Abstract

Introduction: Imatinib have dramatically changed the natural history of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) leading to significant improvement in clinical outcome and survival rates. Recently, treatment free remission (TFR) is one of the goals in CML treatment, and some prospective trials suggest that imatinib therapy may be safely discontinued in CML patients with deep and sustained molecular responses (Mahon Lancet Oncol 2010, Ross Blood 2013, Rousselot JCO 2014). The purpose of this study was to confirm TFR in Japanese CML patients and to define prognostic biomarkers of successful TFR after stopping imatinib.
Methods: Japanese CML patients on imatinib treatment in confirmed deeper molecular response (DMR) for at least two year (>4 log reduction on imatinib therapy for >24 months confirmed by four consecutive PCR tests) and under imatinib treatment for at least 3 years were eligible. Patients treated with other tyrosine kinase inhibitors or who received stem cell transplantations were excluded. MR4.5 was confirmed at the beginning of this study using Ipsogen BCR-ABL1 M-BCR IS-PCR kit in a central laboratory (Sysmex, Kobe, Japan). Primary endpoint was the major molecular remission (MMR) rate at 12 months after stopping imatinib. Molecular recurrence of CML was defined as loss of MMR according to A-STIM criteria (Rousselot JCO 2014).
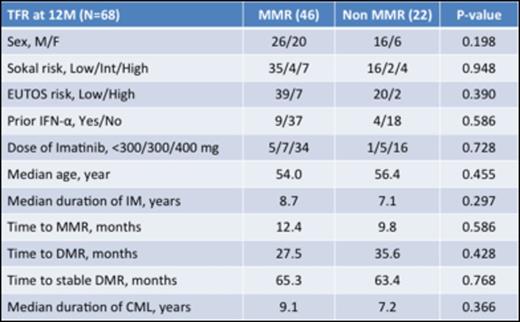
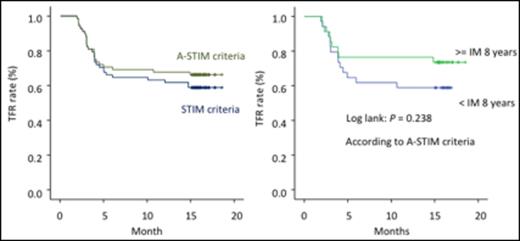
Results: From November 2013 to March 2014, 77 CML patients in chronic phase from 26 institutions were enrolled in this study. Nine were excluded (consent withdrawal n=1, not eligible n=8). Of the eligible 68 patients, 38.2% were female. Median age was 55.0 years (range, 23 to 84), and 13.2% and 16.2 % were high-risk according to EUTOS and Sokal Scores. Thirteen patients were treated with interferon prior to imatinib therapy. Median duration of imatinib treatment was 8 years (range, 3-12 years). The duration of imatinib treatment was less than 5 years in 12%, 5-8 years in 34% and > 8 years in 54% of pts. Time to MMR was 11.5 months (25%-75%, 7.5-22.7 months) and time to DMR (not detected by PCR) was 30.6 months (25%-75%, 17.6-59.9 months). Among the 68 patients, 46 patients (67.6%, 95%CI: [56.5% to 78.8%]) remained without molecular recurrence the first 12 months according to A-STIM criteria, defined as loss of MMR. Moreover, 43 patients (63.2%, 95%CI: [51.8% to 74.7%]) remained without molecular recurrence the first 12 months according to STIM criteria, defined as two consecutive loss of MR4.5 with 1 log increase. On the other hand, 22 patients who lost MMR were treated again with imatinib and all patients achieved MMR within 6 months. Time to 2nd MMR was 40 days. Although there was a trend for a better TFR rate for patients treated longer with Imatinib (Figure 1), no significant difference could be observed for molecular relapse within 12 months according to clinical characteristics including age, sex, Sokal risk score, prior IFN, and time to MMR/DMR (Table 1). Ten patients (15%) showed "withdrawal syndrome" which is transitory musculoskeletal pain within several weeks after imatinib discontinuation, and all patients except one recovered without any treatments.
Conclusion: According to the A-STIM criteria, around 70% of patients with deep and sustained molecular responses could safely stop imatinib. TFR in this prospective Japanese clinical study was higher than previously reported, probably because there were much more patients who treated with imatinib for longer duration than previous studies. We will report prognostic factors in the exploratory research of JALSG-STIM213 study including T/NK-cell profiling in peripheral blood, BIM deletion polymorphism, and ABCG2 421C/A polymorphism at this ASH meeting.
Takahashi:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Otsuka: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Speakers Bureau; Masis: Consultancy; Sysmex: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Hatta:CHUGAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO. LTD: Honoraria; Kyowa Hakko Kirin CO., Ltd, Japan: Honoraria; Celgene K.K.: Honoraria. Usuki:Fuji Film RI Pharma: Other: personal fees; Fujimoto Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Otsuka Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Eisai: Research Funding; Shionogi: Other: personal fees; MSD: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Nippon Shinyaku: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical: Other: personal fees; Takeda Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; SymBio Pharmaceutical: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Sanofi: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Celgene: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Taiho Pharmaceutical: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Shire: Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Other: personal fees, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other. Kobayashi:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding. Naoe:Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Patents & Royalties; Pfizer Inc.: Research Funding; Toyama Chemical CO., LTD.: Research Funding; Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd.: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma Inc.: Research Funding; Celgene K.K.: Research Funding; FUJIFILM Corporation: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd.: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal