Abstract
Abstract 4337
We investigated the molecular genetic basis of an ABO blood group discrepancy found incidentally in an individual with no transfusion or transplantation history. During routine preoperative blood grouping, red blood cells (RBCs) had a weak or mixed field reaction (double populations in a gel column) with anti-A, while serum typing showed the anti-B antibody. We sent the sample to a reference laboratory for ABO genotyping using sequencing analysis, and her genotype was reported to have O/O alleles. To resolve the genotype-phenotype discrepancy, we repeated the direct sequencing analysis and finally found a heterozygous insertion/deletion (indel) on exon 6, involving two major alleles and one minor allele. With cloning and sequencing analysis, we isolated the O01, O02, and A102 alleles, respectively. In addition, tri-allelic or tetra-allelic patterns in short tandem repeat (STR) loci were noted. Chimerism is rare, but it can cause genotype-phenotype discrepancies in blood grouping, parentage, or other genetic laboratory tests. The transfusion of chimeric RBCs was even reported to induce acute intravascular hemolysis. It is very difficult to correctly find heterozygous peaks without assuming their existence, especially when caused by a chimera. Consequently, separation by cloning or enrichment of minor alleles such as using the cold polymerase chain reaction is sometimes needed. A familial study of STR markers could also be a confirmatory test. Here, we report an ABO genotype-phenotype discrepancy due to tri-allelic ABO genotypes and its resolution by cloning sequencing and STR analysis.
By cloning-sequencing analysis, the two major alleles O01 and O02 and one minor allele A102 were separated. A blank means the same base as the reference sequence. Bases in parentheses indicate minor peaks.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
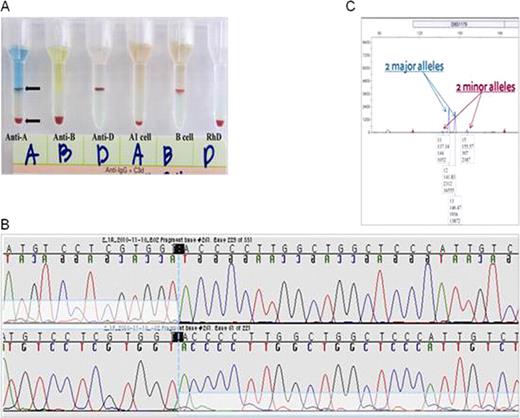
Genotype-phenotype discrepancy due to tri-allelic ABO genotypes. (A) Serologic test using microcolumn agglutination. In the reaction with monoclonal anti-A antibody, double distinct RBC populations are noted. One major (about 70∼80%) population has the O phenotype, while another minor population has the A phenotype. (B) Direct sequencing analysis revealing the heterozygous indel. Small consecutive phase-shifted peaks are seen before and after the site of the deletion (c.261delG) in the reverse and forward reactions, respectively. (C) STR analysis of this patient showing two major and two minor alleles.
Genotype-phenotype discrepancy due to tri-allelic ABO genotypes. (A) Serologic test using microcolumn agglutination. In the reaction with monoclonal anti-A antibody, double distinct RBC populations are noted. One major (about 70∼80%) population has the O phenotype, while another minor population has the A phenotype. (B) Direct sequencing analysis revealing the heterozygous indel. Small consecutive phase-shifted peaks are seen before and after the site of the deletion (c.261delG) in the reverse and forward reactions, respectively. (C) STR analysis of this patient showing two major and two minor alleles.
Summary of polymorphisms of tri-allelic ABO genotypes
| cDNA position . | Reference (A101) . | gDNA . | Allele 1 . | Allele 2 . | Allele 3 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 261 | G | delG+delG+(G) | delG | delG | G |
| 297 | A | R | G | ||
| 467 | C | C+(T) | T | ||
| 646 | T | W | A | ||
| 681 | G | R | A | ||
| 771 | C | Y | T | ||
| 829 | G | R | A | ||
| Alleles | O01,O02, A102 | O01 | O02 | A102 |
| cDNA position . | Reference (A101) . | gDNA . | Allele 1 . | Allele 2 . | Allele 3 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 261 | G | delG+delG+(G) | delG | delG | G |
| 297 | A | R | G | ||
| 467 | C | C+(T) | T | ||
| 646 | T | W | A | ||
| 681 | G | R | A | ||
| 771 | C | Y | T | ||
| 829 | G | R | A | ||
| Alleles | O01,O02, A102 | O01 | O02 | A102 |
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal