Abstract
Despite major advances in chemotherapy, multiple myeloma remains incurable and in need of new therapies that target novel pathways. Insufficient understanding of the molecular pathways that regulate survival in myeloma is a major impediment towards designing better therapies to prolong survival in patients or even cure the disease. This necessitates the identification of new protein targets that are crucial for the growth and survival of multiple myeloma. Just like normal plasma cells, MM cells also depend on their interactions with bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) for survival and production of essential growth factors. We have previously shown that MM cells interact with dendritic cells (DC) in the microenvironment and in vitro can stimulate DC to produce IL-6 (ASH2010#132, ASH2011 #147, ASH2012#722). Our recent publications show that when MM cells are not in direct contact with DC, the IL-6 produced by DC can protect MM cells against dexamethasone induced cell death, while neutralizing the IL-6 with antibodies can reverse that effect (Nair et al., 2011). Unfortunately, exactly how this survival response is mediated in MM is not very clear.
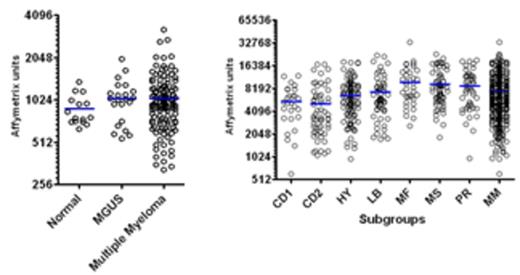
PIM2, a serine threonine kinase, part of the proto-oncogene group of PIM kinases has been implicated in survival in several types of cancers including prostate cancer and multiple myeloma. In our lab, microarray gene expression analysis of publicly available datasets (Figure 1) show a trend towards increased expression of PIM2 in plasma cells from myeloma patients (left panel), and significantly in the poor prognosis subgroup MAF (Zhan et al., 2006) (right panel). For the first time we show that IL-6 produced by DC may be protecting myeloma cells by up regulating PIM2 and inactivating a major protein translation inhibitor 4EBP1, which also happens to be a PIM2 target. We show that silencing PIM2 with siRNA down regulates PIM2 activity and reverses the inactivation of 4EBP1, while the latter is known to cause cell death in myeloma. We also demonstrate that neutralizing IL-6 in MM cells that either don’t produce IL-6 on their own (MM.1S) or those that do (U266), abrogates extraneous DC-IL6 ability to induce PIM2 and its downstream target 4EBP1. Recombinant IL-6 also provided similar induction of PIM2 in myeloma and increased 4EBP1 phosphorylation, which was again reversed by neutralizing the antibody against IL-6.
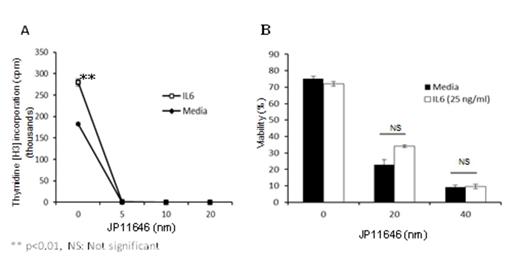
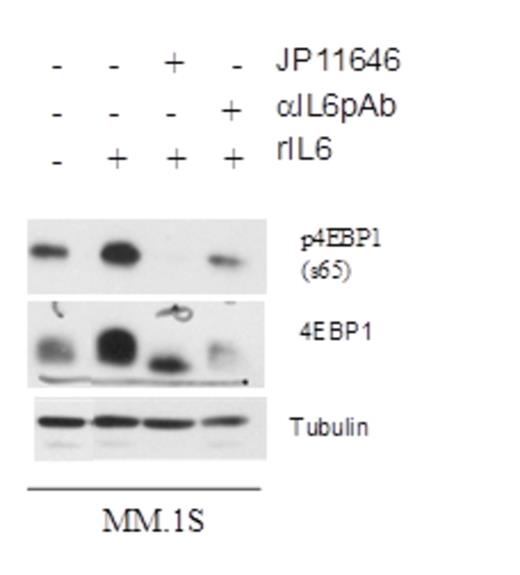
In myeloma patients, the use of dexamethasone in frontline therapies is often complicated by the ability of the bone marrow environment to produce IL-6 that not only induce increased proliferation of MM but also help resist dexamethasone mediated cell death in myeloma. Interestingly, when we used a novel PIM2 inhibitor, JP_11646 (kindly provided by Jasco Pharmaceuticals, LLC), it not only arrested IL-6 induced proliferation even at sub-lethal doses, but also prevented IL-6 mediated rescue of myeloma cells (Figure 2). This suggests that PIM2 might be a major player in IL-6 mediated drug resistance in myeloma and targeting it may help to subvert IL-6 mediated survival in myeloma. Through RT-PCR and westerns, we also show that IL-6 modulates PIM2 expression and activity resulting in increased 4EBP1 phosphorylation (Figure 3). This was abrogated when PIM2 activity was inhibited by JP_11646 (Figure 3). We also present data that suggests IL-6 via PIM2 may be regulating other anti-apoptotic molecules downstream of IL-6 receptors including MCL-1, that is vital to MM survival. Developing PIM2 targeted therapies provides an exciting opportunity to affect the myeloma tumor microenvironment where MM induced IL-6 production from BM could be inducing drug resistance.
PIM2 inhibition abrogates IL-6 induced MM proliferation (A) and protection (B).
Inhibiting PIM2 activity prevents PIM2 induced phosphorylation of 4EBP1 by IL-6 in myeloma
Inhibiting PIM2 activity prevents PIM2 induced phosphorylation of 4EBP1 by IL-6 in myeloma
Caserta:Jasco Pharmaceuticals LLC: Equity Ownership. Baldino:Jasco Pharmaceuticals LLC: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal