Abstract
Nonacog alfa is a recombinant factor IX (rFIX) product for hemophilia B, developed by CJSC «GENERIUM» (Russia). Nonacog alfa is safe with regard to transmitted infections because proteins of animal and human origin (including albumin) are not used in the process of rFIX production. Ðharmacokinetic parameters, safety and efficacy of Innonafactor has been studied in the phase I study in patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B.
The primary aims of the study were to:
1. Determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of nonacog alfa in patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B.
2. Assess the safety and tolerability of different doses of nonacog alfa in patients with severe and moderate hemophilia B.
The secondary aims of this study were to:
1. Set the maximum tolerated dose of nonacog alfa in practically possible range of doses.
2. Evaluate rFIX activity and the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) after nonacog alfa infusions in doses 50 IU kg-1 and 75 IU kg-1.
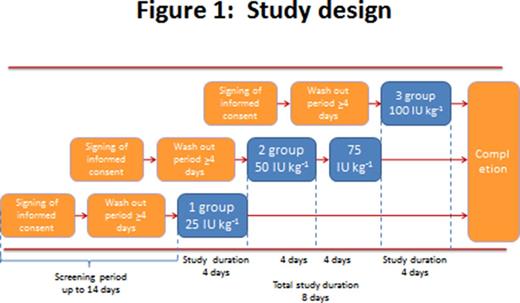
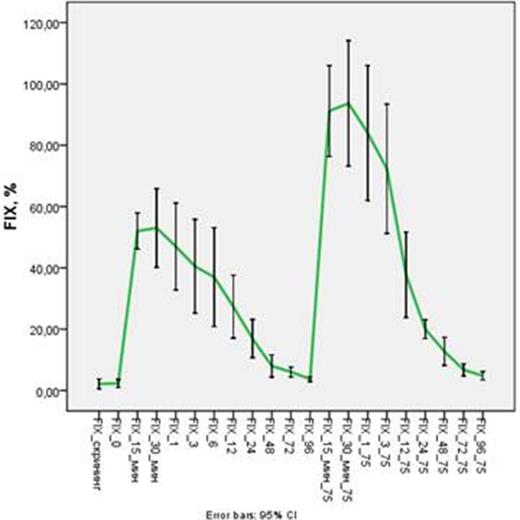
During phase I clinical study the pharmacokinetic properties, safety and tolerability of the new nonacog alpha were evaluated. After screening and washout period lasting at least 4 days 12 men, aged from 23 to 50 years old with severe (n = 6) and moderate (n = 6) hemophilia B were included in the study. Patients consecutively were enrolled in 3 groups: in the 1st group (n = 3) nonacog alfa was injected slowly intravenously in a single dose of 25 IU kg-1, in the 2nd group (n = 6) - a single dose of 50 IU kg-1, then after 4 days of observation and laboratory monitoring - a second single dose of 75 IU kg-1 was administered, in the 3rd group (n = 3) - a single dose of 100 IU kg-1 (fig.1). The introduction of the nonacog alfa in doses of 50 and 75 IU kg-1 resulted in the normalization of FIX activity and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) within 15 min after injection. Normal FIX activity was maintained for at least 1 h after injection of the nonacog alfa at dose of 50 IU kg-1 and for 6 h after drug administration at a dose of 75 IU kg-1. Reduction of the FIX activity less than 5% was observed not earlier than 72 h after injection of the both drug doses. Significant increase of the APTT was observed only after 12 h after injection of the nonacog alfa at a dose of 50 IU kg-1 and after 24 h after administration of the nonacog alfa at a dose of 75 IU kg-1.
The pharmacokinetics of nonacog alfa was studied at doses of 50 and 75 IU kg-1 (fig.1). A single dose injection of nonacog alfa led to a rapid accumulation of drug in the blood [median value of time to reach the maximum concentration (Cmax) - Tmax amounted to 0.33 ± 0,13 h] with the achievement of the average Cmax depending on the input dose (53,18 ± 9,79 IU DL-1 for doses of 50 IU kg-1 and 94,35 ± 18,47 IU DL-1 for doses of 75 IU kg-1) and the gradual elimination of the drug from the body [median value of area under the curve based on the concentration of FIX in plasma from the time of the study (AUC0-96 h) - 1069,9 ± 321,1 IU DL-1 × h for doses of 50 IU kg-1 and 1604,2 ± 389,41 IU DL-1 × h for the dose of 75 IU kg-1, the AUC0-∞ - 1125,49 ± to 300.36 and 1700,82 ± 369,95 IU DL-1 × h, the elimination half-life (T1/2) - is 24.05 ± 7,67 and 25,18 ± 6,16 h, respectively].
Nonacog alfa was well tolerated regardless of the administered dose. The maximum tolerated dose was not established because it exceeds the studied doses of the drug. A single application of the nonacog alfa in doses from 25 to 100 IU kg-1 was not accompanied by toxic, thrombogenic, immunogenic and allergic reactions.
Average pharmacokinetic curve of the coagulation factor IX activity in the blood plasma during administration of two doses of the drug
Average pharmacokinetic curve of the coagulation factor IX activity in the blood plasma during administration of two doses of the drug
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal