Abstract
Natural killer (NK) cells mediate anti-AML responses and previously published clinical trials of adoptive allogeneic NK cell therapy provide proof-of-principle that NK cells may eliminate leukemia cells in patients. However, complete remissions occur in 30-50% of patients with active AML and are typically of limited duration. Thus, improvements are needed for this promising cellular immunotherapy strategy. Following paradigm-shifting studies in mice, it was established that human NK cells exhibit an innate 'memory-like' responses following a brief, combined pre-activation with IL-12, -15, and -18 (Romee R et. al., Blood, 2012). These long-lived memory-like NK cells have an enhanced ability to produce IFN-g in response to restimulation with cytokines or activating receptor ligation, even following extensive proliferation. We hypothesized that memory-like NK cells exhibit enhanced responses to myeloid leukemia.
Compared to control NK cells from the same donor, IL-12/15/18-induced memory-like NK cells produced significantly increased IFN-g upon co-culture with primary AML blasts in vitro (P<0.001), following 7 days of rest in low dose IL-15 vitro. In addition, memory-like NK cells had increased granzyme B expression (P<0.01), and enhanced killing of K562 leukemia targets in vitro (P<0.05). Utilizing an in vivo xenograft model of human NK cells in NSG mice (Leong J et. al., BBMT, 2014), IL-12/15/18-induced memory-like NK cells that differentiated in NSG mice for 7 days exhibited increased IFN-g responses after ex vivo re-stimulation with K562 leukemia, confirming their memory-like functionality (P<0.05). To test in vivo responses to human leukemia in this model, luciferase-expressing K562 cells were engrafted into NSG mice (1x106/mouse, IV), and on day 3, groups of mice were injected with IL-12/15/18-pre-activated or control NK cells from the same donor (4x106/mouse). Mice treated with a single dose of memory-like NK cells exhibited significantly improved in vivo leukemia control measured by whole mouse bioluminescent imaging (P=0.03), as well as overall survival (P<0.05), compared to mice treated with control or no NK cells.
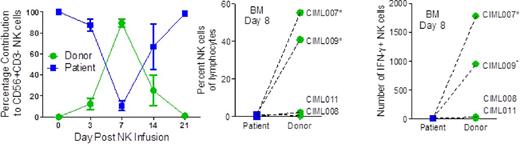
Based on these pre-clinical findings, we initiated a first-in-human clinical trial of HLA-haploidentical IL-12/15/18-induced memory-like NK cells in patients with AML (NCT01898793). Relapsed/refractory (rel/ref) AML patients receive lymphodepleting non-myeloablative flu/cy conditioning, infusion of a single dose of CD56+CD3- memory-like donor NK cells, followed by two weeks of low dose rhIL-2. Three patients were treated at dose level 1 (0.5x106 cells/kg) and two patients treated at dose level 2 (1.0x106/kg) with no DLTs observed, and accrual continues. Correlative analyses utilizing donor-specific HLA mAbs allow tracking of donor memory-like NK cell frequency and function following adoptive transfer. Donor memory-like NK cells were detectable in the PB and BM of all tested patients with informative HLA (4/5), peak in frequency at 7-8 days post-infusion, and contract after 14-21 days as expected following recipient T cell recovery (Figure). Memory-like NK cells exhibit significantly increased Ki67%+ as a marker of proliferation at day 7 [97.8+1.0% (donor) vs. 21.6+5.5% (recipient), mean+SEM, P<0.001]. Moreover, functional analyses of NK cells at days 7-8 post-infusion reveal increased numbers of donor IFN-g+ NK cells following restimulation with K562 leukemia cells in the same blood [1009+590 (donor) vs. 8+3 (recipient) IFN-g+ NK cells] or BM [686+423 (donor) vs. 4+2 (recipient) IFN-g+ NK cells] samples. Two of four evaluable patients treated with memory-like NK cells had leukemia free BM and PB at days 14 post-therapy, which correlated with BM NK cell frequency and IFN-g production (Figure). CIML007 had rel/ref AML with 48% BM blasts pre-therapy, and had no evidence of leukemia on day 14, 28, and 100 BM biopsies, and has an ongoing complete remission more than 100 days after this therapy. CIML009 had 80% BM blasts pre-therapy, and had no evidence of leukemia on day 14 BM biopsy post-infusion. Thus, human IL-12/15/18-induced memory-like NK cells expand and have enhanced anti-AML function following adoptive transfer in patients, thereby constituting a promising translational innovation for immunotherapy of AML.
Fehniger:Celgene: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal