Abstract
The efficacy and safety of the novel agents, lenalidomide and bortezomib, in previously untreated MM has been demonstrated in several randomized controlled trials (Online-OnlyTs). In this study, we examine the cost-effectiveness of lenalidomide-melphalan–prednisone induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance (MPR-R), and bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone (VMP), respectively, versus melphalan-prednisone (MP), in patients with previously untreated MM.
We developed a partitioned-survival model to estimate expected clinical outcomes and costs in newly diagnosed MM patients receiving MPR-R, VMP, or MP as first-line therapy. The model had 3 mutually exclusive health states: (1) “progression-free, alive”; (2) “post-progression, alive”; and (3) “death.” Progression-free survival (PFS) for MP was estimated by aggregating data across five Online-OnlyTs (Palumbo 2012, San Miguel 2008, Facon 2007, Hulin 2009, Palumbo 2006). Estimates of PFS for MPR-R and VMP were based on an adjusted indirect treatment comparison with MP, using data from MM-015 for MPR-R (Palumbo 2012) and VISTA for VMP (San Miguel 2008). Since many MP patients in both MM-015 and VISTA “crossed over” to lenalidomide and bortezomib following disease progression in these trials, we estimated post-progression survival (PPS) for MPR-R and VMP based on a review of novel agents in MM (Messori 2011), which reported mean PPS of 30.9 months. Costs of MPR-R and VMP were estimated based on actual use of study drug in Online-OnlyTs; costs of adverse events as well as other disease-related costs were estimated based on published data. Health-state utilities also were estimated using published data. All costs were expressed in 2012 US$. Cost-effectiveness of MPR-R and VMP versus MP was examined in terms of cost per life-year (LY) gained, cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained, and cost per progression-free life-year gained. Future costs and benefits were discounted at 3% annually.
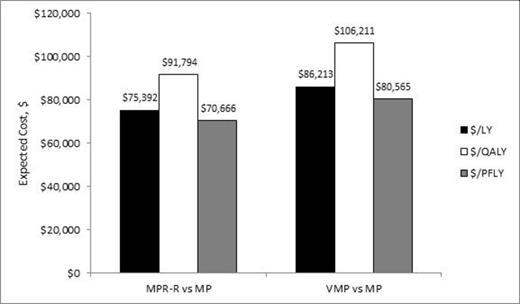
Mean estimated PFS was 3.4 years for MPR-R, 2.6 years for VMP, and 1.7 years for MP; corresponding estimates for OS were 6.0 years, 5.2 years, and 4.3 years, respectively (Table 1). Mean total expected lifetime costs (discounted) are reported in the Table. The incremental cost per life-year (LY) gained versus MP was $75,392 for MPR-R and $86,213 for VMP; corresponding estimates of the incremental cost per QALY gained were $91,794 and $106,211, respectively (Figure 1). The incremental cost per progression-free LY (PFLY) gained versus MP was $70,666 for MPR-R and $80,565 for VMP.
Estimated mean lifetime outcomes and costs for MPR-R, VMP, and MP in previously untreated MM
 |
 |
At 3% annually
Costs were tallied on a discounted basis only
Cost-effectiveness of MPR-R and VMP versus MP in previously untreated MM
In patients with previously untreated MM, cost-effectiveness ratios for MPR-R and VMP are well within the range reported for other well-accepted novel therapies in oncology.
$/LY: Incremental cost per life-year gained; $/QALY: Incremental cost per quality-adjusted life-year gained; $/PFLY: Incremental cost per progression-free life-year gained
Funded by Celgene Corporation
Oster:Celgene: Research Funding. Off Label Use: Lenalidomide (immunomodulatory agent), bortezomib (proteosome inhibitor), melphalan (alkylator), and prednisone (steroid), are all treatments for multiple myeloma. Berger:Celgene: Research Funding. Bornheimer:Celgene: Research Funding. Binder:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Nagarwala:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal