Abstract
Introduction: Pomalidomide is an IMiD that was recently approved for the use of relapsed MM failing lenalidomide and bortezomib. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy of pomalidomide-containing regimens (PCR) for heavily-pretreated relapsed or refractory MM (RRMM) at Tom Baker Cancer Center and the Cross Cancer Institute in Alberta.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the records of all patients with RRMM treated with PCR at our Institutions between 01/10 and 04/15. Patients received oral pomalidomide 2-4mg/d on days 1-21/28, and dexamethasone 20 mg or 40 mg on a weekly schedule, few cases were treated with PD in addition to bortezomib or cyclophosphamide. Definitions of response and progression were used according to the EBMT modified criteria. A p-value was considered statistically significant if <0.05
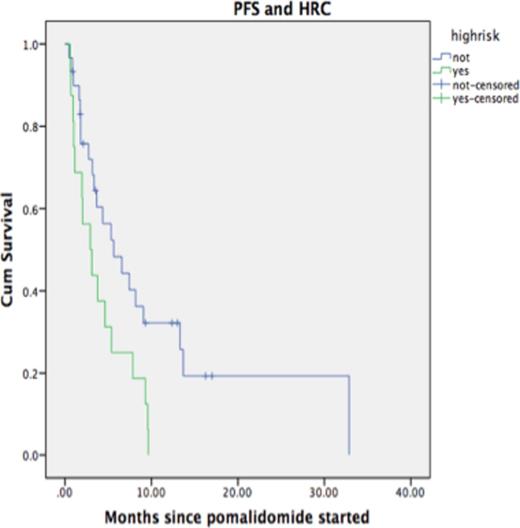
Results: Between 01/10 and 04/15, 90 patients were identified for the study. Clinical and laboratory characteristics are listed in Table 1. The median number of therapies prior to PCR was 3 (2-11). All patients received lenalidomide and bortezomib or another proteasome inhibitor prior to PCR; 47 patients had bortezomib, 31 had lenalidomide and 11 had both immediately prior to PCR. 21 patients out of 47 receiving bortezomib prior to PCR responded (44%) versus 32.2% (10/31), and 27.2% (3/11), for those receiving lenalidomide and lenalidomide/bortezomib, respectively prior to PCR (p=0.5). Four patients received pomalidomide at a dose of 2mg, 3 at 3mg and the rest at 4mg. After a median of 4 cycles, the ORR was 41.1%. The median time to first response was 8 weeks, with majority of cases achieving at least PR after 2 cycles. FISH cytogenetics at relapse, were available in 46 patients and 16 were high risk (HR, 34.8%). At a median follow-up of 8 months, 44% of patients were alive and 77.8% had already progressed. Median OS was 12.2 months and median PFS 4.0 months. Median PFS was 5.6 months in the group with standard risk (SR) disease compared to 2.9 months for the HR group (p=0.022). Median OS for SR patients was 19.4 months compared to 8 months for the HR group (p=0.11). Two patients discontinued therapy due to thrombocytopenia.
Conclusion: Pomalidomide is an efficacious drug for the treatment of RRMM. The current report confirms the ORR seen in previous studies and suggests a trend to poorer outcomes for the HR cytogenetics group. Further assessment of combinations of pomalidomide with newer agents especially in the setting of HR cytogenetics are warranted.
Clinical Characteristics and Response assessment for patients with MM receiving pomalidomide-containing regimens
| Characteristic . | N=90 . |
|---|---|
| Age (median) | 65 |
| Gender Male Female | 46 (51.1%) 44 (48.9%) |
| Hb (g/L) | 108 (75-160) |
| Calcium (µmol/L) | 2.3 (1.98-3.28) |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 85.5 (60-1052) |
| B2microglobulin (µmol/L) | 3.96 (1.38-25.2) |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35.5 (11-52) |
| Stage I Stage II Stage III | 15.9% 52.3% 31.8% |
| LDH (IU/L) | 190 (71-669) |
| BMPC (%) | 40% (5-90%) |
| Heavy chain: IgG IgA IgD Biclonal IgM FLC oncly Non-secretory | 61.1% 20% 0 1.1% 5.6% 10% 2.2% |
| Light chain: Kappa Lambda | 64.4% 33.3% |
| Prior therapies: ASCT Thalidomide Lenalidomide Bortezomib Carfilzomib | 53.3% 21.1% 100% 98.9% 8.9% |
| High risk (t(4;14), t(14;16), and p53 del Standard risk | 34.8% 65.2% |
| Chemotherapy regimen DPPACE Pomalidomide alone Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone Pomalidomide/Bortezomib and Dexamethasone Pomalidomide and Bortezomib Pomalidomide, cyclophosphamide and prednisone | 1.1% 1.1% 88.9% 6.7% 1.1% 1.1% |
| Response rate ORR Complete Response/nCR VGPR PR SD Minimal Response Progression | 41.1% 2.2% 5.6% 33.3% 18.9% 10% 30% |
| Patients that have progressed | 77.8% |
| Patients that have died | 55.6% |
| Characteristic . | N=90 . |
|---|---|
| Age (median) | 65 |
| Gender Male Female | 46 (51.1%) 44 (48.9%) |
| Hb (g/L) | 108 (75-160) |
| Calcium (µmol/L) | 2.3 (1.98-3.28) |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 85.5 (60-1052) |
| B2microglobulin (µmol/L) | 3.96 (1.38-25.2) |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35.5 (11-52) |
| Stage I Stage II Stage III | 15.9% 52.3% 31.8% |
| LDH (IU/L) | 190 (71-669) |
| BMPC (%) | 40% (5-90%) |
| Heavy chain: IgG IgA IgD Biclonal IgM FLC oncly Non-secretory | 61.1% 20% 0 1.1% 5.6% 10% 2.2% |
| Light chain: Kappa Lambda | 64.4% 33.3% |
| Prior therapies: ASCT Thalidomide Lenalidomide Bortezomib Carfilzomib | 53.3% 21.1% 100% 98.9% 8.9% |
| High risk (t(4;14), t(14;16), and p53 del Standard risk | 34.8% 65.2% |
| Chemotherapy regimen DPPACE Pomalidomide alone Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone Pomalidomide/Bortezomib and Dexamethasone Pomalidomide and Bortezomib Pomalidomide, cyclophosphamide and prednisone | 1.1% 1.1% 88.9% 6.7% 1.1% 1.1% |
| Response rate ORR Complete Response/nCR VGPR PR SD Minimal Response Progression | 41.1% 2.2% 5.6% 33.3% 18.9% 10% 30% |
| Patients that have progressed | 77.8% |
| Patients that have died | 55.6% |
BMPC: Bone marrow plasma cells; FLC: Free-light chains only; CC: Conventional cytogenetics
Progression-Free survival according to high-risk cytogenetics by FISH
Progression-Free survival according to high-risk cytogenetics by FISH
Jimenez-Zepeda:J&J: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria. Venner:Amgen: Honoraria; J&J: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Sandhu:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Duggan:Jansen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Neri:Celgene: Research Funding. Bahlis:Johnson & Johnson: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy; Johnson & Johnson: Consultancy; Johnson & Johnson: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal