Abstract
Introduction:
Although bendamustine with or without rituximab has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent B-cell lymphoma (B-NHL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), previous reports showed that the incidence of lymphocytopenia was higher in patients receiving bendamustine with or without rituximab than in those receiving other conventional cytotoxic chemotherapies such as R-CHOP regimen. However, the length of time until recovery of the decreased lymphocytes and CD4-positive T cells to the baseline upon bendamustine treatment is still unclear.
Patients and Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 56 consecutive patients with relapsed or refractory B-NHL and MCL who received bendamustine with or without rituximab at our institution between 2011 and 2014. We analyzed their peripheral blood lymphocytes and CD4-positive T-cell counts at baseline, during, and after bendamustine treatment, the details of infectious events, and their correlations.
Results:
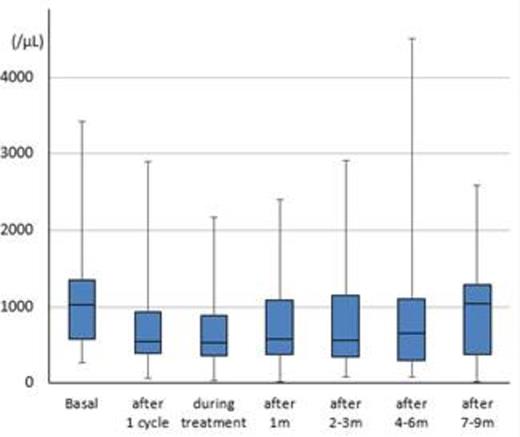
Thirty-one (55%) patients were male and 25 (45%) female, with a median age of 63 years (range: 36-86). Twenty (35%) patients had follicular lymphoma, 14 (25%) MCL, nine (16%) transformed lymphoma, five (9%) extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, four (7%) small lymphocytic lymphoma, two (4%) nodal marginal zone lymphoma, and one (2%) each had lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma and low-grade B-NHL, unclassifiable. The median number of prior regimens administered was two (range: 1-9). Twenty-three (41%) of the 56 patients received rituximab in combination with bendamustine. The median number of bendamustine cycles was four (range: 1-6). The median follow-up period was nine months (range: 0-33 months). At baseline, median lymphocyte and CD4-positive T-cell counts were 1,025/µL (range: 270-3,420/µL) and 282/µL (range: 83-645/µL), respectively. After the first cycle, they immediately decreased to 545/µL (range: 60-2,900/µL) and 190/µL (range: 116-635/µL), respectively. The median lymphocyte and CD4-positive T-cell count nadirs during observation were 365/µL (range: 20-1,310/µL) and 93/µL (range: 7-178/µL), respectively. Significantly decreased lymphocyte counts (median: 260 vs. 410/µL) were detected in the patients who received bendamustine with rituximab compared with those who received bendamustine alone (p=0.03). Recovery of lymphocyte and CD4-positive T-cell counts to those at baseline was observed at 7-9 months after the completion of bendamustine with or without rituximab, and median lymphocyte and CD4-positive T-cell counts were 1,045/µL (range: 170-2,580/µL) and 223/µL (range: 47-709/µL), respectively (Figures A, B). The numbers of patients who received prophylaxis against pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), varicella zoster virus (VZV), and fungal infection were 44 (78%), 37 (66%), and four (7%), respectively, at the physician's discretion. Infectious events were observed in 32 (57%) patients during follow-up. Cytomegalovirus antigenemia was detected in 15 (27%) patients, VZV infection in two (3%), cytomegalovirus colitis in one (2%), and other infectious complications such as sepsis or febrile neutropenia in 20 (35%) patients. Interestingly, all infectious events occurred within nine months after the completion of bendamustine with or without rituximab in patients who received no treatment after bendamustine during follow-up.
Conclusion:
The results of this analysis revealed that the majority of relapsed or refractory patients with indolent B-NHL and MCL showed prolonged lymphocytopenia and low CD4-positive T-cell counts, for at least 7-9 months, after the completion of bendamustine with or without rituximab. Because lymphocytopenia, especially low CD4-positive T-cell counts, may increase the risk of opportunistic infections, the prophylaxis against PCP and VZV deserves consideration for at least 7-9 months after bendamustine treatment. Further investigations, especially a prospective study, are needed to confirm our results.
Box plots of lymphocyte counts (Figure A) and CD4-positive T-cell counts (Figure B) among patients who were treated with bendamustine with or without rituximab.
Maruyama:Eisai Co., Ltd: Honoraria. Kobayashi:Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH: Research Funding; ARIAD Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding. Tobinai:Eisai Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; SymBio Pharmaceuticals Ltd.: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Zenyaku Kogyo Co., Ltd.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal