Abstract
Background: Eltrombopag, an orally bioavailable thrombopoietin receptor agonist, is approved for the treatment of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (adults and children), hepatitis C virus-related thrombocytopenia, in multiple countries. In the US, eltrombopag is also approved for severe aplastic anemia (SAA) in patients with insufficient response to immunosuppressive therapy. In SAA, patients frequently take cyclosporine (CsA), concurrently with eltrombopag. Eltrombopag is a substrate of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), and CsA is reported to be an inhibitor of this transporter. To assess this BCRP interaction further, the effect of CsA on plasma pharmacokinetics (PK) of eltrombopag was assessed in a clinical drug-drug interaction study in healthy human subjects.
Methods: In a phase 1, open-label, randomized, three-period crossover study, healthy subjects were randomized to one of the three treatment sequences: (D0, D1, D2), (D1, D0, D2), or (D1, D2, D0), where D0 = 50 mg eltrombopag, D1 = 50 mg eltrombopag + 200 mg CsA, and D2 = 50 mg eltrombopag + 600 mg CsA. Eltrombopag was administered on the first day of each treatment period. On Day -1 of each treatment period, subjects checked into the clinical research unit, where they remained until the 72-hour PK blood draw on Day 4. After a 3- to 10-day washout period, they returned for Day 1 of the next treatment period. The total duration of a subject's participation in the study from screening to final discharge was approximately 6 weeks (assuming 3-day washouts between treatment periods). Safety and PK were analyzed during each period.
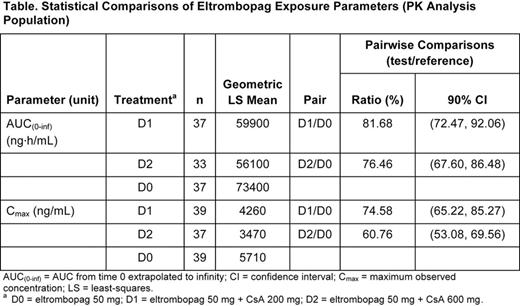
Results: Thirty-nine healthy subjects were randomized to receive treatment (13 subjects per treatment sequence); 28 (72%) were men and 11 (28%) were women. All 39 subjects completed the study; all subjects were included in the PK and safety analyses. In general, the plasma eltrombopag PK profiles were consistent across the three treatment arms and consistent with that previously reported for eltrombopag in healthy adult subjects (see Figure). Plasma eltrombopag PK parameters and their statistical comparisons are shown in the Table below. On average, eltrombopag AUC(0-inf) and Cmax decreased by 18% and 25%, respectively, when coadministered with 200 mg CsA and decreased by 24% and 39% when coadministered with 600 mg CsA. Median time to Cmax (tmax) of eltrombopag increased from 3 hours to 4 hours in the presence of 200 mg and 600 mg CsA. The most common adverse events (AE) were hot feeling (62%), headache (36%), and nausea (18%). Except for one subject who had a Grade 2 headache, all AEs reported during the study were Grade 1 events. No clinically significant abnormal electrocardiograms were reported. There were no severe adverse events in this study.
Conclusions: Given that the eltrombopag dose adjustment is permitted during the course of treatment for achieving the target platelet count, the decrease in exposure following co-administration of 200 mg or 600 mg CsA was not considered clinically meaningful, and therefore no starting dose adjustment is recommended when eltrombopag is co-administered with CsA.
Funding: This study was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline; eltrombopag is an asset of Novartis AG as of March 2, 2015.
Zhang:Parexel: Employment. Erickson-Miller:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties: Patents but no royalties. Chan:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment. Zhou:Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal