Abstract
Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) is an extremely rare disorder during childhood, characterized by clonal expansion of megakaryocytic and thrombocytic lineages in bone marrow, leading to a persistent increase in the number of circulating thrombocytes and thus increasing the risk for thrombotic and hemorrhagic events. Most of children with ET have JAK2 V617F mutation (1). MPL and CALR mutastions have been reported in a small proportion of adult ET patients. However, it is extremely rare in children. Herein we present two cases of pediatric ET with different rare mutations.
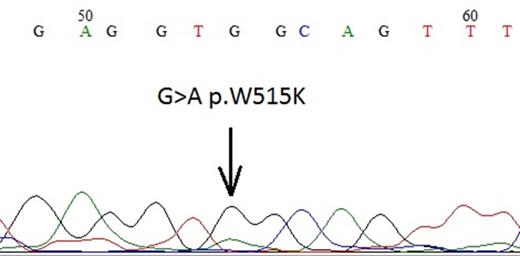
Case 1: 15-year old female presented with Budd-Chiari syndrome and thrombocytosis (1500x109/L). Bone marrow smear and biopsy were consistent with ET. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in this case of ET, we investigated candidate gene alterations. BCRABL, JAK2 V617F and calreticulin mutations were negative. Thus we analyzed codon 515 of MPL gene. The patient was found to have mutation for MPL W515K (figure 1). The patient who presented with BCS was diagnosed as ET with MPL W515K mutation. Hydroxyurea therapy at a dose of 20mg/kg/day was started. After 10 days, enoxaparin dose was reduced to single dose daily (1mg/kg/day) as a maintenance anticoagulation. The patient underwent liver transplantation at the end of the 3rd month of treatment. Warfarin treatment was started to patient after transplantation.
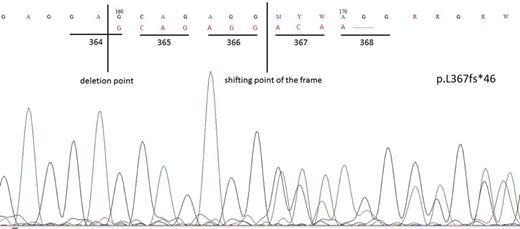
Case 2: Nine year old female was applied to our policlinic because of thrombocytosis identified in routine control (1300x109/L). Secondary causes of thrombocytosis were excluded. Bone marrow smear and biopsy were consistent with ET. We investigated candidate gene alterations. BCRABL, JAK2 V617F and MPL mutations were negative. CALR type I mutation was identified (figure 2). Hydroxyurea treatment was successfully reduced the platelet count.
Discussion: Thrombocytosis occurs in about 6-15% of children, but ET is very rare in children (2). Most of cases with pediatric ET have JAK2V617F mutation. Our first case has MPLW515K mutation. To our knowledge, this is the first pediatric patients of ET mutated W515K. The other patient has CALR mutation. This was also extremely rare mutation in children (3). We believe that our two cases will contribute to the literature.
References
1. Fu R, Zhang L, Yang R. Paediatric essential thrombocythaemia: clinical and molecular features, diagnosis and treatment. Br J Haematol. 2013 Nov;163(3):295-302.
2. Hasle H. Incidence of essential thrombocythaemia in children. Br J Haematol. 2000 Sep;110(3):751.
3. Giona F, Teofili L, Capodimonti S, Laurino M, Martini M, Marzella D, et al. CALR mutations in patients with essential thrombocythemia diagnosed in childhood and adolescence. Blood. 2014 Jun 5;123(23):3677-9.
W515K mutation first case with ET
CALR type I mutation in second case with ET.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal