Abstract
Since the first case report of Gimaz et al., several investigators have reported that the secondary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) can occur in patients with Helicobactor pylori (H. pylori) infection. Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to result in improvement in thrombocytopenia. In one systematic review of 696 patients with H. pylori infection it showed 50.3% overall response (platelet count >= 30 X 109/L and at least a doubling of the base line count) after H. pylori eradication. Under these results, ASH 2011 guidelines for ITP recommended that eradication therapy be administered in adult patients who are found to have H. pylori infection (grade 1b). But also they recommended that treatment be administered for newly diagnosed patients with a platelet count < 30 X 109/L. To the best of our knowledge, there was no prospective study to evaluate the efficacy of H. pylori eradication for ITP patient with moderate thrombocytopenia and positive H. pylori. In Korea, the prevalence of H. pylori was reported as high as 60 – 65% in general adult population. The response rate and price of 1st line triple regimen for H. pylori eradication were known to be 70 - 80% and around 100 US dollars in Korea. With these circumstances, tolerable treatment like H. pylori eradication for ITP patients with platelet count >=30 X 109/L is challengeable. Thus, we performed the prospective multicenter phase II study to evaluate the efficacy of H. pylori eradication for the 1st line treatment of persistent or chronic ITP patients with moderate thrombocytopenia.
We enrolled patients with persistent (3 to 12 months from diagnosis) or chronic (lasting for more than 12 months) ITP defined by international working group. The platelet counts of patients were between 30 X 109/L and 70 X 109/L. And all patients had positive result of C13-urea breath test (UBT) and had never been treated for ITP or H. pylori. Patients with other secondary ITP could not be enrolled. Patients received lansoprazole 30mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000mg twice daily and clarithromycin 500mg, twice daily for one week. Eradication of H. pylori was evaluated at eighth week after treatment by UBT. Platelet counts were monitored at 2 weeks and after then at every month for a year. Complete response (CR) was defined as a platelet count >= 100 X 109/L. Partial response (PR) was defined as a platelet increase of >= 30 X 109/L and at least a doubling of the base line count. The primary endpoint was CR rate at 3 months after treatment. All patients provided written informed consents and this trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01255332).
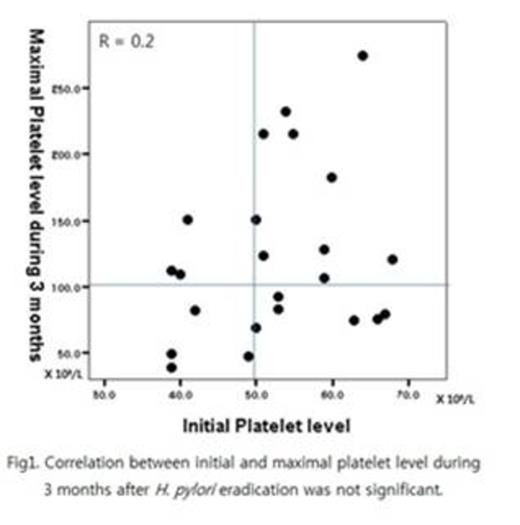
Twenty-six patients were enrolled between November 2010 and May 2013 from 6 medical centers in Korea. Two patients with HCV infection and one patient with more than 70 X 109/L of platelet counts were excluded from analysis. The mean initial platelet counts of 23 patients (7 males, 16 females, median age 43 years and range 19 - 58 years) was 52.7 ± 9.5 X 109/L (range 39 – 68 X 109/L). All patients except one checked UBT after treatment and H. pylori eradication was achieved in 86.3% (19/22) of patients. CR was obtained in 13 of 23 patients (56.5%) within 3 months after treatment. And no PR was found until this time point. The median time to CR after initiating treatment was 4 weeks (range 2 – 8 weeks). CR rate of the patients who achieved H. pylori eradication was 63.2% (12/19). Unlike other reports, there was no significant difference on initial platelet counts among CR group and non-responder group and no significant correlation on the platelet levels between baseline and initial 3 months (Fig 1). Only 2 of 26 patients could not continue medication due to nausea and diarrhea, respectively. There was no other significant adverse event.
The eradication of H. pylori is an effective first line treatment for persistent or chronic ITP with moderate thrombocytopenia with high CR rate and rapid onset. And it has acceptable toxicity and relatively low cost. This study supports routine detection and eradication of H. pylori infection in ITP patients especially in populations with a high prevalence of this infection.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal