Abstract
The micro-environment in multiple myeloma (MM) is highly immunosuppressive with increased numbers of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) favoring tumorcell survival and hampering immunotherapeutic strategies such as dendritic cell vaccination. Immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) are known to enhance T- and NK-cell function. In this study we evaluated the effects of low dose (0.5 microM) lenalidomide (Len) and pomalidomide (Pom) on the functionality of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, MDSCs, Tregs and ex-vivo generated mononuclear derived dendritic cells (moDCs) obtained from MM patients after first autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Peripheral blood mononuclear cell fractions were obtained by leukapheresis from 9 MM patients (age 29-62 years), in very good partial response (4/9) or complete response (5/9) after ASCT.
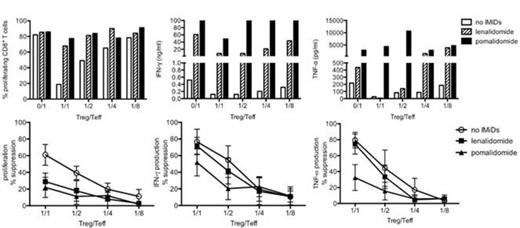
The magnitude of cytokine release (mean +/- standard error of the mean, in ng/ml) by purified CD8+ T cells after 144 hours stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 coated microbeads was significantly increased after addition of Len and Pom to the culture medium, respectively : IFN-gamma (217.5 +/- 62.1 and 437.1 +/- 137.1** vs 66.4 +/- 21.0) , TNF-alpha (21.4 +/- 5.4 and 44.9 +/- 9.4*** vs 4.9 +/- 1.7) and IL-2 (5.3 +/- 2.7 and 12.7 +/- 6.6 vs 1.9 +/- 1.7 ng/ml) (** p< 0.01, *** p< 0.001). We also evaluated the number of different types of cytokines/chemokines on a per cell basis by intracellular flow cytometry staining for IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, IL-2 and MIP-1beta and observed increased polyfunctionality of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells. After 72 h of stimulation with anti-CD3/CD28 microbeads the number of single, double, triple or quadruple functional CD8+ T cells increased from 5.96 %, 2.82 %, 0.1 %, 0 % (culture medium alone) to 9.68 %, 7.57 %, 0.41%, 0.03 % (Len) and 12.57 %, 8.96 %, 0.81 %, 0.03 % (Pom), respectively. A similar observation was made for CD4+ T cells.
TriMix DCs (moDCs matured by electroporation with mRNA encoding TLR4, CD40L and CD70) and cytokine matured moDCs were cocultured with autologous CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and anti-CD3 microbeads. Adding IMiDs resulted in more polyfunctional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells with both types of DCs but effects were most pronounced with the TriMix variant.
Our study shows that Len and Pom restore effector cell functions in myeloma patients with low tumor burden after ASCT. These findings provide a immunomechanistic explanation for IMiD-based maintenance therapy. They also offer a rationale to combine IMiD-based maintenance with immunotherapeutic approaches such as dendritic cell vaccination in this particular setting.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal