Abstract
Abstract  415
415
Genomic gains and losses play a crucial role in the development and progression of DLBCL and are closely related to gene expression profiles (GEP), including the germinal center B-cell like (GCB) and activated B-cell like (ABC) cell of origin (COO) molecular signatures. To identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes (TSG) involved in DLBCL pathogenesis and to determine their prognostic values, an integrated analysis of high-resolution gene expression and copy number profiling was performed.
Two hundred and eight adult patients with de novo CD20+ DLBCL enrolled in the prospective multicentric randomized LNH-03 GELA trials (LNH03-1B, -2B, -3B, 39B, -5B, -6B, -7B) with available frozen tumour samples, centralized reviewing and adequate DNA/RNA quality were selected. 116 patients were treated by Rituximab(R)-CHOP/R-miniCHOP and 92 patients were treated by the high dose (R)-ACVBP regimen dedicated to patients younger than 60 years (y) in frontline. Tumour samples were simultaneously analysed by high resolution comparative genomic hybridization (CGH, Agilent, 144K) and gene expression arrays (Affymetrix, U133+2). Minimal common regions (MCR), as defined by segments that affect the same chromosomal region in different cases, were delineated. Gene expression and MCR data sets were merged using Gene expression and dosage integrator algorithm (GEDI, Lenz et al. PNAS 2008) to identify new potential driver genes.
A total of 1363 recurrent (defined by a penetrance > 5%) MCRs within the DLBCL data set, ranging in size from 386 bp, affecting a single gene, to more than 24 Mb were identified by CGH. Of these MCRs, 756 (55%) showed a significant association with gene expression: 396 (59%) gains, 354 (52%) single-copy deletions, and 6 (67%) homozygous deletions. By this integrated approach, in addition to previously reported genes (CDKN2A/2B, PTEN, DLEU2, TNFAIP3, B2M, CD58, TNFRSF14, FOXP1, REL…), several genes targeted by gene copy abnormalities with a dosage effect and potential physiopathological impact were identified, including genes with TSG activity involved in cell cycle (HACE1, CDKN2C) immune response (CD68, CD177, CD70, TNFSF9, IRAK2), DNA integrity (XRCC2, BRCA1, NCOR1, NF1, FHIT) or oncogenic functions (CD79b, PTPRT, MALT1, AUTS2, MCL1, PTTG1…) with distinct distribution according to COO signature.
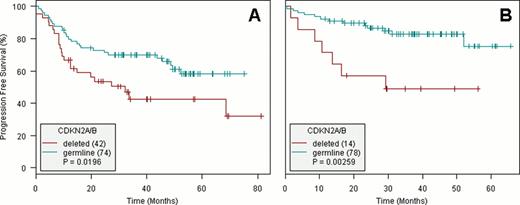
The CDKN2A/2B tumor suppressor locus (9p21) was deleted homozygously in 27% of cases and hemizygously in 9% of cases. Biallelic loss was observed in 49% of ABC DLBCL and in 10% of GCB DLBCL. This deletion was strongly correlated to age and associated to a limited number of additional genetic abnormalities including trisomy 3, 18 and short gains/losses of Chr. 1, 2, 19 regions (FDR < 0.01), allowing to identify genes that may have synergistic effects with CDKN2A/2B inactivation. With a median follow-up of 42.9 months, only CDKN2A/2B biallelic deletion strongly correlates (FDR p.value < 0.01) to a poor outcome in the entire cohort (4y PFS = 44% [32–61] respectively vs. 74% [66–82] for patients in germline configuration; 4y OS = 53% [39–72] vs 83% [76–90]). In a Cox proportional hazard prediction of the PFS, CDKN2A/2B deletion remains predictive (HR = 1.9 [1.1–3.2], p = 0.02) when combined with IPI (HR = 2.4 [1.4–4.1], p = 0.001) and GCB status (HR = 1.3 [0.8–2.3], p = 0.31). This difference remains predictive in the subgroup of patients treated by R-CHOP (4y PFS = 43% [29–63] vs. 66% [55–78], p=0.02), in patients treated by R-ACVBP (4y PFS = 49% [28–84] vs. 83% [74–92], p=0.003), and in GCB (4y PFS = 50% [27–93] vs. 81% [73–90], p=0.02), or ABC/unclassified (5y PFS = 42% [28–61] vs. 67% [55–82] p = 0.009) molecular subtypes (Figure 1 ).
We report for the first time an integrated genetic analysis of a large cohort of DLBCL patients included in a prospective multicentric clinical trial program allowing identifying new potential driver genes with pathogenic impact. However CDKN2A/2B deletion constitutes the strongest and unique prognostic factor of chemoresistance to R-CHOP, regardless the COO signature, which is not overcome by a more intensified immunochemotherapy. Patients displaying this frequent genomic abnormality warrant new and dedicated therapeutic approaches.
Progression free survival (PFS) according to CDKN2A/2B status in patients treated by R-CHOP (A) or R-ACVBP (B).
Progression free survival (PFS) according to CDKN2A/2B status in patients treated by R-CHOP (A) or R-ACVBP (B).
Salles:roche: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal