Abstract
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) represents a post-remission therapy offering potential cure for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients (pts). Reduced-Intensity Conditioning (RIC) is increasingly used in AML pts undergoing HCT ineligible for conventional conditioning.
The ecotropic viral integration site 1 (EVI1) gene maps to chromosome 3q26 and encodes a transcription factor that has an important role during embryogenesis. EVI1 activation, e.g. through chromosome 3 translocations, is found in several human myeloid disorders. The presence of EVI1 expression has been described as a predictor of poor outcome in pts treated with standard cytarabine based chemotherapy. Whether the expression of EVI1 also associates with outcome in AML pts undergoing RIC-HCT, with a therapeutic approach mainly based on a graft-versus-leukemia effect, remains unknown.
Here we tested the prognostic impact of EVI1 expression in RIC-HCT treated AML pts. We analyzed 57 AML pts (median age, 61 years [y]; range 27–74y) who received RIC (Fludarabin 30mg/m^2 at day-4 to -2 & 2Gy total body irradiation at day 0)-HCT at the University of Leipzig, with pretreatment bone marrow material available. Donors were human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-matched related (n=6, 10.5%) or HLA-matched (n=41; 72%) or mismatched (>= 1 antigen; n=10; 17.5%) unrelated. At HCT 82.4% (n=47) of the pts were in complete remission (CR). 28.6% (n=14) had acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD; >= grade 2) and 80.5% (n=33) (31.7% (n=13) limited; 48.8% (n=20) extensive) chronic GvHD. Median follow-up was 7.0 y for pts alive. Medical research council (MRC) genetic classification was: intermediate (n=39; 73.5%) or adverse (n=14; 26.5%). The pts were also characterized for CEBPA and NPM1 mutations, as well as presence of an FLT3-ITD at diagnosis. EVI1 expression was measured with quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and normalized to 18S.
71.9% (n=41) of our pts were EVI1 expressers. The presence of EVI1 expression did not significantly associate with any clinical or biological characteristics. Still, by trend EVI1 expression associated with an adverse karyotype (P=.08) and NPM1 mutations (P=.16).
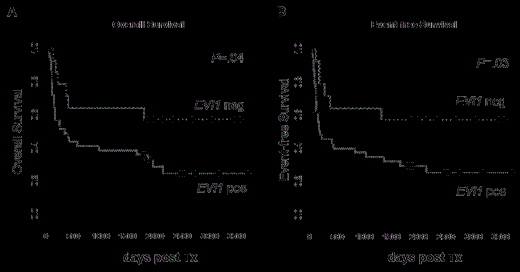
Overall Survival(A) and Event-free Survival (B) in RIC-HCT treated AML pts according to EVI1 expression status
Overall Survival(A) and Event-free Survival (B) in RIC-HCT treated AML pts according to EVI1 expression status
In multivariable analysis in our set, none of the analyzed clinical or biological parameters were significantly associated with OS or EFS. However, in multivariable analysis cytogenetics (intermediate vs. adverse) associated with OS by trend (P=.12); while EVI1 expression status (P=.14), cytogenetics (intermediate vs adverse; P=.11) and remission status at the time point of RIC-HCT (CR vs all other; P=.10) associated with EFS by trend.
In conclusion, the presence of EVI1 expression associated with worse outcome in RIC-HCT treated AML pts. Pretreatment EVI1 expression may refine the risk stratification for AML pts undergoing RIC-HCT.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal