Abstract
T regulatory cells (Tregs) safeguard against autoimmunity, but may compromise antitumor immunity. Aberrant immune signaling via signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins is involved in disease pathobiology in numerous malignancies. Azacytidine treatment affects Treg levels, particularly in responders, but its effect on STAT signaling is unknown. We explored the alterations of STAT signaling profile (SP) of Tregs during azacytidine treatment and their association with clinical and biological parameters.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 19 late-stage MDS patients were obtained before and 15 days after azacytidine initiation. According to WHO, one had RAEB-I (5%), 9(47%) patients had RAEB-II, 7(37%) CMML-II and 2(10%) AML/MDS. Based on the IWG criteria patients were divided into responders (CR, PR and hematologic improvement, n=8) and non-responders (stable disease and failure, n=11). We applied a modified protocol of phospho-specific flow cytometry to measure either basal (untreated) or potentiated (after stimulation with IL-6 and IL-2 for 15’) phospho-STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5 levels with simultaneous staining for FOXP3. The following potentiated, i.e. target/stimuli, nodes were studied: pSTAT1/IL-6, pSTAT3/IL-6 and pSTAT5/IL-2. Comparisons were performed by paired, unpaired t-test or one-way ANOVA as appropriate. Clustering of SPs was performed with hierarchical cluster analysis and was correlated with response, disease subtype, and cytogenetics by using ÷2 or Fisher Exact tests.
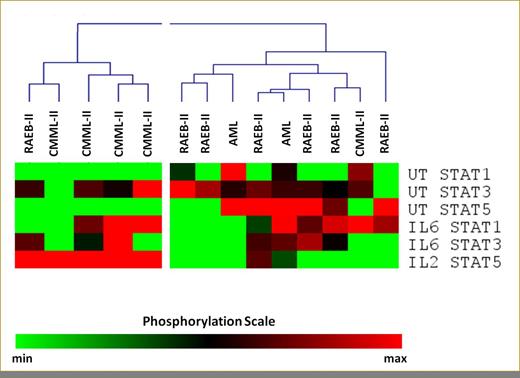
Pretreatment SPs of Tregs in 19 patients.
Ratio of the SPs of Tregs 15 days after/before azacytidine initiation in 19 patients.
Ratio of the SPs of Tregs 15 days after/before azacytidine initiation in 19 patients.
Collectively, consistent with recent data (Constantini B et al, 2012), we observed both arithmetical and functional alterations of Tregs in MDS patients after azacytidine treatment. Moreover, both the pretreatment SP and the differential modulation of STAT signaling in the Tregs of CMML-2 and RAEB-II patients, argue for a potentially diverse epigenetic regulation of tumor immunity among the various MDS subtypes.
Tsatalas:Genesis Hellas: Honoraria. Spanoudakis:Genesis Hellas: Honoraria. Kotsianidis:Genesis Hellas: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal