Abstract
Background: Course of multiple myeloma (MM) is associated with hemostatic disorders that can lead to bleeding or thrombosis. According to previous studies the most risky period of time for thrombotic complication is the first year after diagnosis.
Aims: The study was aimed to analyze of hemostasis conditions in newly diagnosed (ND) MM patients (pts) and to compare their initial status with the status after induction therapy (IT) and with the status of healthy volunteers (HV).
Patients and Methods: 17 pts with ND MM: 10 males, 7 females at the age of 26-72 (median age - 54) were involved in the study. The distribution of the stages among the participants according to Durie-Salmon system: stage I - 1 pts, stage II - 5 pts, stage III - 8 pts, stage III in 8 pts. Immunochemistry variants: IgG - 11 pts, IgA - 2 pts, MM B-J - 4 pts. Average paraprotein (PP) level was 34g/L (0,8 - 78).
HV group consisted of 26 persons without serious diseases, 40 - 70 y.o., (median age 50).
Hemostasis analysis was taken place twice: before and after the IT which included 4-8 bortesomib-containing cycles (PAD, VCD, VD). After the IT 6 pts achieved CR, 5 pts - VGPR, 4 pts - PR and 1pt was resistant. Average value of PP decreased to 8 (0,1 - 29,7).
Routine tests: activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT, normal rate 25-38 sec), international normalized ratio (INR, normal rate 0.85-1.15), D-dimer concentration (normal rate 0-500 mkg/l).
Two global tests: thrombin generation test by using endogenous thrombin potential (ETP, normal rate 760-1450 nM*min) and thrombodinamics (TD), characterized by the initial clot growth velocity (Vi, normal rate 36-56 um/min), stationary velocity (Vst, normal rate 20-30um/min), and density of a fibrin clot measured by light scattering from clot (D, normal rate 16000 - 32000 conventional units).
Hypocoagulability wasassessedby data APTT > 38 sec, INR> 1.15, ETP < 760 nM*min, Vi < 36 um/min, Vst < 20 um/min, D < 16000 cu. Hypercoagulability was considered in cases when APTT < 25 sec, INR < 0,85, D-dimer > 500 ng/ml, ETP > 1450 nM*min, Vi > 56 um/min, Vst > 30 um/min, D > 32000 cu.
Statistics. Ðaired t-test and Pearson correlation coefficient (r) have been got with SAS 9.1. 95- percent CI has been used.
Results: ND MM APTT evaluation demonstrated normal coagulation in 13pts and extended one in 4pts (48 sec [38-57]). INR was normal in 13 and increased in 4 cases (1.3% [1.2-1.5]). Increased concentration of D-dimer was revealed in 7pts (3810 ng/ml [350-7270]). ETP was normal in 12 and increased in 5 cases (1592 nM*min [1406-1779]). Vi was normal in 11 and increased in 6pts (62 um/min [58-65])). Vst was reduced in 1pts (15um/min), normal in 10pts and increased in 6pts (36um/min [28-44]). Density of clot was normal in 8 pts and decreased in 9pts (9769 UE [6379-13160]). (Tab. 1)
After IT only 1 pt had elongated APTT (44sec), the results of the others were normal. INR was normal in all cases. D-dimer concentration was normal in 12pts and increased in 5pts, but this data was statistically less (1080ng/ml [500-1003]) than in ND MM. ETP was normal in 13pts, elevated in 4 pts (1604 nM*min [1099-2109]). Vi was normal in 12pts and increased in 4pts (61 um/min [57-65]). Vst was decreased in 2pts (13 and 14um/min), normal in 13pts and increased in 2 (32 and 43um/min). Density of clot became normal in 14pts, but clot remained not dense enough in 3 pts (9512 [13606-15779]). (Tab. 1)
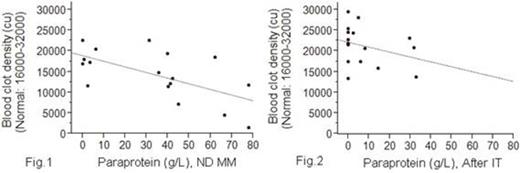
We found that inverse linear relationship between PP level and blood clot density was more significant in ND MM (Fig. 1, fig.2). Statistically significant difference was revealed between clot density in ND MM and pts in PR or CR and between them and HV (Fig. 3). Furthermore, a significant difference was identified between D-dimer concentration in ND MM pts and after IT (Fig. 4).
Conclusions: MM pts have complex disorders of hemostasis characterized by a tendency to hyper- and hypocoagulation at the same time. In spite of an increased tendency to thrombosis confirmed by D-dimer, ETP, TD, pts are under risk of bleeding related to the formation of defective clot and elongated APTT. According to the obtained results one can assume that PP embedded in the clot and disorder its structure. However, further studies are needed to confirmthat assertion.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal