Abstract
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of clonal diseases associated with JAK2 mutation (V617F) in a percentage varying from 50% (Essential Thrombocytemia ET, and Primary Myelofibrosis PMF) to 95% (Polycitemia Vera, PV). The standard method for determining the V617F mutation is today represented by the Real Time PCR (RT-PCR). However, in recent years some studies have focused attention on a new method, the Droplet Digital PCR (DD-PCR), that allows an absolute quantitation of the mutated allele without any reference curve.
The main objective of this study was the comparison of two PCR methods (RT-PCR and DD-PCR) for the analysis of the JAK2V617F mutation in order to assess the sensitivity, specificity and feasibility of the two techniques.
In the study 225 patients with MPNs JAK2V617F-positive were enrolled; in 99 cases, DNA was still available for further assays and so DD-PCR tests were performed and compared with the results coming from RT-PCR (MutaQuant kit, Ipsogen, Luminy Biotech, Marseille, France).
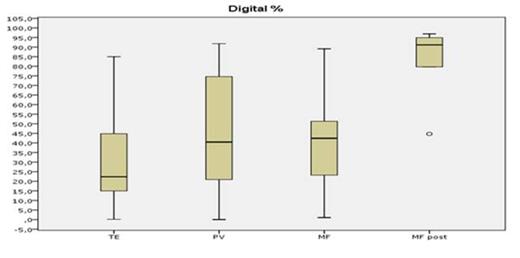
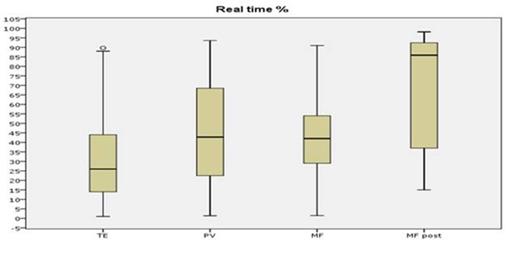
The results show a good sensitivity for both methods; nevertheless, after appropriate dilution tests, the DD-PCR was able to detect the JAK2V617F mutation in the 5x10-4 dilution versus 5x10-3 for the RT-PCR, in front of a fully comparable specificity. A linear regression analysis showed an absolute correlation between the 2 methods (R2=0.91), and the median mutated allele burden was not different when measured by the DD-PCR or the RT-PCR (p=0.67), with the highest median allele burden observed in secondary myelofibrosis (86% by RT-PCR and 91% by DD-PCR) and the lowest one in ET (23% by RT-PCR and 25% by DD-PCR) (see Figure 1 and Figure 2), as expected.
Our study demonstrates that a new molecular technique, the DD-PCR, may represent a new frontier in the world of molecular techniques for the detection of JAK2 mutation with a high sensitivity and specificity. In addition the method allows obtain two types of information, qualitative and quantitative, with one analysis, saving time and at a lower cost than the standard method.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal