Abstract
Abstract 1804
Despite the high response rates of patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) to the fludarabine (F), cyclophosphamide (C), rituximab (R) regimen, relapsed or refractory disease is common. Novel therapeutic approaches are required that are effective in this setting.
Targeting specific signaling molecules is proving an effective strategy for treating patients who are refractory to FCR. Given that the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway (MAPK) pathway is constitutively active in CLL cells and that inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK1) in this pathway are in clinical trials for solid tumors, we sought to investigate the potential of MEK1 as a therapeutic target in CLL.
Inhibition of MEK1/2 using MEK inhibitor I (MEKi; Calbiochem/Merck) induced apoptosis in the MEC1 cell line and in 18 patient samples. Importantly, sensitivity of the patient samples occurred irrespective of ATM/TP53 functional status, of poor prognostic features or of treatment history. MEKi was also effective against 4 CLL patient samples cultured in an in vitro model of the tumor microenvironment, albeit with a significantly higher IC50 than observed against CLL cells cultured in media alone.
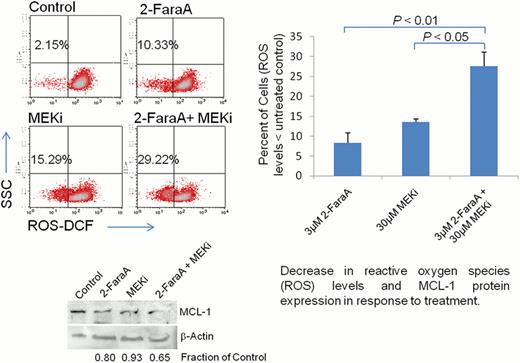
As fludarabine-based therapies have become the mainstay of CLL treatment, we investigated the effect of combining the MEK inhibitor with this purine analogue. Synergy between MEKi and fludarabine was apparent against the MEC-1 cell line and 10 patient samples. Dose reduction indices (DRI) calculated from the drug combination indicate this synergy was predominantly due to an increase in fludarabine sensitivity. Investigation of the mechanisms of the synergy between MEKi and fludarabine suggests decreased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and expression of the pro-survival protein, MCL-1, may be contributing factors (see figure).
These data suggest for the first time that inhibition of MEK1/2 may represent a potential therapeutic option for CLL patients. The efficacy of the MEK inhibitor against CLL cells cultured in the supportive in vitro environment suggest that this approach may also be effective at targeting the proliferative fraction of CLL cells in the tumor microenvironment. As clinical trials of MEK1/2 inhibitors are currently underway in solid tissue malignancies, our data suggest that trials of these agents may also be warranted for high risk CLL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal