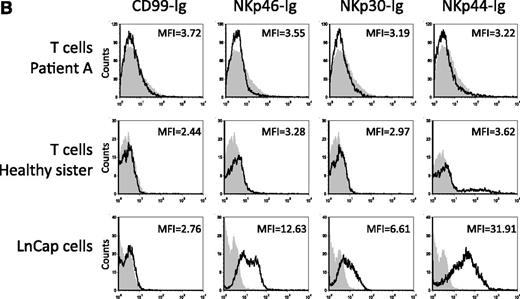
On page 1777 in the 1 March 2004 issue, there are errors in Figure 4. During the preparation of Figure 4B, a flow cytometry analysis plot image was inadvertently duplicated. The negative staining with NKp30-Ig of patient A is duplicated in the NKp44-Ig staining of the healthy sister, and the negative staining of NKp30-Ig of the healthy sister is duplicated in the negative staining of the NKp44-Ig of patient A. This change does not affect the conclusions or interpretations of findings presented in the manuscript. The corrected Figure 4B is shown. The authors apologize for these mistakes.
Killing of PHA-induced T-cell blasts. (A) Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts with various mAbs. Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from patient A and from the healthy sister was performed with the F(ab′)2 fragments of anti-CD3, anti-CEACAM1, and anti-MHC class I mAb HP-1F7. (B) Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts and of the LnCap cell line with various fusion proteins. Staining was performed with the NKp46-Ig, NKp30-Ig, NKp44-Ig, and control CD99-Ig fusion proteins. (C) NK clones derived from patients A, B, and C were assayed for cytotoxic activity against autologous PHA-induced T-cell blasts. The NK clones obtained from the healthy sister were assayed against PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from patient A. NK clones were preincubated with or without F(ab′)2 fragments of polyclonal anti-CEACAM or the control polyclonal antiubiquitin antibodies. The targets, autologous PHA-induced T-cell blasts, were incubated with or without the F(ab′)2 fragments of HP-1F7 or the control 12E7 mAb. Assays were performed at an E/T ratio of 2:1. Shown are the mean results of several NK clones that were obtained from 3 independent experiments. The data represent the mean percentage of killing ± standard deviation. (D) NK clones derived either from the healthy sister or from patients A, B, and C were assayed for killing of PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from the healthy sister. NK clones and target PHA-induced T-cell blasts were pretreated as described for C. Assays were performed at an E/T ratio of 2:1. Shown are the mean results of several NK clones that were obtained from 3 independent experiments. All mAbs used were in the form of F(ab′)2. The data represent the mean percentage of killing ± standard deviation.
Killing of PHA-induced T-cell blasts. (A) Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts with various mAbs. Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from patient A and from the healthy sister was performed with the F(ab′)2 fragments of anti-CD3, anti-CEACAM1, and anti-MHC class I mAb HP-1F7. (B) Staining of PHA-induced T-cell blasts and of the LnCap cell line with various fusion proteins. Staining was performed with the NKp46-Ig, NKp30-Ig, NKp44-Ig, and control CD99-Ig fusion proteins. (C) NK clones derived from patients A, B, and C were assayed for cytotoxic activity against autologous PHA-induced T-cell blasts. The NK clones obtained from the healthy sister were assayed against PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from patient A. NK clones were preincubated with or without F(ab′)2 fragments of polyclonal anti-CEACAM or the control polyclonal antiubiquitin antibodies. The targets, autologous PHA-induced T-cell blasts, were incubated with or without the F(ab′)2 fragments of HP-1F7 or the control 12E7 mAb. Assays were performed at an E/T ratio of 2:1. Shown are the mean results of several NK clones that were obtained from 3 independent experiments. The data represent the mean percentage of killing ± standard deviation. (D) NK clones derived either from the healthy sister or from patients A, B, and C were assayed for killing of PHA-induced T-cell blasts derived from the healthy sister. NK clones and target PHA-induced T-cell blasts were pretreated as described for C. Assays were performed at an E/T ratio of 2:1. Shown are the mean results of several NK clones that were obtained from 3 independent experiments. All mAbs used were in the form of F(ab′)2. The data represent the mean percentage of killing ± standard deviation.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal