Key Points
First therapeutic application that targets Robo4 on the tumor blood vasculature
High-throughput screening system to isolate cell-internalizing monoclonal antibodies useful to develop effective antibody-drug conjugates
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that are internalized into cells are a current focus in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). We describe a phage display–based high-throughput screening system to rapidly isolate cell-internalizing mAbs. We simultaneously examined the cell-internalizing activities of several hundred independent mAbs and successfully isolated cell-internalizing mAbs against the tumor endothelial markers Roundabout homolog 4 (Robo4) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2). Tumor accumulation of mAbs with high cell-internalizing activity was significantly higher than that of mAbs with low cell-internalizing activity. Furthermore, the antitumor effects of ADCs of mAbs with high cell-internalizing activity were significantly stronger than those of mAbs with low cell-internalizing activity. Although anti-VEGFR2 therapy caused a significant loss of body weight, anti-Robo4 therapy did not. These findings indicate that cell-internalizing activity plays an important role in the biodistribution and therapeutic effects of ADCs. Further, Robo4 can be an effective marker for tumor vascular targeting.
Introduction
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), ie, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) labeled with certain anticancer agents, are currently the focus of antibody-based drug discovery. ADCs have mAb-derived specificity and allow for targeted delivery of cytotoxic drugs to a tumor, which is expected to significantly enhance the antitumor activity of mAbs.1 Trastuzumab ematansine (T-DM1)2 for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her-2)–positive breast cancer and brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35)3 for relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders are now in phase 3 clinical trials as effective ADCs.4 ADCs will have an important role in overcoming some types of refractory cancers and will contribute to the field of tumor vascular targeting.5
An essential property of ADCs is that the mAb should be efficiently internalized into the cell where the cytotoxic effects of anticancer drugs occur.1 The isolation of mAbs with high cell-internalizing activity (cell-internalizing mAbs) is a limiting factor in the development of ADCs. The discovery of potent cell-internalizing mAbs, however, requires labor-intensive screening of a massive number of candidates, and therefore the development of phage display–based methods to identify these candidates is highly desirable.6,7 In the phage display–based method, a phage antibody library is added to the desired cells and then phages bound to the cell surface are removed. Only internalized phages are rescued from the intracellular compartment. Even with this method, however, the internalizing activities of individual antibody candidates must be assessed, because the concentrated phage pool comprises a “polyclonal” population. To address this issue, we used high-throughput screening methods to estimate “monoclonal” cell-internalization activities using a protein synthesis inhibitory factor (PSIF),8 which provided a breakthrough in reducing the time-consuming screening of the cell-internalizing activity.
PSIF is a fragment of a bacterial exotoxin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.9 PSIF lacks its cell binding domain, and its cytotoxic portion is used in a recombinant immunotoxin.10 Upon entry into the cell, PSIF has strong cytotoxicity by inducing ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor-2, which is essential for protein synthesis.11 Our group previously accelerated the identification of cell-internalizing novel protein transduction domains (PTDs) by expressing PTD-PSIF fusion proteins in the supernatant of Escherichia coli.8 Using this system, we successfully discovered superior HIV-Tat PTD mutants by simultaneously estimating the cell-internalizing activities of several hundred monoclonal PTD-PSIF fusions.8 Therefore, we expect this method to contribute to the identification of mAbs with high cell-internalizing activity (cell-internalizing mAbs) by expressing single-chain antibody Fv (scFv)-PSIF fusion proteins to estimate the cell-internalizing activities of a very large number of antibodies.
Roundabout homolog 4 (Robo4) is a potential tumor angiogenesis marker.12 Robo4 expression is restricted to areas of in vivo angiogenesis13,14 and the subpopulation of hematopoietic stem cells localized in the bone marrow.15 At angiogenic sites, Robo4 is present in the endothelial lining of blood vessels in the developing embryo,16 placenta,14 and tumors.17 We previously confirmed the endothelial cell–specific expression of Robo4 using transgenic mouse lines.18,19 Robo4 acts as a receptor that modulates vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF)–VEGF receptor (VEGFR) signaling.20-23 Therefore, Robo4 is a potential marker for tumor vascular targeting because angiogenesis is only activated in tumors in the adult,24 with the exception of some pathological states.25,26 Another potential tumor angiogenesis marker is VEGFR2, a well-established tumor endothelial marker.27 The VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway plays a crucial role in angiogenesis, and anti-VEGF mAbs and small molecule inhibitors against VEGFR are approved for various types of cancers.28 Anti-VEGFR2 mAbs are also used for tumor vascular targeting.29 Although VEGFR2 is strongly expressed in active angiogenic sites, its expression is also observed in normal tissues.30 Hypertension and proteinuria are common side effects of anti-VEGF therapy because VEGF-VEGFR signaling is also inhibited in normal tissue, including the kidney, heart, and resistance vessels.31-33
Here we applied the PSIF system to search for novel cell-internalizing mAbs from an immune phage antibody library. Application of this method to Robo4 and VEGFR2 led to the successful discovery of anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 cell-internalizing mAbs, as well as mAbs with low cell-internalizing activity (low-internalizing mAbs) to be used as controls. Comparing mAbs with different cell-internalizing activities revealed that higher cell-internalizing activity enhanced the tumor targeting potency of mAbs. Furthermore, comparative studies with anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 cell-internalizing mAbs in vivo indicated that Robo4 was superior to VEGFR2 in terms of the therapeutic window. This is the first report demonstrating the benefits of cell-internalizing mAbs in tumor vascular targeting. Further, these findings demonstrate the potential of Robo4 as a target for further development of novel ADCs against tumor blood vasculature.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
MS1 immortalized murine endothelial cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium containing 5% fetal bovine serum 1% antibiotic-antimycotic mixed solution. B16BL6 murine melanoma cells were cultured in minimum essential medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic mixed solution at 37°C. These cells were maintained at 37°C under a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere.
B16BL6 tumor-bearing mice
B16BL6 cells (1 × 106 cells/100 μL) were inoculated intracutaneously into 6-week-old female C57BL6 mice (Japan SLC Inc., Shizuoka, Japan) (day 0). Biodistribution was analyzed on the day that the tumor width reached 10 mm. The therapy experiment was started on day 3. As a validation of the model, we confirmed the expressions of VEGFR2 and Robo4 on the tumor endothelium, based on the immunofluorescence against B16BL6 tumor sections.
Antigens
Human VEGFR2 (hVEGFR2) and mouse VEGFR2 (mVEGFR2) were commercial recombinant proteins (Merck Chemicals, Inc., Darmstadt, Germany, or R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN). Human Robo4 (hRobo4) and mouse Robo4 (mRobo4) were produced as described previously.34
Immune phage antibody libraries
Phage antibody libraries were constructed from the spleen and bone marrow cells of immunized mice as previously described.35,36 Our phage antibody library comprised single-chain Fv fragment (scFv) fused with pIII phage coat protein. Four rounds of affinity panning were performed against hVEGFR2 and mVEGFR2 for the anti-VEGFR2 immune library, and against hRobo4 and mRobo4 for the anti-Robo4 immune library. Anti-FLAG panning was followed by each panning to concentrate the scFv-displaying phages, as described previously.36
ELISA and cytotoxicity assay using TG1 supernatant
Plasmids were extracted from TG1 cells after the fourth panning against mVEGFR2 or mRobo4. These “enriched” scFv gene libraries were cloned into a PSIF-fusion expression vector derived from pCANTAB5E.8 Monoclonal scFv-PSIF protein was induced in the TG1 supernatant, as previously described.8 mVEGFR2 or mRobo4 was immobilized on an immunoassay plate and blocked with 4% skim milk in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (4% MPBS) at 37°C for 2 hours. TG1 supernatant containing 2% MPBS was reacted with antigens at room temperature for 1 hour. Bound scFv-PSIFs were detected by anti–FLAG-horseradish peroxidase (M2, Sigma-Aldrich Corporation, St. Louis, MO). For the cytotoxicity assay, MS1 cells were seeded on a 96-well plate at 1.0 × 104 cells/well. After incubation at 37°C for 24 hours, TG1 supernatant was diluted in MS1 culture medium, and then added to the MS1 cells. After incubation at 37°C for 24 hours, cell viability was assessed using a WST-8 assay (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc., Kumamoto, Japan). The viability of nontreated MS1 and completely killed MS1 with 1 mM cycloheximide were defined as 100% and 0%, respectively.
Expression and purification of scFv, dscFv, and scFv-PSIF recombinant protein
The isolated scFv gene with 15 amino acids linker (VL-GGGGSGGGGSGGGGS-VH) was cloned into modified pET15b vector, resulting in the scFv fused by FLAG-tag and His×6 tag at the C-terminus. A scFv gene with a 5–amino acid linker (VL-GGGGS-VH) was also cloned into modified pET15b, resulting in a noncovalent scFv dimer (dscFv) fused by FLAG-tag and His×6 tag at the C-terminus. An anti-His scFv gene was also cloned but only a FLAG-tag was fused at the C-terminus. A scFv gene with a 15–amino acid linker was cloned into pYas-PSIF vectors.37 ScFvs, dscFvs, and scFv-PSIFs were purified from inclusion bodies in E coli according to the previously described methods.37 The binding affinity of each recombinant protein was assessed by surface plasmon resonance using BIAcore3000 (GE Healthcare UK Ltd., Chalfont, United Kingdom).
Expression and purification of IgG recombinant protein
IgG recombinant proteins were expressed using an OptiCHO antibody expression kit (Invitrogen Corporation, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. IgGs were purified from cell culture supernatant with protein G column (GE Healthcare). Eluted fractions were further purified with Superdex 200 column (GE Healthcare). Anti-FLAG[IgG] (anti-FLAG M2 antibody) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Preparation of IgG-NCS
NCS was kindly provided by Kayaku Co, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan. NCS was thiolated by incubating it with 10 molar excess 2-iminothiolane (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA) for 1 hour at room temperature. IgG recombinant proteins were reacted with 10 molar excess of SPDP crosslinker (N-succinimidyl 3-[2-pyridyldithio]-propionate; Thermo Fisher) for 30 minutes on ice. SPDP-modified IgGs and thiolated NCS were separately purified using NICK columns (GE Healthcare). They were then mixed for 8 hours at room temperature. IgG-NCS were purified with a Superdex 200 column. Modification efficiency was quantified after sodium-dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using a Gel DOC EZ system and Image laboratory software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA).
Labeling of purified mAbs
For fluorescent labeling, mAbs were labeled using Cy5.5-NHS (GE Healthcare). For 125I labeling, 100 μg mAbs in 0.4 M phosphate buffer were labeled with 0.2 mCi Na125I (PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA) based on the chloramine-T method.38 For biotin labeling, mAbs were biotinylated using EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-Biotin (Thermo Fisher). Each mAb was purified using a NICK desalting column (GE Healthcare).
Flow cytometry
Cy5.5-labeled mAb (mAbCy5.5; 4 μM) was incubated with 5.0 × 105 cells of MS1 cells in 6-well plates for 2 hours at 4°C. After washing three times, the cells were incubated for an additional 0.5 to 8 hours at 37°C. At each time point, cells were collected in 2-mM ethylenediaminetetraacedtic acid/PBS. Bound mAbs were digested using 0.1% trypsin/PBS at 37°C for 20 minutes (trypsinized group) or PBS (nontrypsinized group). Cellular fluorescence was measured by Gallios flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Miami, FL). The ratio of internalization was calculated using the following formula: internalization (%) = {internalized mAbCy5.5}/{total bound mAbCy5.5} × 100 (%) = {(MFI of mAb)T – (MFI of anti-His[mAb])T}/{(MFI of mAb)N – (MFI of anti-His[mAb])N} × 100 (%). MFI indicates mean fluorescence intensity. T and N indicate trypsinized and nontrypsinized groups, respectively.
In vivo biodistribution
dscFvs125I (0.2 nmol) was intravenously injected into B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice. At 2 hours and 24 hours after injection, the radioactivity of each organ was counted using the Wizard 2480 γ-ray counter (PerkinElmer). %ID/g tissue was calculated using following formula: %ID/g tissue = (count/g tissue)/(total injected count) × 100 (%). Two individual experiments were combined for the final data (total 11 mice/group).
Immunofluorescence of the tissue sections
B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were administered 2 nmol of dscFvsBio. At 2 hours after the injection, the tumors, kidneys, and hearts were embedded in optimal cutting temperature compound (Sakura Finetek, Inc., Torrance, CA) and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Thin sections (7 μm) were prepared using a Cryostat CM1850 (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. DscFvsBio in the sections were stained with streptavidin phycoerythrin conjugate (eBioscience Inc., San Diego, CA) in Dako REAL Antibody Diluent (DAKO Corporation, Carpinteria, CA). CD31+ vascular endothelial cells were stained with rat anti-CD31 antibody (MEC13.3; Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ) in Dako REAL Antibody Diluent and Alexa488 conjugated anti-rat IgG (A11006; Invitrogen). The samples were embedded with Prolong Gold antifade reagent with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Invitrogen) and observed with a fluorescence microscope FSX100 (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
In vivo therapy experiments
Activities of scFv-PSIFs and IgG-NCSes were confirmed by WST-8 assay as described before. B16BL6 cells were inoculated intracutaneously into C57BL6 mice (Japan SLC) on day 0. Mice were intravenously injected with 15 pmol scFv-PSIFs and 10 pmol IgG-NCSs on days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 (7 mice/group). The volume of the tumor was calculated according to the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = {major axis of tumor (mm)} × {minor axis of tumor (mm)}2 × 0.4.
Results
High-throughput screening for cell-internalizing mAbs
To identify cell-internalizing mAbs, we applied the phage immune scFv library to high-throughput screening of cell-internalizing molecules based on the PSIF system8 (Figure 1). Our anti-Robo4 or anti-VEGFR2 phage library comprised approximately 3.0 × 108 or 5.0 × 108 independent scFvs, which was validated by sequence analysis. To assess the qualities of the libraries, affinity panning was performed against each antigen. During the panning, output phages were increased, suggesting that the desired scFvs were enriched in the library (supplemental Figure 1A-B,E-F). After the fourth panning, >40% of monoclonal scFvs showed specific binding in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (supplemental Figure 1C-D,G-H).
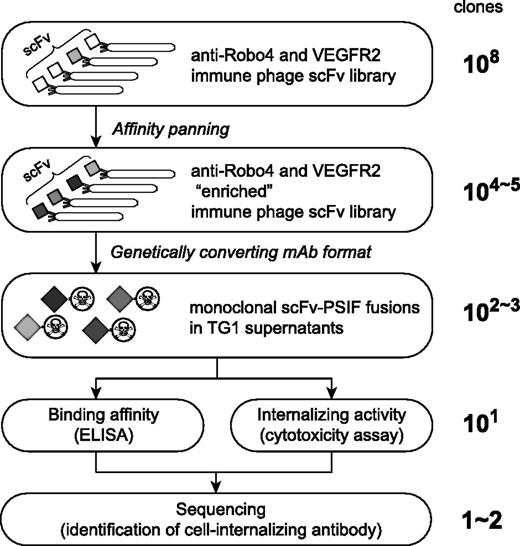
Phage display-based method to search for cell-internalizing mAbs. The phage antibody library was “enriched” by affinity panning against the desired antigens. Plasmids encoding scFvs were collected from TG1 E coli strains infected by “enriched” phage libraries. Genes of scFvs were digested out and ligated into a PSIF fusion protein expression vector. These plasmids were then transformed to TG1, and then single colonies were picked up. From these individual colonies, monoclonal scFv-PSIF fusions were induced in TG1 supernatants. Using these fusion proteins, binding affinities and internalizing activities of several hundreds of scFv-PSIFs were easily estimated by ELISA and cytotoxicity assays, respectively. Finally, genes of positive scFvs were collected from TG1, and cell-internalizing scFvs were identified by sequencing. In this report, we used anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 immune phage scFv libraries as the phage antibody libraries, and mRobo4 and mVEGFR2 as the desired antigens.
Phage display-based method to search for cell-internalizing mAbs. The phage antibody library was “enriched” by affinity panning against the desired antigens. Plasmids encoding scFvs were collected from TG1 E coli strains infected by “enriched” phage libraries. Genes of scFvs were digested out and ligated into a PSIF fusion protein expression vector. These plasmids were then transformed to TG1, and then single colonies were picked up. From these individual colonies, monoclonal scFv-PSIF fusions were induced in TG1 supernatants. Using these fusion proteins, binding affinities and internalizing activities of several hundreds of scFv-PSIFs were easily estimated by ELISA and cytotoxicity assays, respectively. Finally, genes of positive scFvs were collected from TG1, and cell-internalizing scFvs were identified by sequencing. In this report, we used anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 immune phage scFv libraries as the phage antibody libraries, and mRobo4 and mVEGFR2 as the desired antigens.
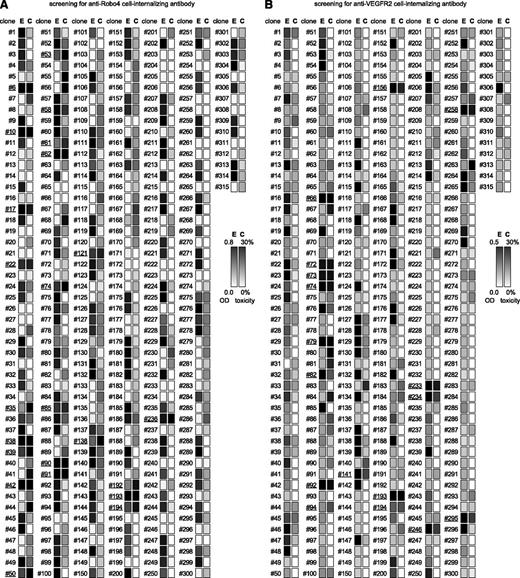
To validate the efficacy of cell-internalizing mAbs in a mouse model, we selected libraries enriched against murine antigens (mRobo4 and mVEGFR2) and chose MS1 murine endothelial cells for the screening of cell-internalizing mAbs because we confirmed the expressions of both mRobo4 and mVEGFR2 in MS1 cells using reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reactioin. For the screening, scFv genes obtained after the fourth round of panning were cloned into the PSIF expression vector. Monoclonal scFv-PSIFs were expressed in TG1 supernatants (315 clones per library). For anti-Robo4s, 178 of 315 clones bound to mRobo4 in ELISA and 20 of these 178 binders were cytotoxic against MS1 cells (Figure 2A). In a similar manner, for anti-VEGFR2s, 156 of 315 clones bound to VEGFR2 and 17 of the 156 binders were positive in the ELISA and cytotoxicity assays (Figure 2B). Sequence analysis to omit redundant clones revealed that these clones comprised 1 anti-Robo4 cell-internalizing mAb, 2 anti-Robo4 low-internalizing mAbs, 2 anti-VEGFR2 cell-internalizing mAbs, and 14 anti-VEGFR2 low-internalizing mAbs. For anti-Robo4s, only one anti-Robo4 cell-internalizing mAb was named “R4-13i” and a low-internalizing mAb with high affinity and low cytotoxicity was named “R4-16.” In a similar manner, “V2-05i” and “V2-02” were selected as an anti-VEGFR2 cell-internalizing mAb and a low-internalizing mAb, respectively. After purification of the recombinant proteins, both anti-Robo4 scFvs bound to hRobo4, similar to mRobo4. Conversely, anti-VEGFR2 scFvs bound to mVEGFR2, but not to hVEGFR2. We also confirmed using competitive ELISA that the mAbs did not share their antigen-binding epitopes (supplemental Figure 2).
Screening of cell-internalizing mAbs (ELISA and cytotoxicity assay). To screen for cell-internalizing mAbs, 315 clones per antigen were analyzed by ELISA and cytotoxicity assay. (A) Result for Robo4, (B) Result for VEGFR2. Monoclonal scfv-PSIFs were induced in TG1 supernatant. The binding properties and cytotoxicities to MS1 cells were then assessed by an ELISA and WST-8 assay, respectively. E, ELISA results; C, WST-8 assay results. Individual results from ELISA (OD = 0.8 or 0.5∼0.0) and WST-8 assay (cytotoxicity = 30%∼0%) were mapped in grayscale densities. The 24 candidates against Robo4 and 17 candidates against VEGFR2 are indicated by the underline (ELISA OD ≥0.2 and cytotoxicity ≥20%). After omitting redundant clones by sequencing, 1 cell-internalizing mAb and 2 low-internalizing mAbs against mRobo4, and 2 cell-internalizing mAbs and 14 low-internalizing mAbs against mVEGFR2 were identified.
Screening of cell-internalizing mAbs (ELISA and cytotoxicity assay). To screen for cell-internalizing mAbs, 315 clones per antigen were analyzed by ELISA and cytotoxicity assay. (A) Result for Robo4, (B) Result for VEGFR2. Monoclonal scfv-PSIFs were induced in TG1 supernatant. The binding properties and cytotoxicities to MS1 cells were then assessed by an ELISA and WST-8 assay, respectively. E, ELISA results; C, WST-8 assay results. Individual results from ELISA (OD = 0.8 or 0.5∼0.0) and WST-8 assay (cytotoxicity = 30%∼0%) were mapped in grayscale densities. The 24 candidates against Robo4 and 17 candidates against VEGFR2 are indicated by the underline (ELISA OD ≥0.2 and cytotoxicity ≥20%). After omitting redundant clones by sequencing, 1 cell-internalizing mAb and 2 low-internalizing mAbs against mRobo4, and 2 cell-internalizing mAbs and 14 low-internalizing mAbs against mVEGFR2 were identified.
Characterization of mAbs
We purified scFvs, dimerized scFvs (dscFvs), IgGs, and scFv-PSIF as recombinant proteins. IgGs conjugated with neocarzinostatin (IgG-NCSes) were also prepared for in vivo experiments. NCSes were confirmed to be conjugated to IgG molecules in the purified IgG-NCS fraction, and the efficiencies of the NCS modifications were similar in all IgG-NCSes (1.6∼1.8 NCSes per single IgG). Surface plasmon resonance analysis revealed that cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs had similar affinities against antigens in all antibody forms (Table 1).
Binding kinetics of antibodies in surface plasmon resonance analysis
| Antibody . | Target . | Format . | ka (M−1s−1) . | kd (s−1) . | KD (M) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R4-13i | mRobo4 | scFv | 1.25 ± 0.36 × 105 | 5.82 ± 0.95 × 10−4 | 5.03 ± 1.95 × 10−9 |
| (internalizing) | dscFv | 1.15 ± 0.34 × 106 | 5.98 ± 0.61 × 10−4 | 5.64 ± 2.21 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.14 ± 0.55 × 106 | 4.19 ± 1.70 × 10−4 | 2.22 ± 0.51 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 7.22 ± 4.31 × 104 | 4.28 ± 1.60 × 10−3 | 6.47 ± 1.61 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.02 ± 0.15 × 106 | 4.66 ± 0.86 × 10−4 | 4.59 ± 0.74 × 10−10 | ||
| R4-16 | mRobo4 | scFv | 1.30 ± 0.33 × 105 | 5.82 ± 1.50 × 10−4 | 4.77 ± 1.96 × 10−9 |
| (low-internalizing) | dscFv | 1.12 ± 0.03 × 106 | 5.91 ± 1.50 × 10−4 | 5.31 ± 1.96 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.06 ± 0.24 × 106 | 3.60 ± 0.85 × 10−4 | 2.76 ± 0.16 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 8.90 ± 1.42 × 104 | 6.10 ± 2.45 × 10−3 | 7.24 ± 3.74 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.07 ± 0.12 × 106 | 3.93 ± 0.54 × 10−4 | 3.72 ± 0.89 × 10−10 | ||
| V2-05i | mVEGFR2 | scFv | 9.66 ± 3.57 × 104 | 4.40 ± 0.95 × 10−4 | 5.13 ± 2.61 × 10−9 |
| (internalizing) | dscFv | 8.75 ± 2.03 × 105 | 5.59 ± 2.57 × 10−4 | 6.16 ± 1.47 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.14 ± 0.09 × 106 | 3.21 ± 0.35 × 10−4 | 2.84 ± 0.52 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 9.57 ± 0.84 × 104 | 6.51 ± 1.87 × 10−3 | 6.94 ± 2.63 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 0.96 ± 0.06 × 106 | 4.37 ± 0.90 × 10−4 | 4.52 ± 0.79 × 10−10 | ||
| V2-02 | mVEGFR2 | scFv | 7.94 ± 1.24 × 104 | 4.28 ± 3.23 × 10−4 | 5.07 ± 3.05 × 10−9 |
| (low-internalizing) | dscFv | 8.94 ± 2.55 × 105 | 5.57 ± 1.25 × 10−4 | 6.60 ± 2.39 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.13 ± 0.22 × 106 | 3.25 ± 1.10 × 10−4 | 2.90 ± 0.98 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 9.84 ± 1.52 × 104 | 5.75 ± 2.05 × 10−3 | 5.81 ± 1.93 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.08 ± 0.08 × 106 | 5.25 ± 1.58 × 10−4 | 4.85 ± 1.30 × 10−10 |
| Antibody . | Target . | Format . | ka (M−1s−1) . | kd (s−1) . | KD (M) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R4-13i | mRobo4 | scFv | 1.25 ± 0.36 × 105 | 5.82 ± 0.95 × 10−4 | 5.03 ± 1.95 × 10−9 |
| (internalizing) | dscFv | 1.15 ± 0.34 × 106 | 5.98 ± 0.61 × 10−4 | 5.64 ± 2.21 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.14 ± 0.55 × 106 | 4.19 ± 1.70 × 10−4 | 2.22 ± 0.51 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 7.22 ± 4.31 × 104 | 4.28 ± 1.60 × 10−3 | 6.47 ± 1.61 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.02 ± 0.15 × 106 | 4.66 ± 0.86 × 10−4 | 4.59 ± 0.74 × 10−10 | ||
| R4-16 | mRobo4 | scFv | 1.30 ± 0.33 × 105 | 5.82 ± 1.50 × 10−4 | 4.77 ± 1.96 × 10−9 |
| (low-internalizing) | dscFv | 1.12 ± 0.03 × 106 | 5.91 ± 1.50 × 10−4 | 5.31 ± 1.96 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.06 ± 0.24 × 106 | 3.60 ± 0.85 × 10−4 | 2.76 ± 0.16 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 8.90 ± 1.42 × 104 | 6.10 ± 2.45 × 10−3 | 7.24 ± 3.74 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.07 ± 0.12 × 106 | 3.93 ± 0.54 × 10−4 | 3.72 ± 0.89 × 10−10 | ||
| V2-05i | mVEGFR2 | scFv | 9.66 ± 3.57 × 104 | 4.40 ± 0.95 × 10−4 | 5.13 ± 2.61 × 10−9 |
| (internalizing) | dscFv | 8.75 ± 2.03 × 105 | 5.59 ± 2.57 × 10−4 | 6.16 ± 1.47 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.14 ± 0.09 × 106 | 3.21 ± 0.35 × 10−4 | 2.84 ± 0.52 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 9.57 ± 0.84 × 104 | 6.51 ± 1.87 × 10−3 | 6.94 ± 2.63 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 0.96 ± 0.06 × 106 | 4.37 ± 0.90 × 10−4 | 4.52 ± 0.79 × 10−10 | ||
| V2-02 | mVEGFR2 | scFv | 7.94 ± 1.24 × 104 | 4.28 ± 3.23 × 10−4 | 5.07 ± 3.05 × 10−9 |
| (low-internalizing) | dscFv | 8.94 ± 2.55 × 105 | 5.57 ± 1.25 × 10−4 | 6.60 ± 2.39 × 10−10 | |
| IgG | 1.13 ± 0.22 × 106 | 3.25 ± 1.10 × 10−4 | 2.90 ± 0.98 × 10−10 | ||
| scFv-PSIF | 9.84 ± 1.52 × 104 | 5.75 ± 2.05 × 10−3 | 5.81 ± 1.93 × 10−8 | ||
| IgG-NCS | 1.08 ± 0.08 × 106 | 5.25 ± 1.58 × 10−4 | 4.85 ± 1.30 × 10−10 |
Binding kinetics were analyzed against mRobo4 (R4-13i and R4-16) or mVEGFR2 (V2-05i and V2-02). Values are shown as means ± SD from three different preparations.
ka, association rate constant (M−1s−1); kd, dissociation rate constant (s−1); KD, equilibrium dissociation constant (kd/ka) (M).
To quantify the internalization, flow cytometry analysis was performed with Cy5.5-labeled mAbs (scFvCy5.5, dscFvCy5.5, and IgGCy5.5; Figure 3A,C). After mAbsCy5.5 bound to the cell surface, internalization was induced by incubation at 37°C for 2 hours. By removing cell-surface mAbsCy5.5 with trypsinization, the internalized mAbsCy5.5 were quantified by flow cytometry. At 2 hours, approximately 30% of cell-internalizing mAbs remained after trypsinization, whereas most of the low-internalizing mAbs were degraded (Figure 3A,C). This result clearly suggested that the internalization efficiencies differed between cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs, even among the three different mAb forms. In a similar manner, a time-shift analysis revealed that >40% of cell-internalizing mAbs were internalized after 8 hours of incubation (Figure 3B,D). These findings indicate that only cell-internalizing mAbs were efficiently internalized into the cells, although low-internalizing mAbs had affinities similar to those of cell-internalizing mAbs (Table 1).
Cell internalization analyzed by flow cytometry. (A,C) Trypsinization to quantify internalized mAbs. Different forms of mAbsCy5.5 bound to the MS1 cells at 4°C. After washing out the unbound mAbs, internalization was induced for 2 hours at 37°C. To detect only internalized mAbs, cell surface proteins were trypsinized. The remaining cellular fluorescence was then analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Anti-Robo4 mAbsCy5.5, (C) Anti-VEGFR2 mAbsCy5.5. Black, nontrypsinized group; gray, trypsinized group; white, negative control (anti-His[scFv]Cy5.5, anti-His[dscFv]Cy5.5, or anti-FLAG[IgG]Cy5.5). (B,D) Time course of the internalization. After binding at 4°C, internalization was induced for 0.5, 1, 2, 4, or 8 hours at 37°C. The ratio of internalization was calculated using the following formula: internalization (%) = {internalized mAb}/{total bound mAb} × 100 (%) = {(MFI of mAb)T – (MFI of negative control)T}/{(MFI of mAb)N – (MFI of negative control)N} × 100 (%). T, trypsinized group; N, nontrypsinized group; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (B) Closed and open markers indicate R4-13i and R4-16, respectively. (D) Closed and open markers indicate V2-05i and V2-02, respectively. (B,D) Circles, diamonds, and squares indicate scFv, dscFv, and IgG, respectively. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Values are shown as means ± SD. **P < .01; internalizing mAb versus low-internalizing mAb in each form by 2-way ANOVA (n = 3).
Cell internalization analyzed by flow cytometry. (A,C) Trypsinization to quantify internalized mAbs. Different forms of mAbsCy5.5 bound to the MS1 cells at 4°C. After washing out the unbound mAbs, internalization was induced for 2 hours at 37°C. To detect only internalized mAbs, cell surface proteins were trypsinized. The remaining cellular fluorescence was then analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Anti-Robo4 mAbsCy5.5, (C) Anti-VEGFR2 mAbsCy5.5. Black, nontrypsinized group; gray, trypsinized group; white, negative control (anti-His[scFv]Cy5.5, anti-His[dscFv]Cy5.5, or anti-FLAG[IgG]Cy5.5). (B,D) Time course of the internalization. After binding at 4°C, internalization was induced for 0.5, 1, 2, 4, or 8 hours at 37°C. The ratio of internalization was calculated using the following formula: internalization (%) = {internalized mAb}/{total bound mAb} × 100 (%) = {(MFI of mAb)T – (MFI of negative control)T}/{(MFI of mAb)N – (MFI of negative control)N} × 100 (%). T, trypsinized group; N, nontrypsinized group; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (B) Closed and open markers indicate R4-13i and R4-16, respectively. (D) Closed and open markers indicate V2-05i and V2-02, respectively. (B,D) Circles, diamonds, and squares indicate scFv, dscFv, and IgG, respectively. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Values are shown as means ± SD. **P < .01; internalizing mAb versus low-internalizing mAb in each form by 2-way ANOVA (n = 3).
Intracellular localization
The intracellular behaviors of cell-internalizing mAbs were analyzed with a confocal laser-scanning microscope. In MS1 cells, intracellular fluorescence derived from scFvCy5.5 was observed with cell-internalizing scFvs, but not with low-internalizing scFvs (supplemental Figure 3A,D,E,H). Fluorescence was suppressed, however, under the inhibition of energy-dependent endocytosis (supplemental Figure 3B-C,F-G). These results suggested that cell-internalizing scFvs entered into the cells via energy-dependent endocytosis.
For in-depth analysis of the intracellular behavior, confocal laser-scanning microscope analysis was performed with immunostaining of endosome markers (supplemental Figure 3Iab). After scFvsCy5.5 were bound to the cell-surface, the cells were incubated for an additional 1 to 8 hours at 37°C. The early endosome marker, early endosome antigen 1 (EEA1), and the late endosome marker, lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1), were visualized using Alexa488-conjugated antibodies. Colocalization with EEA1+ early endosomes decreased over time (supplemental Figure 3I-M,S-W), whereas colocalization with LAMP1+ late endosomes increased (supplemental Figure 3N-R,Xab). These findings suggested that cell-internalizing scFvs were encapsulated in EEA1+ early endosomes at an early stage and eventually accumulated in LAMP1+ late endosomes. This is thought to be a typical endocytotic molecular sorting pathway.39
Influence of cell-internalizing activity on biodistribution
To assess the biodistribution of cell-internalizing mAbs, 125I-labeled dscFvs (dscFv125I) were intravenously injected into B16BL6 tumor-bearing mice. In this experiment, we selected the dscFv form because dscFv has superior in vivo tumor-targeting potency compared with scFv.40 At 2 hours, the tumor distribution of anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I was similar to but significantly higher than that of a negative control dscFv125I (anti-His[dscFv]125I; Figure 4A-B). This finding suggested that the anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs had tumor-targeting properties. Anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I also accumulated in the kidney, indicating a nonspecific distribution of dscFvs for their elimination,41,42 because no significant difference was observed between anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I and anti-His[dscFv]125I (Figure 4A). Importantly, the accumulation of anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I in the kidney was significantly greater than that of anti-His[dscFv]125I (Figure 4B). A similar accumulation of anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I, but not anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I (Figure 4A), was observed in the heart (Figure 4B).
In vivo tumor-targeting activity of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Biodistribution of dscFvs in B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered with anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I (A,C) or anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I (B,D). Each organ was extracted after 2 hours (A,B) or 24 hours (C,D), and the radioactivity was measured using a γ counter. %ID/g tissue was calculated using the following formula: %ID/g tissue = (count/g tissue)/(total injected count) × 100 (%). Tu, tumor; Li, liver; Ki, kidney; Sp, spleen; Lu, lung; He, heart; Br, brain; Bl, blood. (A,C) black; R4-13i[dscFv]125I; gray, R4-16[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. (B,D) black, V2-05i[dscFv]125I; gray, V2-02[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. Values are shown as means ± SEM. *P < .05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant in Student’s t-test (n = 11). (E-S) Co-immunostaining of dscFvs with CD31+ blood endothelial cells on the tissue section. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered dscFvsBio. The tumor, kidney, and heart were extracted after 2 hours. Tissue sections of tumor, kidney, and heart were stained with streptavidin-PE conjugate. The blood vasculature was also stained with anti-CD31 antibody. Images were digitally merged. Red, dscFvBio; green, CD31; blue, DAPI (nucleus); yellow, colocalized region of red and green. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (E-G) R4-13i[dscFv]; (H-J) R4-16[dscFv]; (K-M) V2-05i[dscFv]; (N-P) V2-02[dscFv]; (Q-S) anti-His[dscFv]. (E,H,K,N,Q) Tumor section, (F,I,L,O,R) kidney section, and (G,J,M,P,S) heart section.
In vivo tumor-targeting activity of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Biodistribution of dscFvs in B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered with anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I (A,C) or anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I (B,D). Each organ was extracted after 2 hours (A,B) or 24 hours (C,D), and the radioactivity was measured using a γ counter. %ID/g tissue was calculated using the following formula: %ID/g tissue = (count/g tissue)/(total injected count) × 100 (%). Tu, tumor; Li, liver; Ki, kidney; Sp, spleen; Lu, lung; He, heart; Br, brain; Bl, blood. (A,C) black; R4-13i[dscFv]125I; gray, R4-16[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. (B,D) black, V2-05i[dscFv]125I; gray, V2-02[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. Values are shown as means ± SEM. *P < .05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant in Student’s t-test (n = 11). (E-S) Co-immunostaining of dscFvs with CD31+ blood endothelial cells on the tissue section. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered dscFvsBio. The tumor, kidney, and heart were extracted after 2 hours. Tissue sections of tumor, kidney, and heart were stained with streptavidin-PE conjugate. The blood vasculature was also stained with anti-CD31 antibody. Images were digitally merged. Red, dscFvBio; green, CD31; blue, DAPI (nucleus); yellow, colocalized region of red and green. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (E-G) R4-13i[dscFv]; (H-J) R4-16[dscFv]; (K-M) V2-05i[dscFv]; (N-P) V2-02[dscFv]; (Q-S) anti-His[dscFv]. (E,H,K,N,Q) Tumor section, (F,I,L,O,R) kidney section, and (G,J,M,P,S) heart section.
To confirm this phenomenon, the localization of dscFvs in the tissues was analyzed by immunofluorescence studies (Figure 4E-S). Biotin-labeled dscFvs (dscFvsBio) were intravenously administered to B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice and the tumors, kidneys, and hearts were extracted 2 hours after injection. The dscFvBio and vascular endothelial cells were stained by streptavidin-AP and anti-CD31 antibody, respectively. In the tumor sections, all of the anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 dscFvsBio were clearly detected with CD31+ tumor blood vasculature, whereas anti-His[dscFv]Bio was not detectable (Figure 4E,H,K,N,Q). This finding suggested that both anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs recognized tumor endothelial cells in vivo, which contributed to their accumulation in the tumor. Interestingly, in the kidney and heart sections, signals around CD31+ blood vasculature were detectable only with the anti-VEGFR2 dscFvsBio, and not with anti-Robo4 dscFvsBio or anti-His[dscFv]Bio (Figure 4F-G,I-J,L-M,O-P,R-S). This finding was compatible with the biodistribution results (Figure 4A-B), which suggested that anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs recognized VEGFR2 on normal blood vessels because VEGFR2 plays an important role in normal tissues, including the kidney and heart.31-33 No specific accumulation of anti-Robo4 dscFvs was observed in normal tissues, suggesting that the anti-Robo4 mAbs were useful for specific tumor vascular targeting.
Comparison of the cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs revealed a significantly greater accumulation of cell-internalizing dscFvs125I in the tumors compared with low-internalizing dscFvs125I at 24 hours (Figure 4C-D), whereas no differences were observed at 2 hours (Figure 4A-B). This finding suggested that cell-internalizing mAbs were retained in the tumor for a longer time than the low-internalizing mAbs. This phenomenon was also observed in the kidney and heart with the anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs (Figure 4D). This retention might be caused by the mAb internalization, which allowed the mAb to escape from the bloodstream and accumulate in the tumor blood endothelial cells. Taken together, these results suggest that mAb internalization into the tumor endothelium improves mAb-based drug-delivery in vivo.
Enhanced antitumor effect depends on the cell-internalizing activity
To assess the antitumor potencies of the cell-internalizing mAbs, we selected the scFv-PSIF and IgG-NCS forms. Both forms were suitable models of ADCs because both drugs are used clinically as successful anticancer medicines.10,43 First, the in vitro cell-killing activities of scFv-PSIFs and IgG-NCSes were estimated by a cytotoxicity assay with MS1 cells (Figure 5A-D). Both forms of cell-internalizing mAbs showed an approximately 10-fold higher cytotoxicity than the low-internalizing mAbs. These findings clearly suggest that internalization enhanced the delivery of conjugated drugs into the cells because our cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs had similar affinities against antigens (Table 1).
Enhanced anti-tumor effect of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Cytotoxicity of scFv-PSIF and IgG-NCS against MS1 cells. MS1 cells were incubated with serially diluted mAb-drug conjugates for 24 hours. Cell viability was then measured using a WST-8 assay. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls. (A) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (B) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (C) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (D) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Anti-His[scFv]-PSIF and anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS were used as negative controls. Values are shown as means ± SD. (E-H) Antitumor effects of scFv-PSIFs or IgG-NCSes. B16BL6 cells were inoculated intracutaneously into C57BL6 mice on day 0. On days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11, mAb-drug conjugates were intravenously administered (arrow heads). Tumor volume was calculated using the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = {major axis of tumor (mm)} × {minor axis of tumor (mm)}2 × 0.4. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (E) Anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (F) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (G) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (H) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus low-internalizing mAbs by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6). (I-L) Change in body weight during therapy experiment. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (I) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (J) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (K) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (L) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus PBS by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6).
Enhanced anti-tumor effect of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Cytotoxicity of scFv-PSIF and IgG-NCS against MS1 cells. MS1 cells were incubated with serially diluted mAb-drug conjugates for 24 hours. Cell viability was then measured using a WST-8 assay. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls. (A) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (B) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (C) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (D) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Anti-His[scFv]-PSIF and anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS were used as negative controls. Values are shown as means ± SD. (E-H) Antitumor effects of scFv-PSIFs or IgG-NCSes. B16BL6 cells were inoculated intracutaneously into C57BL6 mice on day 0. On days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11, mAb-drug conjugates were intravenously administered (arrow heads). Tumor volume was calculated using the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = {major axis of tumor (mm)} × {minor axis of tumor (mm)}2 × 0.4. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (E) Anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (F) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (G) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (H) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus low-internalizing mAbs by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6). (I-L) Change in body weight during therapy experiment. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (I) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (J) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (K) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (L) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus PBS by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6).
As the therapy experiment in vivo, scFv-PSIFs and IgG-NCSes were intravenously injected into B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice once every 2 days for a total of 5 injections (Figure 5E-H). All cell-internalizing mAbs significantly suppressed tumor growth, whereas the antitumor effects of the low-internalizing antibodies were similar to those of the negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF and anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS). The antitumor effects of R4-13i and V2-05i were similar in both ADC forms. These findings strongly suggest that the cell-internalizing activity of the mAbs was essential to maximize the delivery of the conjugated drug into the target cells, which significantly enhanced the antitumor effect of the ADCs.
Interestingly, the group of mice administered V2-05i[scFv]-PSIF had a significant loss of body weight, whereas the other groups did not (Figure 5I-L). As a preliminary result, 6 of 7 mice died in the V2-05i[scFv]-PSIF group with a similar protocol but with a fourfold higher dosage (60 pmol/mouse), perhaps because of the disruption of VEGFR2-positive cells in normal tissues by V2-05i[scFv]-PSIF, as shown in Figure 4. This side effect was not observed in the V2-05i[IgG]-NCS group. Therefore, we also hypothesized that the toxicity of NCS in normal cells was weak because NCS inhibits DNA synthesis in growing cells, such as tumor cells.44 At a higher dosage, however, V2-05i[IgG]-NCS carries the risk of side effects. With regard to this point, none of the anti-Robo4 ADCs induced a loss of body weight; therefore, we concluded that Robo4 is a potential target for tumor vascular targeting with ADC.
Discussion
This study led to three novel findings. First, we demonstrated a rapid screening system for cell-internalizing mAbs in combination with the phage antibody library, which accelerated the identification of desired cell-internalizing mAbs. Second, comparative in vivo studies using cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs with the same affinity values revealed that mAb internalization contributed to tumor targeting and enhanced the antitumor effects of the ADCs. Third, the first in vivo therapeutic application with anti-Robo4 mAb revealed that Robo4 is a therapeutic target on the tumor endothelial cells. The first and second findings will greatly contribute to the development of antibody therapies based on cell-internalizing antibodies such as ADCs, targeted liposomal drugs, or imaging. The third finding provides a new focus regarding the role of Robo4 biology in the body, such as the decreased side effects associated with depleting Robo4-positive endothelial cells in vivo.
This method allowed us to successfully isolate anti-Robo4 and anti-VEGFR2 cell-internalizing mAbs in combination with a phage antibody library and a PSIF-based screening system. This method provided one-step screening of cell-internalization of hundreds of “monoclonal” candidates. This is the main advantage of the present system over the old screening system, which required handling a “polyclonal” pool of mAbs.6,7 The innovative feature of our method is the use of PSIF as a fusion partner for antibodies in scFv format, thus facilitating the identification of antibody fragments capable of efficient internalization. The scFv fusion is much easier than the chemical conjugation of the antibody to a cytotoxic drug. In principle, this method can be applied to other phage libraries, such as nonimmune phage antibody libraries35,45 or synthetic human phage antibody libraries,46,47 which have already been developed. This system can expand the versatility of phage display systems, which will thus contribute to the development of other cell-internalizing antibodies against various types of antigens for effective cancer therapy.
A comparison of cell-internalizing mAbs with low-internalizing mAbs revealed the strength of the cell-internalizing mAbs in terms of the biodistribution and therapeutic effects. Until now, how internalization contributes to the biodistribution of mAbs has been unclear. In this report, we could use a comparative study to clarify this question because we produced both cell-internalizing mAbs and low-internalizing mAbs with similar binding affinities. As a result, more cell-internalizing mAbs than low-internalizing mAbs were significantly accumulated in the tumor. This is the first evidence to support that mAbs with high internalization activity have greater tumor-targeting potency. This information is also useful for other applications that benefit from cell-internalizing mAbs, such as liposomal drugs, bioactive proteins/peptides, and viral vectors.48,49
Until now, the usefulness of Robo4-targeted therapy has not been established. Therapy to target VEGF-VEGFR signaling is already common, but the risk of side effects must be addressed.31-33 Although VEGFR expression is upregulated on tumor vessels, it is also observed on the endothelium in healthy tissues. Previous reports also mentioned the toxicity associated with the anti-VEGFR therapies in mouse models50 and the clinical trial.51 Therefore, alternative therapies that target tumor angiogenesis are desired. In the present study, we revealed the possibility that anti-Robo4 ADCs were safer than anti-VEGFR2 ADCs, although they had similar antitumor effects. The findings from immunofluorescence and biodistribution studies also support the notion that anti-Robo4 mAbs could accumulate in the tumor without distributing to normal tissues. This is the first finding of Robo4-targeted therapy and suggests that Robo4 is a potential alternative target for tumor vascular targeting. Of course, additional experiments are needed to establish anti-Robo4 as a novel tool in tumor vascular targeting. For example, the pathological observations of normal blood vessels, in-depth toxicological analysis, or the efficacy against other clinical relevant tumor models, are important for the successful story. Such basic analyses regarding Robo4 might accelerate the development of novel medicines that target tumor angiogenesis, including anti-Robo4 ADCs.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific research (B) and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science; Strategic Japanese-Swiss Cooperative Program from Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich.
Authorship
Contribution: Y.M. designed the study; M.Y. and Y. Tsumori performed the experiments; Y.M. and M.Y. analyzed the data; Y.M. and M.Y. wrote the initial manuscript; S.T. and Y. Tsutsumi contributed to the phage display; Y.Y. and N.O. contributed to animal experiments; Y.O., W.C.A., and T.D. contributed to Robo4 related analysis; Y.M. and S.N. were responsible for the overall project. All authors edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Yohei Mukai and Shinsaku Nakagawa, Laboratory of Biotechnology and Therapeutics, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, 1–6 Yamadaoka, Suita, Osaka 565–0871, Japan; e-mail: y-mukai@nibio.go.jp and nakagawa@phs.osaka-u.ac.jp.
References
Author notes
M.Y. and Y.M. contributed equally to this study.

![Figure 3. Cell internalization analyzed by flow cytometry. (A,C) Trypsinization to quantify internalized mAbs. Different forms of mAbsCy5.5 bound to the MS1 cells at 4°C. After washing out the unbound mAbs, internalization was induced for 2 hours at 37°C. To detect only internalized mAbs, cell surface proteins were trypsinized. The remaining cellular fluorescence was then analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Anti-Robo4 mAbsCy5.5, (C) Anti-VEGFR2 mAbsCy5.5. Black, nontrypsinized group; gray, trypsinized group; white, negative control (anti-His[scFv]Cy5.5, anti-His[dscFv]Cy5.5, or anti-FLAG[IgG]Cy5.5). (B,D) Time course of the internalization. After binding at 4°C, internalization was induced for 0.5, 1, 2, 4, or 8 hours at 37°C. The ratio of internalization was calculated using the following formula: internalization (%) = {internalized mAb}/{total bound mAb} × 100 (%) = {(MFI of mAb)T – (MFI of negative control)T}/{(MFI of mAb)N – (MFI of negative control)N} × 100 (%). T, trypsinized group; N, nontrypsinized group; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (B) Closed and open markers indicate R4-13i and R4-16, respectively. (D) Closed and open markers indicate V2-05i and V2-02, respectively. (B,D) Circles, diamonds, and squares indicate scFv, dscFv, and IgG, respectively. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Values are shown as means ± SD. **P < .01; internalizing mAb versus low-internalizing mAb in each form by 2-way ANOVA (n = 3).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/121/14/10.1182_blood-2012-12-468363/4/m_2804f3.jpeg?Expires=1769085212&Signature=QkHZwwCtODrWkDtLt6RUZ~0rsNPZKKUOAJRG4xVlmg~nqzY8y0OvCwSrdLS5ql8P4MjxPDDHqAF9lGQJNRRlIPsx~Q-U2UnoQs7y7n0HYMWxfubfRE-pzmbVHMOUCK05ifVrhIrnRo4~8fdkzfH8KhNKtfPRaNB-0kVIiGWUJQ-HBMPUk3RdF0OT4Ca0mBYbMdOHqb4pXRvdeGmkbyqIJGVQquunov-6WaW-GDp1V9dYyHdo6Sk0DSFTqiAPlYa1-VvEacfK1CgwkOohiW09FW~4qgxT0mv8yoaEHCDtRcrL28ZHqD1pqxIsbwPvcdJGUCVBoeBIOiuoCvAG12-COw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 4. In vivo tumor-targeting activity of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Biodistribution of dscFvs in B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered with anti-Robo4 dscFvs125I (A,C) or anti-VEGFR2 dscFvs125I (B,D). Each organ was extracted after 2 hours (A,B) or 24 hours (C,D), and the radioactivity was measured using a γ counter. %ID/g tissue was calculated using the following formula: %ID/g tissue = (count/g tissue)/(total injected count) × 100 (%). Tu, tumor; Li, liver; Ki, kidney; Sp, spleen; Lu, lung; He, heart; Br, brain; Bl, blood. (A,C) black; R4-13i[dscFv]125I; gray, R4-16[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. (B,D) black, V2-05i[dscFv]125I; gray, V2-02[dscFv]125I; white, anti-His[dscFv]125I. Values are shown as means ± SEM. *P < .05; **P < 0.01; NS, not significant in Student’s t-test (n = 11). (E-S) Co-immunostaining of dscFvs with CD31+ blood endothelial cells on the tissue section. B16BL6 tumor–bearing mice were intravenously administered dscFvsBio. The tumor, kidney, and heart were extracted after 2 hours. Tissue sections of tumor, kidney, and heart were stained with streptavidin-PE conjugate. The blood vasculature was also stained with anti-CD31 antibody. Images were digitally merged. Red, dscFvBio; green, CD31; blue, DAPI (nucleus); yellow, colocalized region of red and green. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (E-G) R4-13i[dscFv]; (H-J) R4-16[dscFv]; (K-M) V2-05i[dscFv]; (N-P) V2-02[dscFv]; (Q-S) anti-His[dscFv]. (E,H,K,N,Q) Tumor section, (F,I,L,O,R) kidney section, and (G,J,M,P,S) heart section.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/121/14/10.1182_blood-2012-12-468363/4/m_2804f4.jpeg?Expires=1769085213&Signature=3c4fuOdFJfAhhsiVTnmWNfmR-9EhRtJzvfCG90oj3g2qZ2jX92XLLFo4VAR2LUAJy~gJ6ZmpVOummTU50E4OpeEzY31WeWw5obbX4t3bl-2ypZz~-7lD1GUQ9E52r-DoAZKRGghZND4T-CkbOnMOcYFfPx7aiNDz1ddep4EunCxM8D~i0H1zsv9fMUkLcQADI7cx4mVqgMvLLXDrph1Mh2Tyj5M3vFXoovndz9zq-oj9PYeIOeaPtBL7tzrf9OfuUC1i5La9UKl2lyUIAKRQa8-LpEJwWuOsG2rPe8LbvgcSnBo2igddHVqXwWjsIXYLWucSXCjPD5ZrTzySVVW21Q__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
![Figure 5. Enhanced anti-tumor effect of cell-internalizing mAbs. (A-D) Cytotoxicity of scFv-PSIF and IgG-NCS against MS1 cells. MS1 cells were incubated with serially diluted mAb-drug conjugates for 24 hours. Cell viability was then measured using a WST-8 assay. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls. (A) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (B) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (C) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (D) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Anti-His[scFv]-PSIF and anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS were used as negative controls. Values are shown as means ± SD. (E-H) Antitumor effects of scFv-PSIFs or IgG-NCSes. B16BL6 cells were inoculated intracutaneously into C57BL6 mice on day 0. On days 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11, mAb-drug conjugates were intravenously administered (arrow heads). Tumor volume was calculated using the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = {major axis of tumor (mm)} × {minor axis of tumor (mm)}2 × 0.4. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (E) Anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (F) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (G) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (H) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus low-internalizing mAbs by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6). (I-L) Change in body weight during therapy experiment. Closed square, internalizing mAbs; open circle, low-internalizing mAbs; open triangle, negative controls (anti-His[scFv]-PSIF or anti-FLAG[IgG]-NCS); open diamond, PBS. (I) anti-Robo4[scFv]-PSIFs, (J) anti-Robo4[IgG]-NCSes, (K) anti-VEGFR2[scFv]-PSIFs, (L) anti-VEGFR2[IgG]-NCSes. Values are shown as means ± SEM. **P < 0.01; internalizing mAbs versus PBS by Bonferroni post hoc analysis with two-way ANOVA (n = 6).](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/121/14/10.1182_blood-2012-12-468363/4/m_2804f5.jpeg?Expires=1769085213&Signature=ccZpWregt5VKRiWNSNIzrOTWqVt5x3K0bFqdG2KIdH-8pbIiXrV~bDRV8Y49eqfVIBVZKqqldNsyNxeiaa80LQezBbC6iRjXleWZd~H6Gp2evV0~v2y0mMtS8awfzlKk8Ifb7dPU9QyGDxu1y0-QkueMyxatWefCtBTqMnpUmsrm7qbiQxFZewR7krp6mCJsS27NvafDCJiUSZv7g9dCVrzk-2lhuPZSfKpYB~gDms9SQOPw6KWpJteJ8mBPTeCETvEGgVEghXBm63U7reag5SAtKAswiyEohKDtHYo2PGwo24kYSyTL23Wuo1sqwZZg2Hl0z8y14WhYZdctdqsrSQ__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal