Abstract
Background and Objective:
There are 3 members in Pim family, Pim-1, Pim-2 and Pim-3. They are serine/threonine kinase coding proto-oncogene. It is reported that Pim-1 plays a role in solid tumor, leukemia and polycythemia vera, et al. Pim-3, as a newly cloned oncogene has discovered to functioning in hepatic carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, et al. We are trying to find out the roles of Pim1 in acute myeloid leukemia.
Methods:
1 Evaluate the expressions of Pim family genes in acute myeloid leukemia patients and analysis the profile of Pim expressions with clinical characteristics.
2 Up-regulating the expression of Pim1 in AML cell lines by transient transfection or long-term infection through GFP-expressing plasmids and lenti-virus system and analyze the proliferation, apoptosis and chemotaxis features of the transfected AML cell lines.
Results:
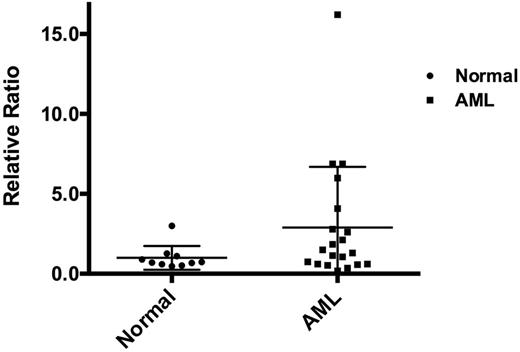
1 Our investigation showed that Pim-1 is up-regulated in around 15% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients.
2 As shown in growth curves and apoptosis assays, over expression of Pim-1induces growth up-regulation and anti-apoptosis. We hypothesized that phenomenon could be originated from the enhanced expression of c-myc, cyclin D1 and Bad phosphorylation shown in western blotting analysis.
3 Our chemotaxis assay and bone marrow stromal cell co-culture model demonstrated that overexpression of Pim-1can enhance the AML cells chemotactic movement toward SDF-1¦Á, with calcium influx increment and phosphorylation of CXCR4.
4 Flow cytometry analysis and confocal immunofluorescence observation demonstrated the up-regulated CXCR4 expression and internalization induced by SDF-1¦Á.
5 We also checked the angiogenesis and adhesion molecule during the process but did not show any contribution.
Conclusion:
Pim-1, beyond as an oncogene, can promote growth or anti-apoptosis of AML cells, can interact with microenviroment through SDF-1¦Á-CXCR4 axis. The interplay between AML cells and microenviroment mediated by Pim-1 can make sense in AML target therapy and make a good adjunctive for transplantation conditioning regimen.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal