Abstract
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an aggressive subtype of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma associated with poor prognosis. Constitutive activation of B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling plays an essential role for the survival and proliferation of malignant B-cells. Targeting Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK), a component of BCR signaling pathway, with ibrutinib is a promising strategy. As a single agent, complete and partial response rates of 21% and 47%, respectively, were observed in a phase 2 study for relapsed or refractory MCL. Simultaneous inhibition of multiple biologic pathways has the potential to result in a synergism. We combined ibrutinib with ABT-199, a BH3 mimetic that selectively targets the BCL-2 pathway, and tested their in vitroefficacy against MCL.
A novel MCL cell line, CCMCL1, and four other MCL cell lines (Jeko-1, Mino, JVM2, Rec-1) were used for flow cytometry-based apoptosis and cell cycle analyses to evaluate the combinational effect of ibrutinib with ABT-199 (ChemieTek. Indianpolis. IN). The interaction between drugs was examined with Calcusyn software and combination index values served to determine the combined effect as synergistic (<1), additive (=1), or antagonistic (>1). Immunoblotting was performed to investigate signaling pathways of MCL cells exposed to these agents.
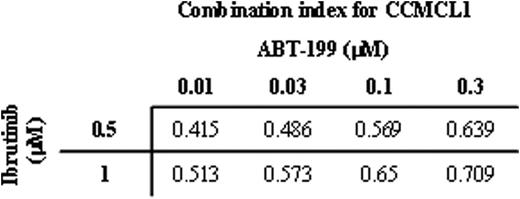
CCMCL1 was derived from primary leukemic MCL cells. Cells were initially directly injected via tail vein into an NSG mouse. Engrafted cells were then isolated at 10 weeks from spleen and placed into routine cell culture. Immunophenotyping showed CCMCL1 cells have similar characteristics as the primary patient MCL cells, which expressed CD5, CD19, CD20, FMC7 and monotypic kappa light chain. Immunohistochemical staining of engrafted mouse spleen tissue showed expression of cyclin D1 and SOX11. The karyotype is highly complex with an IGH@/CCND1 fusion by metaphase FISH. In addition to spleen, MCL cell infiltration was observed in mouse liver, bone marrow, blood, brain, lung, kidney and intestine. In vitro cultured CCMCL1 cells underwent apoptosis upon expose to ibrutinib and ABT-199 as single agents. Combination of these two drugs resulted in synergistic induction of apoptosis (Table 1). Synergism was also observed with Jeko-1, Mino, JVM-2 and Rec-1 cells. Immunoblotting showed CCMCL1 cells have constitutive expression of cyclin D1, SOX11, PAX5 and MCL1. Ibrutinib as a single agent induced a rapid down-regulation of SOX11 and MCL1, while combination of ibrutinib with ABT-199 further enhanced down regulation of SOX11, followed by down-regulation of PAX5 at a later time point. We are currently testing the in vivo efficacy of combining these two drugs in a CCMCL1 NSG mouse model.
Our CCMCL1/NSG mouse model is a new model for pre-clinical assessment of MCL treatment approaches. Combination of ibrutinib with ABT-199 has synergistic effect of apoptotic induction in CCMCL1 as well as four other MCL cell lines tested. Ibrutinib or ibruitnib/ABT-199 combination induced apoptosis of MCL is associated with down-regulation of SOX11 and PAX5. Simultaneous down regulation of MCL1 via ibrutinib and targeting of BCL2 may contribute to the in vitrosynergism observed. These data support further investigation of this novel therapeutic strategy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal