to investigate whether increased doses of rituximab induction would increase the complete response rate (CRR) over that expected from standard dose rituximab. We also sought to assess whether high-dose induction followed by standard maintenance would produce a PFS comparable with that of combination chemoimmunotherapy strategies.
We conducted a phase II trial of increased-dose rituximab monotherapy induction, followed by a standard maintenance schedule. Eligible patients were adults with previously untreated low-grade B-cell lymphomas with measurable disease >2cm and were not candidates for potentially curative radiotherapy to localized disease. Subjects were treated with induction rituximab at a dose of 750 mg/m2 on days 1,8,15, and 22. Patients without progressive disease were then treated with maintenance rituximab at 375mg/m2 every 3 months for 8 doses or until disease progression. The primary end point was CRR as defined by the International Workshop Response Criteria (1999). Secondary endpoints included overall response rate (ORR), PFS, and toxicity. The study was designed with 90% power to show a 50% CRR, with a 30% CRR considered unworthy of further study.
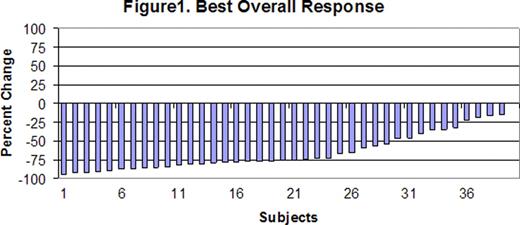
Between August 2009 and August 2010, 40 eligible subjects were enrolled (31 grade 1–2 follicular lymphomas, 4 marginal zone lymphomas, 3 small lymphocytic lymphomas, and 2 indolent B cell lymphoma not otherwise specified). The median age was 60 (range 36–88) All subjects had advanced Ann Arbor stage disease. Twenty-two subjects (55%) had involvement of >4 nodal sites, 6 (15%) had a Hgb <12 and 9 (23%) had an elevated LDH. Six subjects (15%) were low risk by the follicular lymphoma prognostic index(FLIPI), 15 (38%) were intermediate risk, and 17 (43%) were high risk. The FLIPI was not available for 2 patients. One patient was not evaluable for the 4 week response assessment in induction due to withdrawal of consent after 3 weeks of therapy. After induction therapy, 1 subject had a CR (3%), 18 had a PR (46%), and 20 had SD (51%). No subjects had progressive disease after induction and all evaluable patients had a reduction in tumor size. With a median number of 4 (range 1–6) maintenance cycles, the CRR increased to 30%, with PRR of 38% and SD in 15% (fig. 1). The PFS at 12 months was 89% [95% CI, 73– 96]. A total of 5 subjects progressed during maintenance therapy, 2 subjects after 3 cycles, 1 after 2 cycles and 2 after 1 cycle. Treatment was well tolerated with only 3 cases (7.5%) of grade 3/4 neutropenia. Twenty three (58%) subjects had allergic reactions with infusions but only 2 (5%) were grade 3 reactions.
Increased dose rituximab monotherapy is well tolerated, but does not improve the CRR compared to what would be expected from rituximab at standard doses. Significant improvement in the CRR occurred with ongoing maintenance therapy, and the vast majority of patients remain in remission after 1 year. Ongoing follow-up will determine whether this approach produces a PFS comparable to a chemoimmunotherapy treatment program.
Hochberg:Genentech: Consultancy. Fisher:Genentech: Consultancy. Abramson:Genentech: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal