Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is a vasoactive molecule that can bind to hemoglobin (Hb) in the form of S-nitrosothiol (SNO) functionalities at the β93 cysteine residues. Red blood cells (RBCs) containing S-nitrosohemoglobin (SNO-Hb) are able to not only deliver oxygen, but release vasodilatory NO/SNO equivalents to enhance blood flow in order to match tissue oxygen demand (e.g., during hypoxic vasodilation). Newborn babies normally carry two variants of hemoglobin, adult (Hb A) and fetal (Hb F). It is well known that Hb F binds oxygen more tightly than Hb A in order to facilitate oxygen scavenging across the placenta from maternal Hb A. Given that SNO-Hb is preferentially formed on oxygenated Hb, we hypothesized that Hb F may also bind a higher concentration of NO. Previous studies examining the NO content of cord blood were disadvantaged by looking at cord blood Hb as a whole. To date, no attempt has been made to determine the basal levels of NO bound to each Hb variant independently. Therefore, we aimed to separate the variants and measure the NO/SNO content of Hbs F and A in order to establish basal levels for each variant in cord blood at term. We reasoned that the results could improve insight into mechanisms of abnormal perinatal transitions and the selection of therapies involving NO signaling and/or RBC transfusion.
Venous and arterial umbilical cord blood samples were collected immediately after normal term cesarean sections of infants with minimum gestational age of 37 weeks. RBC samples were washed in pH 7.4 phosphate buffered saline (PBS) with 100 µM diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA) chelator to preserve SNOs, and hypotonically lysed. Total Hb was obtained through purification of the lysate through a Sephadex G-25 column. Partially purified Hb (200 µL) was loaded onto a HiTrap Q HP anionic exchange column (5 mL column volume with 34 µm bead size) and subjected to an increasing ionic strength gradient of 0–0.15M NaCl in pH 8.4 Tris buffer. Spectrophotometric analysis corroborated the complete separation of the variants. Isoelectric focusing on a Perkin Elmer Hemoglobin Resolve gel for 50 minutes at 1500 V and 10–15 °C was used in conjunction with an AFSC Hemopure control to identify the respective variants in each fraction. Each Hb variant was reconcentrated in pH 7.4 PBS with 100 µM DTPA via centrifugation through pre-rinsed 10 kDa MW cutoff centrifugal filters. The SNO/NO content of each variant was analyzed by photolysis-chemiluminescence of paired samples diluted to 100 μM Hb with/without 600 μM HgCl2. For samples with lower Hb concentration, a 6-fold molar excess of HgCl2 was also used. The Hg (mercury) acts to cleave NO bound to thiols (i.e., SNO) and is unreactive towards FeNO complexes; thus the difference in the paired sample peaks indicates the amount of SNO-Hb present in the sample.
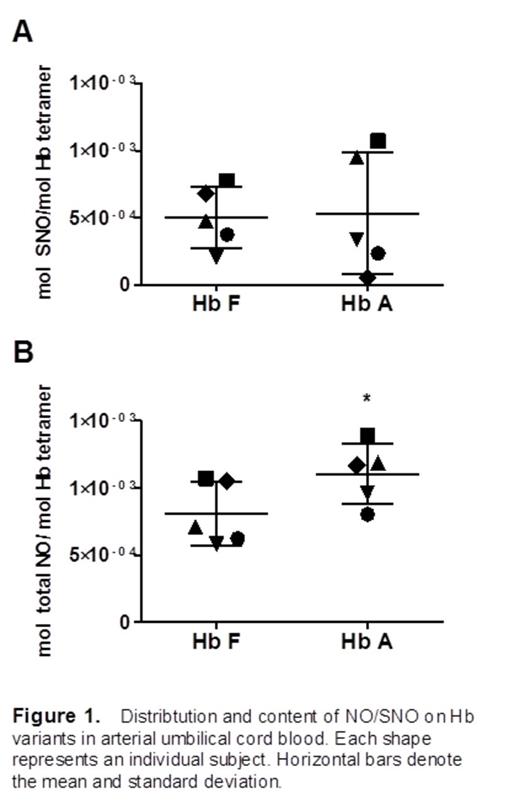
In arterial cord blood samples, the amount of SNO-Hb bound to each variant (i.e., fetal and adult) was found to average ∼5 x 10-4 mol SNO per mol of Hb tetramer (Figure 1A). There was no significant difference between Hb F and Hb A with regards to SNO-Hb. Venous cord blood samples had similar results. The amount of total NO (i.e., SNO-Hb and heme-bound NO) bound to each variant was significantly higher on Hb A in arterial samples. (Figure 1B, *, p value < 0.05 vs. Hb F by paired t-test).
Both Hb A and Hb F carry substantial and similar amounts of SNO adduct. Given the lower percentage (∼15-20%) of Hb A as a constituent in the total Hb of cord blood at term, the finding of a higher total NO content on Hb A than Hb F suggests that the presence of Hb A may be important to the total NO bioavailability in newborns. Vasodilator NO/SNO is known to be essential in the healthy cardiopulmonary transition to air breathing at birth. Thus, fundamental and translational studies assessing these species in newborns experiencing difficult transitions or pathophysiological states (e.g., persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, PPHN) may provide potential biomarkers with utility in early detection of disease, prognosis, and intervention selection and management. The results and methodology presented here have broad applications to numerous areas of hematology and other medicine including neonatal intensive care, therapeutic induction of HbF in sickle cell disease patients, and decision-making in transfusion medicine.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal