Abstract

Background
The combination of a myeloablative dose of intravenous (iv) busulfan with cyclophosphamide is the standard preparative regimen for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. However, in patients older than 40 years, this conditioning can be associated to high non relapse mortality (NRM). A similar myeloablative dose of busulfan combined to fludarabine was found associated to a lower NRM in older AML (Alatrash, BBMT 2011).
Patients and study design
The Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo (GITMO) conducted a Phase III, randomized, multicenter, trial to compare the standard myeloablative combination of iv busulfan (Busilvex®, Pierre Fabre, Boulogne, France) at a dose of 0.8 mg/kg/6h over two hours infusion for 4 consecutive days (16 doses), for a total dose of 12.8 mg/kg, in combination with cyclophosphamide at the dose of 60 mg/kg/day for 2 consecutive days for a total dose of 120 mg/kg (BUCY2 arm) or fludarabine at the dose of 40 mg/m2/day for 4 consecutive days, for a total dose of 160 mg/m2 (BUFLU arm). Eligible were patients with a diagnosis of AML in 1st or 2nd complete remission (CR) with an age ≥40 and ≤ 65 years, and the availability of an HLA compatible sibling or unrelated donor as defined by molecular high-resolution typing (4 digits) of the HLA gene loci class I (HLA- A, B, and C) and class II (DRB1). Excluded were patients with a t(15;17) or PML/RARα positive APL or with a t(8;21)(q22;q22) or an inv(16) or t(16;16)(p13;q22) positive AML in 1st CR. The GvHD prophylaxis was based on conventional Cyclosporine A and Methotrexate. In case of unrelated donors, anti Thymocyte Globulin (Thymoglobuline®, Sanofi-Aventis) was given at a total dose of 5 mg/kg (or 7.5 mg/kg, in case of HLA acceptable disparity) (one antigen/allele disparity in class I, or one allele disparity in class II). The primary study end-point was the one-year NRM using an intent-to-treat analysis. The required sample size was calculated assuming that the one-year NRM would have been halved (from 25% to 12.5%) in the BUFLU arm. The cumulative incidence of NRM was estimated by considering relapse as a competing event. All outcomes were evaluated from the date of transplantation. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of each center.
Results
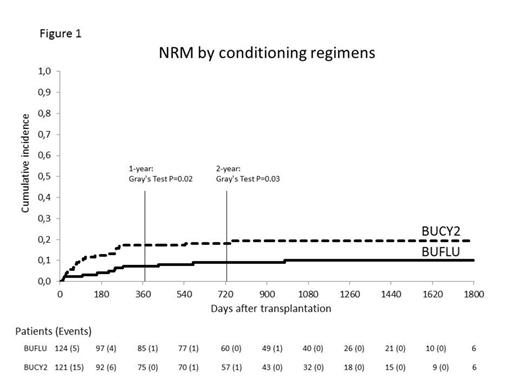
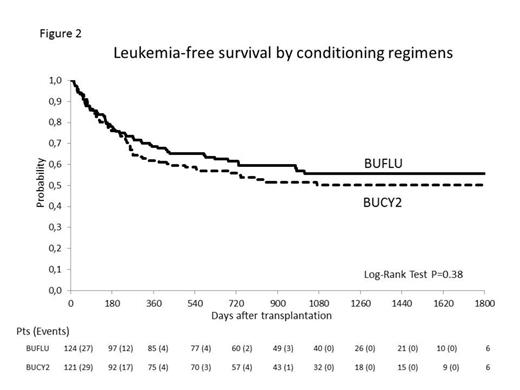
From July 2008 to February 2013, 25 centers in Italy and 1 in Israel, enrolled 245 patients who were randomly assigned to BUCY2 (n=121) or BUFLU (n=124), stratified according to donor type and remission (1st vs. 2nd or more). The main clinical features (balanced between the randomization arms) were as follows: the median age was 50 years, 209 patients (85%) were in 1st and 36 (15%) in 2ndCR and the ELN risk subgroups were good (11%), intermediate-1 (46%), intermediate-2 (20%) and adverse (23%). The donor was a sibling related (n= 112, 46%) or matched unrelated (n= 133, 54%) while the stem cell graft was the peripheral blood (PB, n= 168, 69%) or the bone marrow (BM, n= 77, 31%). The overall survival rate in the BUCY2 and BUFLU arm was 71% vs. 78% at 1 year, 65% vs. 62 % at 2 years and 56% vs. 57% at 5 years, respectively (P=ns). A non-significant lower incidence of relapse was documented in the BUCY2 vs. the BUFLU arm being 20.7% vs. 24.2% at 1 year, 25.6% vs. 29% at 2 years and 28.9 vs. 32.3 at 5 years, respectively. On the contrary, at 1 year, the overall NRM in the BUCY2 arm was 17.4% vs. 7.3% in the BUFLU (Gray Test P=0.02). At 2 years and throughout the study, the same significantly different NRM was observed between study arms being respectively 18.2% vs. 8.9% and 19% vs. 9.7% (Gray Test P=0.03) (Figure 1). Causes of NRM in the BUCY2/BUFLU arms were: infections 8/6, organ failures 9/0, GvHD 5/3, hemorrhage 1/1, others 0/2. All in all, at 1, 2 and 5 years the leukemia free survival of the BUCY2 and BUFLU arm was similar being 62% vs. 69%, 56% vs. 62% and 50% vs. 56%, respectively (P=ns) (Figure 2). The number of patients with grade III-IV acute GvHD was higher in the BUCY2 arm (P= 0.02). There were no significant between-group differences in the incidence of chronic GvHD.
Conclusion
In AML patients older than 40 years, the reduced toxicity conditioning with iv BUFLU significantly reduced the NRM compared to BUCY2. The increased incidence of leukemia relapse in the BUFLU arm was not associated with a detrimental effect on overall and leukemia free survival. (Funded by a grant from the Agenzia Italiana per il Farmaco (AIFA), ClinicalTrial.gov Identifier: NCT1191957).
Rambaldi:Pierre Fabre Pharma: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal