Abstract
Background and objectives. PIM kinases (PIM1, PIM2, PIM3) are proteins known to be overexpressed in several hematological malignancies. In particular, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) they are involved in cell survival, resistance to apoptosis (especially PIM2 and PIM3) and interactions with the microenvironment (PIM1).
The aim of this study was dual: I) to evaluate the preclinical efficacy of PIM447, a pan PIM kinase inhibitor, in CLL and to study potential synergies with other drugs; and II) to evaluate the expression of PIM-kinases in different stages of the disease and correlate it with the prognosis and the sensitivity to the drug.
Methods. Peripheral blood samples from untreated patients with different stages of the disease (monoclonal B lymphocytosis (MBL), stable CLL not requiring treatment (sCLL), and active CLL requiring treatment (aCLL)) were collected after informed consent. The ex vivo efficacy of PIM447 was analyzed by flow cytometry with annexin V in these samples. Moreover, PIM447 efficacy was also analyzed in two cell lines (MEC-1 and JVM-2) by MTT assay. Synergy with other drugs effective in CLL (bendamustine and fludarabine) was evluated with the calcusyn software. Protein levels of PIM Kinase proteins were evaluated by capillary electrophoresis immunoassay (WESTM ProteinSimple) in monoclonal B cells purified by CD19 selection with anti-CD19 magnetic microbeads and the autoMacs Cell separator (both from Miltenyi Biotec) from a subset of patients.
Results. The pan PIM inhibitor, PIM447 was active in both cell lines tested, MEC-1 (IC50 5μM) and JVM2 (IC50 7μM), and also in monoclonal B cells from freshly isolated patients samples (sCLL=11; aCLL=5), with no difference in sensitivity between the different stages of the disease (IC50 of 4,8 μM and 4,7 μM for sCLL and aCLL respectively).
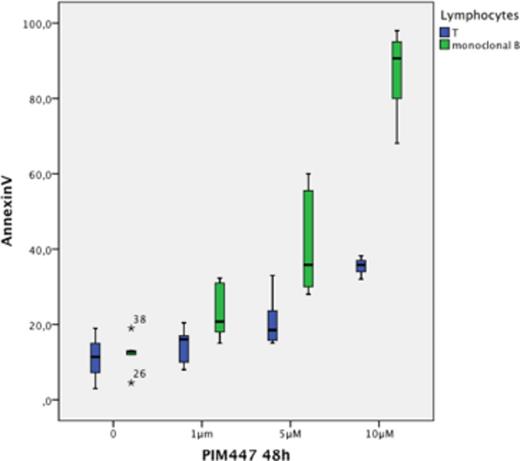
There was a clear therapeutic window as treatment with PIM447 at doses toxic for monoclonal B cells, preserved T lymphocytes (figure 1) (median % of apoptosis for B cells and T lymphocytes respectively of 23 vs 20 at 5μM and 87 vs 35 at 10 μM).
Moreover, PIM447 demonstrated to potentiate the activity of both bendamustine and fludarabine, being especially synergistic with this last one (combination index 0.1-0.6).
A second objective was to analyze PIM2 protein expression by western blot in monoclonal B cells from these samples and correlate it with clinical and biological features. Up to now, it has been evaluated in 18 samples (MBL=4; sCLL=8; aCLL=6,). All of them expressed PIM-2. Expression levels of this protein were significantly higher in active CLL as compared with indolent stages of the disease (p=0,012). Patients with an unmutated IGHV status also displayed higher levels of PIM2 (p=0,01). Finally, samples with high PIM2 levels were slightly more resistant to PIM447 as compared with samples with lower protein levels (IC50 of 7,7 μM vs 5 μM, respectively).
We are currently completing the analysis of the PIM2 levels of remaining samples and we are also measuring the levels of PIM1 protein, what will be available at the meeting.
Conclusions: PIM-Kinase inhibition with PIM447 is effective in vitro in CLL cell lines and ex vivo in samples from patients. It synergizes with other agents especially fludarabine. PIM2 protein levels correlated with the clinical activity of CLL and with the mutational state of IGHV. Although all patients appear sensitive ex vivo to PIM447, further work is required to define PIM2 expression as a marker of sensitivity.
Ocio:Array BioPharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen/Onyx: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Mundipharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Pharmamar: Consultancy, Research Funding; Jassen: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal