Abstract
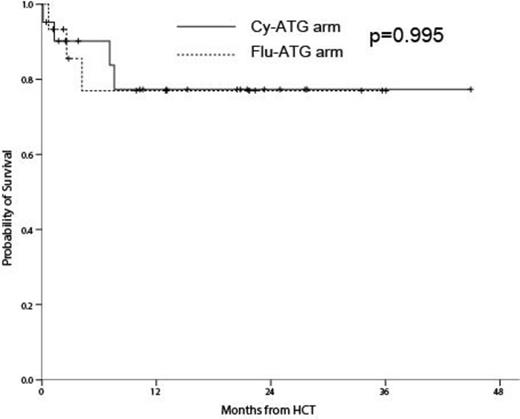
Our previous study showed that a less toxic regimen comprising reduced cyclophosphamide (Cy), fludarabine and anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) (Cy-Flu-ATG), was less toxic for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) compared with standard Cy-ATG in patients with adult severe aplastic anemia (AA). We postulated that replacing Cy with Flu (Flu-ATG) would be more beneficial. Therefore we performed a randomized phase III study to compare the regimen-related toxicities (RRTs) of two different conditioning regimens: Cy-ATG vs. Flu-ATG. We present the interim alaysis. Patients in the Cy-ATG arm received Cy at 200 mg/kg. Those in the Flu-ATG arm received fludarabine (Flu) at 180 mg/m2. A total of 36 patients (21 in the Cy-ATG and 15 in the Flu-ATG) were enrolled. The basic patientsÕ characteristics were similar between both arms except for donor type and HLA-matching. There were more unrelated donor (38.1% vs. 73.3%; p=0.037) and HLA mis-matching (0% vs. 40%; p=0.001) in Flu-ATG arm. All predefined RRTs were similar between Cy-ATG and Flu-ATG (33.3% vs. 33.3%; p=1.000). There was no primary engraftment failure in both arms and only one patients in Cy-ATG died of treatment-related hepatic toxicity before engraftment. Also there were no differences between Cy-ATG and Flu-ATG arms in terms of secondary engraftment failure (20% vs. 20%; p=1.000), hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (0% vs. 0%; p=1.000), hemorrhagic cystitis (4.8% vs. 0%; p=1.000), pulmonary complications (12.5% vs. 16.7%; p=1.000). The incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) (14.3% vs. 20.0%; p=0.677) and chronic GvHD (11.8% vs. 7.7% ; p=1.000) were also similar. The 3-year survival rate did not differ (77.3% vs. 77.0%; p=0.995; Figure 1). Flu-ATG can be
promising in terms of RRT without increasing engraftment failure in Flu-ATG arm when considering more unrelated and HLA-mismaching patients were enrolled. We will continue this phase III trial.
promising in terms of RRT without increasing engraftment failure in Flu-ATG arm when considering more unrelated and HLA-mismaching patients were enrolled. We will continue this phase III trial.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal