Abstract
Abstract 2905
Bendamustine, a unique alkylating agent with a multifaceted mechanism of action is effective front-line therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In vitro studies showing that cytotoxic activity of bendamustine against CLL-derived cell lines is synergized by rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, have led to investigation of combination bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) as first-line therapy and treatment of relapsed disease. This retrospective analysis assessed real-world efficacy and safety of bendamustine alone and combined with rituximab in treatment-naïve CLL patients from Projektgruppe Internistische Onkologie, the largest registry of treatment data from private medical oncology practices in Germany.
Records were obtained for all CLL patients in a registry from 57 German oncology practices from May 2008 to July 2011. Patients who received ≥3 cycles of first-line bendamustine monotherapy or BR were divided into the following age/treatment groups: ≤60 years treated with BR ± prednisone (P) [≤60 BR]; >60 to <70 years treated with bendamustine monotherapy [60–70 B]; >60 to <70 years treated with BR ± P [60–70 BR]; ≥70 years treated with bendamustine monotherapy [≥70 B]; and ≥70 years treated with BR ± P [≥70 BR].
The primary efficacy measure was ORR (complete response [CR] plus partial response [PR]); secondary efficacy measures included CR, PR, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Adverse events (AEs) were assessed.
A total 217 patients (≥61.1% male in each group) were included in the analysis (Table). At diagnosis, all patients had an ECOG score of 0–2; most had RAI stage 0-II (16 had stage III/IV) and Binet stage A or B (29 had stage C). Mean number of treatment cycles (28 days/cycle) per group ranged from 5.1 to 5.9. Mean dose per cycle ranged from 133.6 to 165.9 mg/m2 for bendamustine and 391.1 to 412.1 mg/m2 for rituximab in those groups (Table). Median follow-up was 3 years (range 1–5).
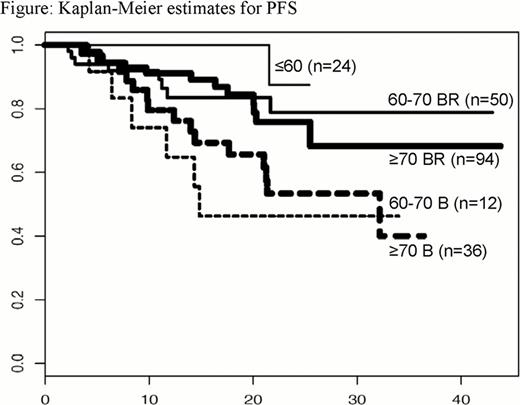
Observed ORRs were >83% in all groups (Table); 1 patient each in the 60–70 B and 60–70 BR groups had progressive disease, and 1 in the ≥70 BR group was not assessable. By Kaplan-Meier analysis, median PFS and OS have been reached in the 60–70 B (PFS: 14.8 months, OS: 41.0 months) and ≥70 B (PFS: 32.5 months, OS: 40.1 months) groups only. PFS results are shown in the Figure.
There were 26 deaths at the time of analysis. The most common grade 3/4 hematologic AEs were febrile neutropenia (n=28) in the ≥70 BR group, leukopenia (n=15) in the ≤60 BR group, and leukopenia (n=25) in the ≥70 BR group. Depression was the most common grade 3/4 nonhematologic AE, affecting all patients in the ≤60 BR and 60–70 B groups, 48/50 patients in the 60–70 BR group, 35/36 in the ≥70 B, and 94/95 in the ≥70 BR. Other common grade 3/4 nonhematologic AEs included fatigue (2 patients in ≥70 BR and 1 patient each in 60–70 B and ≥70 B) and infections/infestations (2 patients in ≤60 BR and 3 in ≥70 BR). Thirty patients were hospitalized (Table). Dose reductions were most frequent in the ≥70 B group (67%) and least in the 60–70 B and 60–70 BR groups (17% and 12.0%, respectively) (Table). Dose delays occurred for 1 patient each in the ≤60 BR, 60–70 B, and ≥70 BR groups and 4 patients in the ≥70 B group.
Data from this real-world chart review indicate that bendamustine alone or with rituximab provides high response rates and an acceptable safety profile with low rates of dose delay in all patient age groups (≤60, 60–70, and ≥70) with previously untreated CLL. These findings are similar to those reported in large clinical trials.
| . | <60 BR n=24 . | 60–70 B n=12 . | 60–70 BR n=50 . | >70 B n=36 . | >70 BR n=95 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) age | |||||
| At diagnosis | 50.3 (6.4) | 62.6 (4.9) | 63.2 (4.3) | 74.5 (5.6) | 72.5 (5.5) |
| Start of therapy | 53.1 (6.2) | 65.9 (2.1) | 65.7 (2.5) | 76.9 (4.8) | 75.5 (4.5) |
| Mean dose (mg/m2) per cycle | |||||
| Bendamustine | 154.0 (41.5) | 153.7 (32.5) | 165.9 (27.0) | 133.6 (39.0) | 147.7 (37.6) |
| Rituximab | 412.1 (107.6) | NA | 392.1 (100.4) | NA | 402.5 (71.4) |
| Response | |||||
| ORR % | 100 | 83 | 88 | 97 | 90 |
| CR | 58 | 33 | 44 | 19 | 37 |
| PR | 42 | 50 | 44 | 78 | 53 |
| Hospitalizations, patients (%) | 3 (13) | 2 (17) | 6 (12) | 5 (14) | 14 (15) |
| Dose reductions, patients (%) | 9 (38) | 2 (17) | 9 (18) | 24 (67) | 30 (32) |
| Dose delays, patients (%) | 1 (4) | 1 (8) | 0 | 4 (11) | 1 (1) |
| . | <60 BR n=24 . | 60–70 B n=12 . | 60–70 BR n=50 . | >70 B n=36 . | >70 BR n=95 . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) age | |||||
| At diagnosis | 50.3 (6.4) | 62.6 (4.9) | 63.2 (4.3) | 74.5 (5.6) | 72.5 (5.5) |
| Start of therapy | 53.1 (6.2) | 65.9 (2.1) | 65.7 (2.5) | 76.9 (4.8) | 75.5 (4.5) |
| Mean dose (mg/m2) per cycle | |||||
| Bendamustine | 154.0 (41.5) | 153.7 (32.5) | 165.9 (27.0) | 133.6 (39.0) | 147.7 (37.6) |
| Rituximab | 412.1 (107.6) | NA | 392.1 (100.4) | NA | 402.5 (71.4) |
| Response | |||||
| ORR % | 100 | 83 | 88 | 97 | 90 |
| CR | 58 | 33 | 44 | 19 | 37 |
| PR | 42 | 50 | 44 | 78 | 53 |
| Hospitalizations, patients (%) | 3 (13) | 2 (17) | 6 (12) | 5 (14) | 14 (15) |
| Dose reductions, patients (%) | 9 (38) | 2 (17) | 9 (18) | 24 (67) | 30 (32) |
| Dose delays, patients (%) | 1 (4) | 1 (8) | 0 | 4 (11) | 1 (1) |
Support: Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Günther:Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bartels:rgb Onkologisches Management GmbH, which received research funding from Teva Pharmaceuticals: Employment, Research Funding. Sterchele:Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal