Abstract
Early stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a highly curable disease with the combined use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy (RT). There has been a recent trend to abandon RT, driven mostly by concerns of development of secondary malignancies (SMN). However, it is unknown whether the omission of RT in adolescents and young adults (AYA) with early stage HL affects survival and the risk of developing SMN.
We used data from the National Cancer Institute's Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results program (SEER-13) to determine the overall survival (OS) and the risk of SMN among AYA with early stage HL treated or not with radiation therapy. Inclusion criterion was the diagnosis of stage I or II HL in the period of 1995-2010 as first malignant neoplasm among patients age 13 to 40 years. Patients with less than 6 months of follow up and patients with unknown use of RT were excluded. Follow up was updated to the end of 2012 (November 2012 submission). Cases were divided in two “eras”, 1995-2002 and 2003-2010, with the latter being expected to reflect changes in the use of RT. The impact of the era, RT, age, race, gender, and stage on survival were accessed utilizing multivariate analysis. Cumulative incidence of SMN among early stage HL survivors was calculated using a competing risk model, treating death from any cause in absence of SMN as the competing risk.
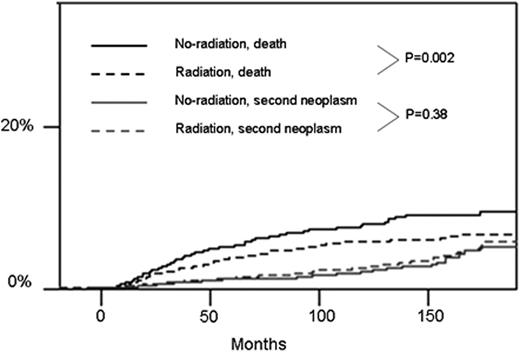
A total of 5,336 early stage HL cases were included in the analysis with median follow up of 89 months (range 7-191). Median age of patients was 27 years, 2,459 (46%) were male, 1,327 (24.8%) had stage I, 512 (9.7%) had classical HL non otherwise specified, 4,231 (79.2%) had nodular sclerosing HL, 442 (8.3%), had mixed-cellularity HL, 130 (2.4%) had lymphocyte-rich HL, and 21 (0.4%) had lymphocyte depleted HL. Most patients were white (4,438; 83.2%), 513 (9.6%) black, 337 (6.4%) other ethnicity, and 44 (0.8%) unknown. There where 2,793 patients in the 1995-2002 era and 2,542 patients in the 2003-2010 era. Radiation was included in the initial treatment of 1,659 (59.4%) patients in the former and 1,351 (53%) patients in the latter era (P<0.001). Factors associated with use of RT were earlier era, white race and stage II HL. Within the 1995-2002 era, there was a trend towards better survival among patients treated with RT (5-year survival 95.0% vs. 93.6%, P=0.058). In the 2003-2010 cohort survival was superior among patients treated with RT (5-year survival 97.3% vs. 95.9%, P=0.008). In multivariate analysis, diagnosis of HL in the 1995-2002 era (HR=1.73, 95% C.I. 1.31-2.28, P < 0.001), black race (HR= 2.18, 95% C.I. 1.63-2.91, P <0.001), male sex (HR=1.55, 97% C.I. 1.24-1.93, P < 0.001), and omission of RT (HR=1.31, 95% C.I. 1.05-1.64, P=0.017) were associated with higher mortality. The cumulative incidence of SMN was not significantly different between patients treated or not with radiation, while the risk of death was higher among patients not treated with RT (Figure).
There has been a reduction in utilization of RT among AYA with early stage HL in the US. Omission of RT was associated with increased overall mortality but no reduction in incidence of SMN and should not be adopted outside clinical trials.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal