Abstract
Abstract 4870
Dendritic cells (DC) are a heterogeneous population of lineage-negative antigen-presenting cells derived from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors, present in tissue, blood and bone marrow (BM), where plasmacytoid DC (pDC) are a normal finding, representing 0.2 ± 0.1% of cell populations (Matarraz et al, 2010).
DC neoplasms include solid tumors (such as DC sarcomas) and an entity classified by the World Health Organization (2008) as an acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-related precursor neoplasm: blastic pDC neoplasm/leukemia, an aggressive disease with poor prognosis, with no clinical trials to orient consensus regarding the most effective treatment; it is usually chemo-resistant, although some cases respond to AML-like regimens and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
It is not clear if the presence of an increased DC population in non-DC AML confers pDC neoplasm-like biological characteristics to the former.
This study aims to evaluate whether an increase in the size of DC populations in newly-diagnosed non-DC AML affects the latter's biological behavior, as represented by the overall survival (OS) of patients with the disease.
We reviewed all AML diagnosed in our Hospital between January 1st 2008 and December 31st 2010, identifying 146 patients. We excluded 9 patients who had no flow cytometry immunophenotyping (IP) performed, and 7 whose first IP was performed after treatment was instituted. In that time frame, we also diagnosed 4 pDC neoplasms.
Of the 130 patients included, 91 had their presenting IP performed on BM aspirate, while the remaining 39 were phenotyped on blood samples. The size of the DC populations and blastic DC maturation were determined on these samples.
Patients were classified into 2 groups according to the size of the DC component; one (the Non-DC Group) had a DC component of up to 0.3% (in practice, the highest value in this group was 0.2%); the other (DC Group) had a percentage over this limit (the lowest value being 1.0%).
OS data was determined for both groups; special consideration was given to age strata, separating patients under 65 years of age (Under-65) from those 65 or older (Over-65) and etiology (distinguishing de novo AML from AML secondary to therapy, myelodysplasia or myeloproliferative diseases). The percentage of DC identified by IP did not influence nor alter the type of treatment instituted.
We found that the presence of a DC component above the normal BM interval (as determined by Matarraz et al) was associated with a significantly decreased OS, with patients with DC components over 0.3% presenting with a median OS of 2.4 months (mean: 6.4 ± 1.6) and those with a component under 0.3% with a median OS of 8.6 months (mean: 17.0 ± 1.9) (p = 0.033).
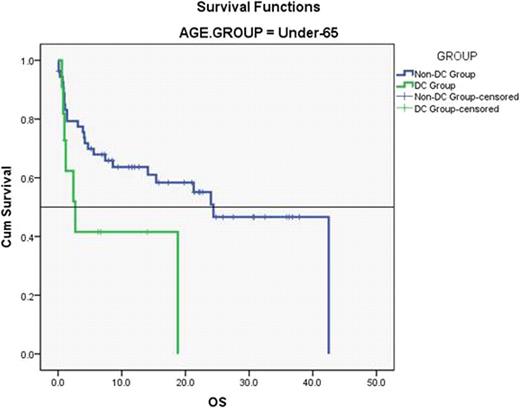
In our series, patients Over-65 had a median OS of 2.9 months (mean = 6.9 ± 1.0) and those Under-65 a median of 21.3 months (mean = 22.5 ± 2.5), p < 0.001. The differences in OS according to DC component were attenuated in patients Over-65 (median = 1.8 vs. 3.9 months, p = NS), whereas in patients Under-65 the median survival was 2.7 months (mean: 8.7 ± 2.9) for the DC Group and 24.4 months (mean: 24.3 ± 2.7) for the non-DC Group (p = 0.035).
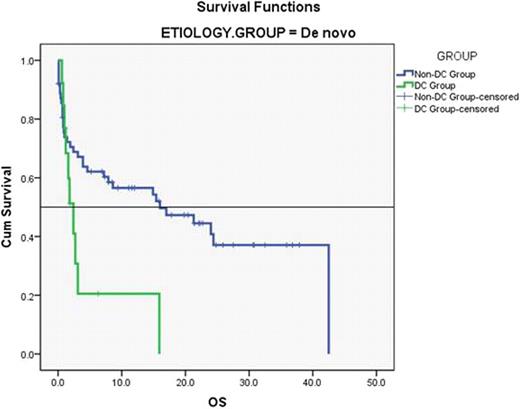
The differences in OS were also significant for de novo AML (median = 2.4 vs. 16.0 months, mean = 4.7 ± 1.9 vs. 20.5 ± 2.6, p = 0.017), but not statistically relevant for secondary AML (median = 4.4 vs. 5.5 months, mean = 8.4 vs. 10.8, p = NS).
In this study, we found that an increase in the size of the DC component as determined by IP at diagnosis on newly-diagnosed AML had a negative impact on prognosis, with a significant decrease in median and mean OS in patients with a percentage of DC over the upper limit of the normal interval.
We also determined that the decreased survival was primarily attributed to the better-prognosis groups (patients under 65 and with de novo AML), whereas the effect of the worsened prognosis was attenuated in those patients with a bad prognosis at the outset (patients over 65 and with secondary AML).
If data from DC neoplasms could be extrapolated, we could suggest that AML with increased DC components are less chemo-sensitive, which would explain the OS differences found in the Under-65 group, as well as the no-difference found in the Over-65 Group, which is frequently undertreated due to comorbidities.
Our study suggests that the size of the DC component at diagnosis as determined by IP is a new prognostic marker predictive of decreased survival.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal