Abstract
Introduction: ADAMTS13 is a multidomain protein with metalloprotease (M), disintegrin-like (D), thrombospondin-1 (T), Cys-rich (C) and spacer (S) domains, followed by 7 T domains and 2 CUB domains. ADAMTS13 cleaves the cryptic Tyr1605-Met1606 bond in the A2 domain of von Willerbrand factor (VWF), which inhibits the growth of platelet-rich thrombi. When subjected to tensile stress in solution, bound to platelets, or on endothelial cell surfaces, VWF interacts with multiple exosites on ADAMTS13, changing the conformation of both proteins. These close contacts enhance the highly specific interaction between ADAMTS13 and VWF in vivo. Interactions between VWF and proximal MDTCS domains of ADAMTS13 have been investigated extensively. ADAMTS13 distal domains T8-CUB2 are required to bind the D4 domain of VWF, and the CUB domains promote the cleavage of platelet-decorated VWF strings. However, the functional relationship between distal and proximal domains is not understood. Using mutagenesis, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and enzyme kinetics, we now have shown that distal T8-CUB domains interact with and inhibit the proximal MDTCS domains.
Methods: Recombinant ADAMTS13, MDTCS, and variants truncated after each distal T domain (MT2, MT3ÉMT8), and VWF D4 domain were produced in T-Rex 293 cell lines and purified to homogeneity. Similar inactive variants of each protein were prepared with the mutation E225Q, which abolishes catalytic activity but does not affect protein folding (MT2Q, MT3QÉMT8Q). SAXS data were collected at the SIBYLS beamline (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory) for ADAMTS13 (E225Q) and truncated variants. The radius of gyration (Rg) and maximum particle size (Dmax) were calculated from scattering profiles using DATGNOM. Ab initio envelopes were generated from scattering profiles using DAMMIN. A molecular model of ADAMTS13 was built from crystal structures of ADAMTS4 MD domains (2rjp) and ADAMTS13 DTCS domains (3ghm), and using HHpred to model distal T domains, CUB domains, and linkers after T4 and T8. Plasma VWF was purified from Facteur Willebrand-LFB concentrate on Superdex 200. ADAMTS13 activity assays were performed at pH 6 and pH 7.4 with fluorogenic substrate FRETS-rVWF71.
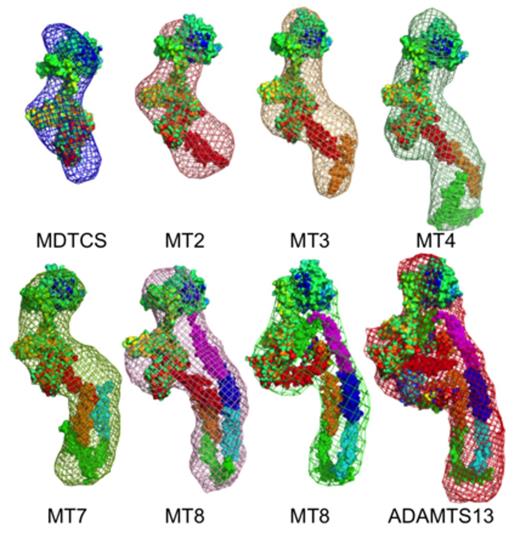
Results: Rg and Dmax progressively increased for variants MDTCS, MT2, MT3, MT4 and MT5, but did not increase proportionately for MT7, MT8 and ADAMTS13 despite a 50% increase in mass (Table 1). This behavior is consistent with a folded conformation. Fitting ADAMTS13 into ab initio envelopes for these variants requires a bend after domain T4, which is followed by a flexible linker that could serve as a hinge. As a consequence, distal T8-CUB2 domains are positioned near the proximal MDTCS domains (Figure 1). At pH 7.4, variants MDTCS through MT7 had similar activity toward FRETS-rVWF71. Full length ADAMTS13 was only ~10% as active at pH 7.4, but was ~7-fold more active at pH 6. MT8 had intermediate activity at pH 7.4 and was not activated by lowering the pH to 6. Adding VWF or recombinant VWF D4 increased the cleavage of FRETS-rVWF71 by full-length ADAMTS13 up to 4-fold at pH 7.4, but had no effect at pH 6 and did not change the activity of MT8 or MDTCS.
Conclusions: ADAMTS13 adopts a folded conformation with distal T8-CUB2 domains close to the proximal MDTCS domains and a hinge point between the T4 and T5 domains. The T8-CUB domains inhibit ADAMTS13 activity, and this autoinhibition can be relieved by low pH or by binding to VWF. Thus, VWF functionally serves as both an ADAMTS13 activator and substrate. This allosteric mechanism would localize and concentrate ADAMTS13 activity on VWF multimers at sites of thrombosis.
Properties of ADAMTS13 Variants
| Variant . | Mass (kDa) . | Rg (Angstrom)a . | Dmax (Angstrom)b . | kcat, pH 6 (min-1)c . | kcat, pH 7.4 (min-1)c . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDTCS | 67 | 45.2 ± 1.1 | 148.3 ± 2.0 | 9.86 ± 0.04 | 10.94 ± 0.01 |
| MT2 | 73 | 47.8 ± 2.8 | 154.8 ± 6.1 | 9.19 ± 0.24 | 10.23 ± 0.07 |
| MT3 | 79 | 54.3 ± 4.8 | 179.5 ± 10.1 | 9.69 ± 0.27 | 9.69 ± 0.27 |
| MT4 | 90 | 58.7 ± 3.7 | 193.1 ± 15.9 | 7.85 ± 0.04 | 9.80 ± 0.27 |
| MT5 | 96 | 63.4 ± 3.0 | 210.1 ± 8.9 | 7.23 ± 0.23 | 9.43 ± 0.22 |
| MT7 | 109 | 63.8 ± 2.0 | 210.5 ± 11.5 | 8.34 ± 0.25 | 8.90 ± 0.10 |
| MT8 | 121 | 64.7 ± 2.5 | 206.2 ± 2.5 | 3.01 ± 0.02 | 2.44 ± 0.01 |
| ADAMTS13 | 147 | 67.2 ± 1.9 | 228.9 ± 6.2 | 7.15 ± 0.20 | 1.05 ± 0.11 |
| Variant . | Mass (kDa) . | Rg (Angstrom)a . | Dmax (Angstrom)b . | kcat, pH 6 (min-1)c . | kcat, pH 7.4 (min-1)c . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDTCS | 67 | 45.2 ± 1.1 | 148.3 ± 2.0 | 9.86 ± 0.04 | 10.94 ± 0.01 |
| MT2 | 73 | 47.8 ± 2.8 | 154.8 ± 6.1 | 9.19 ± 0.24 | 10.23 ± 0.07 |
| MT3 | 79 | 54.3 ± 4.8 | 179.5 ± 10.1 | 9.69 ± 0.27 | 9.69 ± 0.27 |
| MT4 | 90 | 58.7 ± 3.7 | 193.1 ± 15.9 | 7.85 ± 0.04 | 9.80 ± 0.27 |
| MT5 | 96 | 63.4 ± 3.0 | 210.1 ± 8.9 | 7.23 ± 0.23 | 9.43 ± 0.22 |
| MT7 | 109 | 63.8 ± 2.0 | 210.5 ± 11.5 | 8.34 ± 0.25 | 8.90 ± 0.10 |
| MT8 | 121 | 64.7 ± 2.5 | 206.2 ± 2.5 | 3.01 ± 0.02 | 2.44 ± 0.01 |
| ADAMTS13 | 147 | 67.2 ± 1.9 | 228.9 ± 6.2 | 7.15 ± 0.20 | 1.05 ± 0.11 |
aCalculated using the program AutoRg, errors are SD. bCalculated using the program DATGNOM, errors are SD. cErrors are SE
Sadler:XO1 Limited: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BioMarin: Consultancy; Band Therapeutics: Consultancy; Baxter HealthCare: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal