Abstract
Tumor-Associated Antigen Presentation by γδ T-Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy
Human γδ T-cells are considered to represent a link between innate and adaptive immunity. Their innate killing properties display a potent cytotoxic activity against solid tumors as well as lymphoid and myeloid malignancies. Subsequently, by lysing affected target cells and liberating antigen for uptake, they can differentiate into professional antigen presenting cells (pAPCs) for induction of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses. The degree of antigen-specific stimulation of responder T cells is increased in the presence of antibody(Ab)-assisted opsonized target cells, involving the low-affinity receptor for IgG CD16 (Fc γRIII), equivalent to that seen with mature antigen-loaded DCs.
To elaborate the implications of this combined killing and pAPC function we have studied how freshly isolated as well as expanded and cloned populations of γδ T-cell subsets kill a target tumor cell, and take up and cross-present tumor-associated antigens (TAA). We performed quantitative analysis on the cellular uptake of different sizes of microspheres, analyzing the correlation between opsonization and internalization.
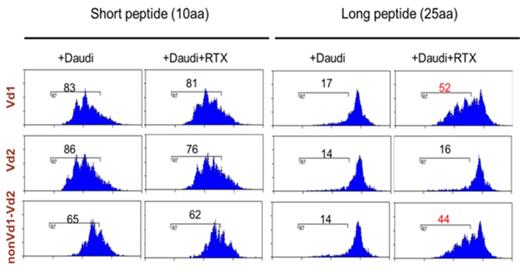
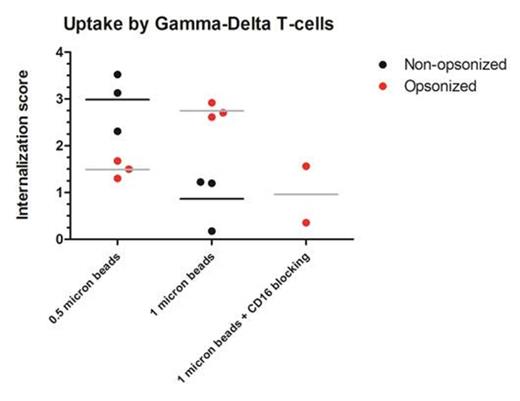
All γδ T-cell subtypes were expanded using artificial APC, engineered to express CD86, CD137L and IL-15, and anti- γδ TCR Ab (B1). Short (EAAGIGILTV) and long (GHSYTTAEEAAGIGILTVILGVLLL) MART-1 peptides were used as antigens for γδ T-cell presentation to MART-1 TCR-transduced cytotoxic T-cells. A CFSE assay was performed to assess cytotoxic T-cell proliferation. Target cells and polysterene microspheres were opsonized with human anti-CD20 IgG1, Rituximab (RTX). CD16 function was blocked with a mouse monoclonal IgG1 anti-CD16 blocking Ab (clone LNK16). Imaging flowcytometry allowed us to quantify internalization of FITC-labeled microspheres. The Internalization Score is defined as the ratio of intensity inside the cell to the intensity of the entire cell.
Both γδ T-cell lines and expanded γδ T-cell clones cultured long-term, remarkably, retain both tumor cell killing and take up tumor cell lysates or long synthetic TAA peptides and cross-present these on MHC class I to CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells in a dynamic, controllable fashion, dependent on Ab-opsonization. (Figure 1). The Ab-opsonization of 1 µm microspheres correlates with a higher receptor-mediated phagocytic uptake, in a CD16 dependent manner (Figure 2). The opsonization of 0,5 µm microspheres led to clumping of the microspheres, accounting for the lower uptake in this particular subgroup.
For a lack of better alternative, moDCs have been widely used in experimental immunotherapy settings. The ease of manipulation of human γδ T-cells, the ability to be expanded ex-vivo combined with antigen presentation makes them a great potential tool for immunotherapy as a complementary or integrative strategy. Ligation of the γδ T-cell receptor at the tumor site will activate their expansion and innate killing. Yet, antigen presentation will only occur after binding of an immunoglobulin to the tumor cell, thereby activating their dual role. Our goal is to define an effective adjuvant vaccine formulation for inducing leukemia-specific cytolytic effects. We are currently investigating whether γδ T-cells can directly present and/or cross-present to cytotoxic T-cells in-vivo in a humanized mouse model. We believe that the uptake of microspheres by γδ T-cells has an impact on the development of vaccination strategies for cancer immunotherapy, as the immunization of γδ T-cells is a powerful method for the induction or reactivation of cytotoxic T cell specific responses.
CFSE assay of γδ T-cell lines cross-presenting short and long MART-1 peptides to MART-1 TCR-transduced cytotoxic T-cells in a dynamic, controllable fashion, dependent on Ab-opsonization
CFSE assay of γδ T-cell lines cross-presenting short and long MART-1 peptides to MART-1 TCR-transduced cytotoxic T-cells in a dynamic, controllable fashion, dependent on Ab-opsonization
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal