Abstract
Objective: To investigate the autophagy and apoptosis on acute myelogenous leukemia U937 cell induced by rapamycin.
Methods: U937 cells was subcultured, and was set up blank control group (normal) and rapamycin treated groups (3 groups, 12h, 24h, 48h). The rapamycin treated groups were separately treated by 2¦ÌM concentration of rapamycin after 12h, 24h and 48h. The cell morphology of U937 cells treated by rapamycin was observed after 12h 24h and 48h. The survival rate of cells was detected by CCK-8 method. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC/PI double labeled. Use real-time PCR to detect the level of mRNA expression in autophagy specific protein maker LC3-¢òin different treated times by rapamycin. Rapamycin LC3 protein expression levels after treatment was detected by western blot method.
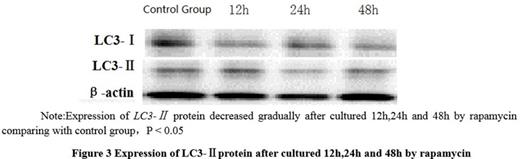
Results: Visible under inverted microscope, the rapamycin treatment groups¡¯ cell number reduced gradually after cultured 12h, 24h and 48h, smaller volume, cell rupture, increase the nucleus pycnosis and cellular debris(Figure 1). With the extension of time, U937 cells survival rate is falling, compared with control group, with statistical significance(P=0.031; P<0.05). Rapamycin treatment U937 cells after 12 h, 24 h and 48 h, U937 cell apoptosis rate increased, compared with control group, with statistical significance (P=0.027; P< 0.05, Figure2). Rapamycin treatment U937 cells after 12 h, 24 h and 48 h, LC3-¢ò mRNA expression and protein expression were cut, compared with control group, with statistical significance(P=0.029; P<0.05, Figure 3).
Conclusion: Rapamycin can induce autophagy and apoptosis of U937 cells. Autophagy protein LC3-¢ò in gene and protein expression level lowered, LC3-¢ò may play an important role in regulating the leukemia cell autophagy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal