Abstract
Olaptesed pegol (NOX-A12), an SDF-1 binding Spiegelmer® was found to detach SDF-1 from the surface of BMSCs (Hoellenriegel et al., Blood 2013) and to mobilize CXCR4 expressing, malignant cells from protective niches in the bone marrow or other secondary lymphoid tissues, thereby sensitizing them to the action of standard therapy. In addition to malignant cells CXCR4 expressing immune cells, e.g. T cells, neutrophils and monocytes are effectively mobilized by olaptesed (Vater et al., Clin Pharmacol Ther 2013). Here we investigated the combination of olaptesed with an immunotherapeutic agent, in particular rituximab (RTX). Several mechanisms of action (MoA) of RTX have been described including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and phagocytosis (ADCP). The aim was to analyze whether olaptesed influences the immune effector cell activation by RTX as has been shown for the Btk or PI3Kd inhibitors ibrutinib and idelalisib, respectively.
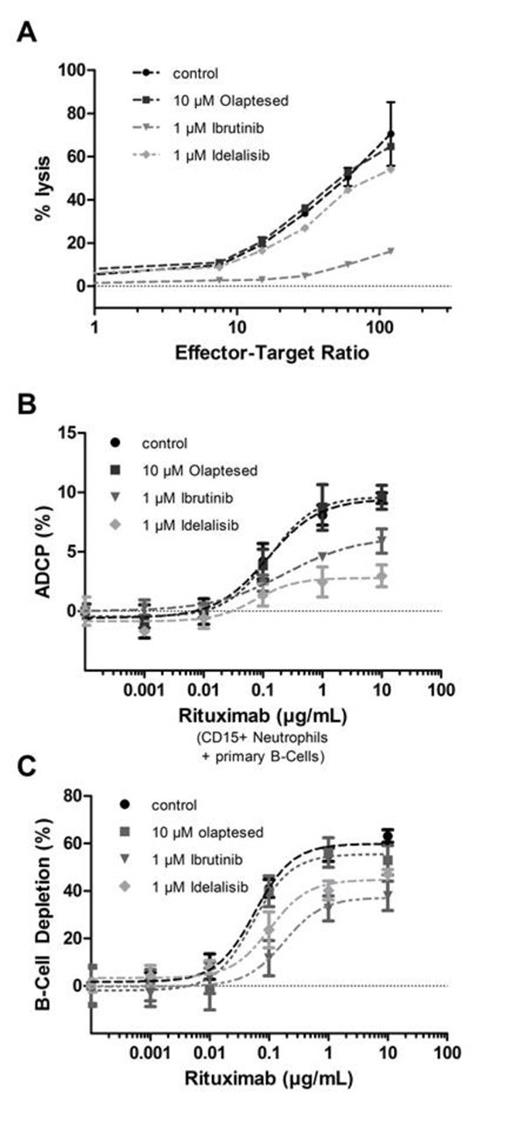
ADCC activity was measured by the calcein release assay. Raji lymphoma cells were labeled with calcein, treated with 10 µg/mL RTX and co-cultured for 4 hours with various ratios of PBMCs as effector cells, which have been incubated with either 10 µM olaptesed, 1 µM ibrutinib or 1 µM idelalisib, respectively, overnight. In order to analyze the impact on phagocyte function, ADCP assays with neutrophils and monocytes were performed. Phagocytes were preincubated with either 10 µM olaptesed, 1 µM ibrutinib or 1 µM idelalisib, respectively, for 6 hours, and cocultured overnight with DiD-labeled primary B-cells or Raji cells which were opsonized with different concentrations of RTX. ADCP was quantified in a guava easyCyte flow cytometer by counting the CD15+ (or CD14+) and DiD+ population (gated on CD19-negative cells) and normalizing to total phagocyte counts. To analyze B-cell depletion, heparinized whole blood from healthy volunteers was diluted with HBSS (1:2.5) and incubated with either 10 µM olaptesed, 1 µM ibrutinib or 1µM idelalisib, respectively, for 6 hours followed by the addition of different RTX concentrations. After incubation for 16 hours B-cell depletion was evaluated by determining the CD19+ B-cell and CD3+ T-cell populations.
We found that preincubation of PBMCs with 1 µM ibrutinib significantly decreased calcein release. 1 µM idelalisib led to a slight decrease of calcein release, while 10 µM olaptesed did not influence ADCC activity (Figure 1A). Preliminary results from ADCP assays point to a decreased phagocytic activity in terms of maximal ADCP for neutrophils after preincubation with ibrutinib or idelalisib (Figure 1B). Importantly, although olaptesed is being endocytosed by phagocytes, the uptake of the drug did not inhibit ADCP. In accordance, the whole blood assay showed that olaptesed had no negative impact on RTX-mediated B-cell depletion, while ibrutinib and idelalisib were found to decrease B-cell depletion regarding EC50 and maximal killing (Figure 1C). Taken together, we found that olaptesed retains the immune functional repertoire of RTX, whereas ibrutinib and idelalisib decrease the immune effector function. These small molecule kinase inhibitors possess low specificity and are inhibiting also other kinases which may be important for immune cell activation, such as ITK which is blocked by ibrutinib. The MoA of olaptesed is partially overlapping with kinase inhibitors with regard to lymphoid cell mobilization; however, olaptesed is highly selective and therefore does not impair immune-cell mediated contribution to monoclonal antibody efficacy. Instead, olaptesed may further enhance the contribution of immune effector cells through mobilization of T cells from the bone marrow which are described to be exhausted in the peripheral blood of hematological malignancies like CLL. Furthermore, neutrophils and monocytes which contribute to ADCP are effectively mobilized with olaptesed.
Based on their complementary mechanisms of action involving direct and immune-mediated cell death (RTX) or long-term mobilization of not only the malignant cells but also effector immune cells (olaptesed), the combination has the potential for greater efficacy in treating B lymphoid malignancies without impairing immune effector activity. Olaptesed is currently being tested in a Phase 2a clinical trial in combination with RTX and bendamustine in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL (#NCT01486797).
Zboralski:NOXXON Pharma AG: Employment. Vater:NOXXON Pharma AG: Employment. Kruschinski:NOXXON Pharma AG: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal