Abstract
A 88 year-old woman was referred to our center for 3 weeks of gastrointestinal bleeding and a spontaneous right rectus femoris hematoma. The prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), thrombin time (TT) and reptilase time (RT) were markedly prolonged (Table 1). Assays for coagulation factors V, VIII, IX and X were normal. A fibrinogen concentration of < 50 mg/dl was measured by Clauss method while fibrinogen concentration measured by radial immunodiffusion was 180 mg/dl. Following infusions of cryoprecipitate there was accelerated clearance of fibrinogen as measured by the Clauss method. An inhibitor of fibrinogen function was suspected.
| Test . | Time (sec) . | 1:1 mix (sec) . | Normal Range (sec) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT | >90 | 22 | 12-15 |
| aPTT | 70.7 | 39 | 23-36 |
| TT | >120 | >120 | 15-19 |
| Reptilase Time | >120 | >120 | 14.8-20.4 |
| Test . | Time (sec) . | 1:1 mix (sec) . | Normal Range (sec) . |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT | >90 | 22 | 12-15 |
| aPTT | 70.7 | 39 | 23-36 |
| TT | >120 | >120 | 15-19 |
| Reptilase Time | >120 | >120 | 14.8-20.4 |
The patient was treated with rituximab and steroids. After four, weekly doses of rituximab, fibrinogen levels by Clauss method normalized (450 mg/dl). There was no detectable antibody to fibrinogen and no further bleeding was noted.
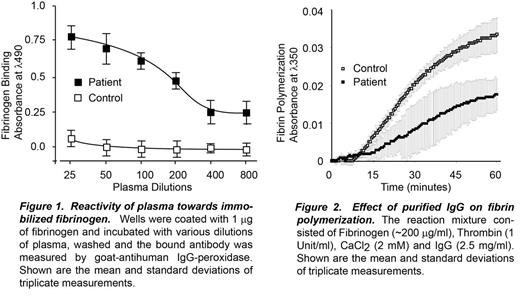
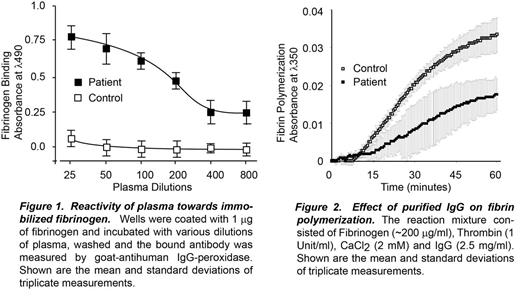
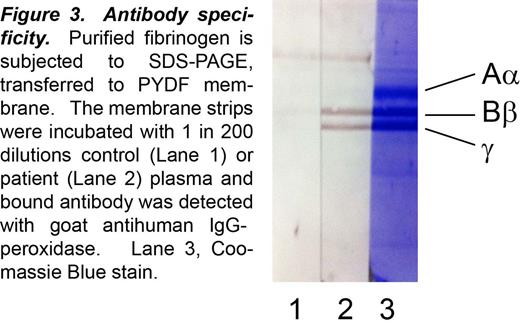
This is a description of a rare case of a polyclonal autoantibody to Bβ and γ chains of fibrinogen that inhibited fibrin polymerization leading to a severe bleeding diathesis.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal