Abstract
The effects of certain risk factors on the survival of adults undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) have been the subject of research for many years. The impact of graft source and donor type, for instance, has already been examined closely. Lately iron parameters like ferritin became point of interest. Several prognostic scores utilizing those risk factors have been proposed. However, observations of pediatric populations considering those factors remain rare and no score in this regard for children with HSCT is available yet.
We retrospectively analyzed the effects of patient sex, recipient-donor sex match status, patient age, donor age, disease risk, graft source, donor HLA match as well as ferritin, albumin, total bilirubin, aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), cholinesterase (CHE), gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), C-reactive protein (CRP) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) taken at the time of transplantation on the 5-year-overall survival of 132 children with malignant or non-malignant diseases undergoing allogeneic HSCT between 2001 and 2011 in a single center. The graft source was either bone marrow (n=82) or peripheral blood stem cells (n=50). The patients had the following underlying diseases: acute lymphoblastic leukemia (n=44), acute myeloid leukemia (n=29), chronic myeloid leukemia (n=5), myelodysplastic syndrome (n=16), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (n=7), solid tumor (n=4), severe aplastic anemia (n=7), myelofibrosis (n=2) and genetic disease (n=18). Conditioning regimen was myeloablative in all cases. The disease risk was formed by dividing the patients into two groups according to their clinical risk. Patients with genetic diseases, severe aplastic anemia, refractory cytopenia, myelofibrosis, leukemia and lymphoma in first or second remission as well as chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase were low risk, while patients with solid tumors, leukemia and lymphoma in relapse or in more than second remission and refractory anemia with excess blast in or not in transformation were high risk. For statistics we used Kaplan-Meier-method for univariate analysis and Cox regression for multivariate analysis.
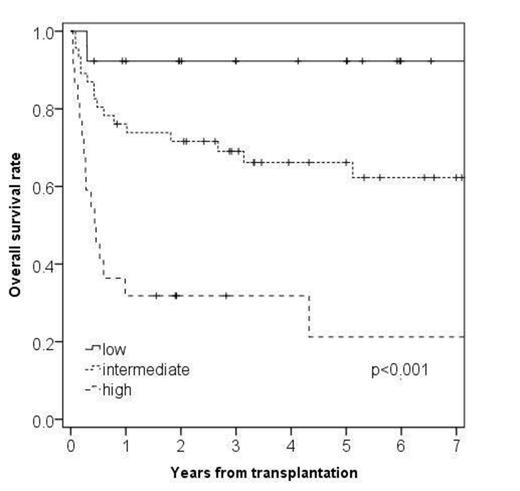
On univariate analysis 5-year-overall survival decreased significantly in patients with ferritin >1500 µg/L (40.8% versus 78.8%, p<0.001), GGT >1 µmol/L∙s (43.2% versus 67.9%, p=0.032), CRP >10 mg/L (54.6% versus 69.4%, p=0.017), LDH >6 µmol/L∙s (22.2% versus 66.8%, p=0.001), CHE <60 µmol/L∙s (35.7% versus 70%, p=0.002) as well as in patients with high disease risk (38.3% versus 74.7%, p<0.001), peripheral blood stem cells as graft source (47.1% versus 72.2% for bone marrow, p=0.001). For HLA donor match there was a 5-year-overall survival of 82.0% for matched related, 58.4% for matched unrelated, 56.3% for mismatched unrelated and 50.0% for haploidentical related donors (p=0.020). Other factors did not show a significant correlation. We subsequently developed a score of those parameters that were significant in multivariate analysis, i.e. disease risk (HR=3.744, p=0.035), ferritin (HR=6.860, p=0.002) and cholinesterase (HR=4.556, p=0.043), dividing the patient population into three groups: low with no risk factor, intermediate with one risk factor and high with two or three risk factors. For this score we found a 5-year-overall survival of 92.3% for low risk group, 66.2% for intermediate risk and 17.4% for high risk (p<0.001).
Our data show that ferritin, cholinesterase and disease risk are factors that decisively influence the prognosis after allogeneic HSCT in children. They should be evaluated in further trials as well as our proposed score. The characteristics that showed up significant in univariate but not in multivariate analysis appear to have an influence as well and might show a stronger correlation in larger trials.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal