Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia with chromosomal alterations impacting the core binding factor transcription complex (CBF-AML), specifically t(8;21) and inv(16), are associated with a greater responsiveness to cytarabine-based chemotherapies and a more favorable prognosis. The latter has been primarily gleaned from outcomes of large clinical trials of AML. However, to date, there is limited population-based outcomes data on CBF-AML. We therefore performed an epidemiologic retrospective cohort study using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database to assess survival trends for CBF-AML at the population level between 2000 and 2010.
Patients with a diagnosis of CBF-AML between 2000 and 2010 were identified using the SEER 18 registries database. We included patients with a diagnosis code of inv(16)/t(16;16) AML (Code 9871) or t(8;21) AML (Code 9896) diagnosed between January 2000 and December 2010. Patients were divided into cohorts based on age at diagnosis: 15-44 years old, 45-64 years old, 65-74 years old, and 75-84 years old. Disease incidence was calculated, as were early mortality rates, defined as death within 1 month. Overall survival (OS) was estimated using the method of Kaplan and Meier. Cox regression was performed to estimate predictors of survival by specific CBF-AML type, age cohorts, race/ethnicity, gender, year of diagnosis, number of primary malignancies, and residence.
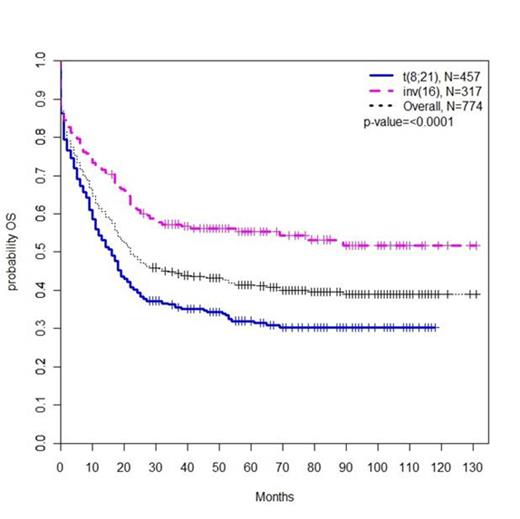
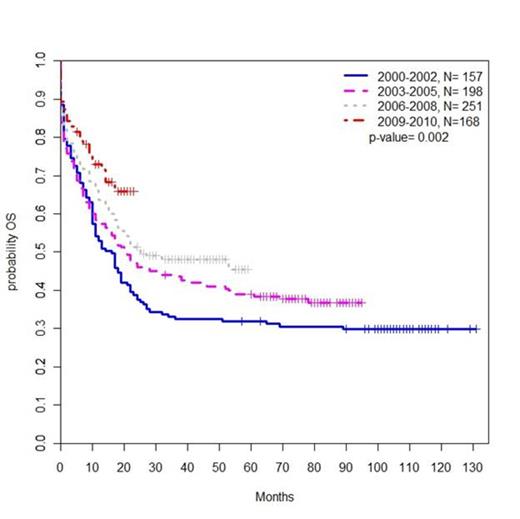
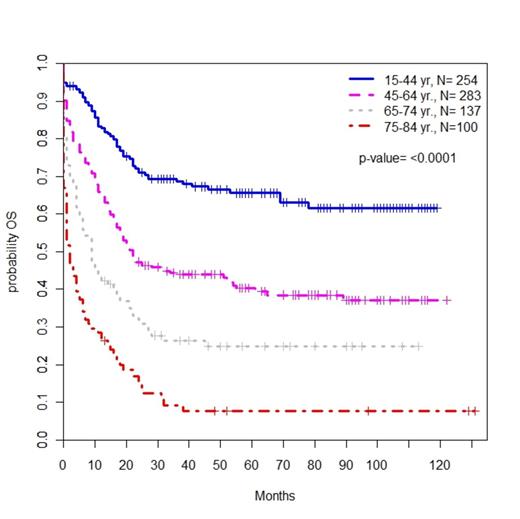
We identified 777 patients with a new diagnosis of CBF-AML between 2000 and 2010. The incidence of CBF-AML increased with advancing age (ages 15-44, 0.06 per 100,000 people; ages 45-64, 0.13; ages 65-74, 0.25; ages 75-84, 0.28). Median OS for all patients was 22 months, and the combined 3-year OS was 44.3% (Fig. 1). Median OS increased from 16 months during the period encompassing 2000 and 2002 to 25 months during the period from 2006 to 2008 (p=0.002) (Fig. 2). The rate of early death was 13%, which increased with age (15-44 5%, 45-64 10%, 65-74 20%, 75-84 33%; P<0.0001). OS also worsened with advancing age; patients ages 75-84 had a 3 year OS of 9.3% and an increased HR for mortality compared to patients ages 15-44, who had a 3 year OS of 68.7% (HR 5.61, P<0.0001) (Fig. 3). Of note, worsening OS with advancing age was observed even among the subset of patients alive at 1 month. Black race was associated with an increased HR for mortality compared to white non-Hispanic patients (HR 1.50, P=0.03). Patients with inv(16) disease had an improved OS compared to patients with t(8;21) disease (HR for mortality 0.65, P<0.0001). The 3 year OS for patients with inv(16) disease was 57.3%, while for those with t(8;21) disease it was only 35.5% (Fig. 1).
Kaplan Meier estimate of OS by CBF-AML subtype and overall.
Kaplan Meier estimate of OS by year at diagnosis.
Kaplan Meier estimate of OS by age at diagnosis
In spite of historically favorable prognoses associated with CBF-AML in clinical trials, we found poorer survival in the general population. Unlike inv(16) disease, patients with t(8;21) CBF-AML did not appear to have a favorable OS. Survival was significantly worse among African Americans and the elderly. The reason for these differences is unknown, and merits further evaluation.
Chen:Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bayer / Onyx: Research Funding. Fathi:Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Teva: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millenium: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal