In this issue of Blood, Juilland and colleagues reveal the expression pattern and the role of different members of the activating transcription factor (ATF) family in survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells.1
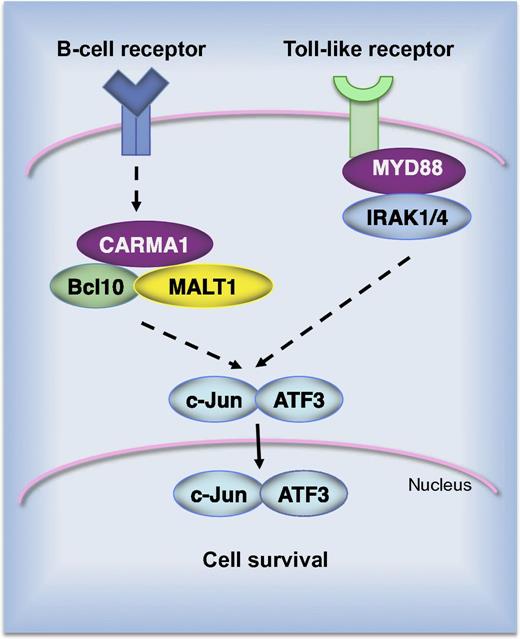
AP-1 complexes of the c-Jun/ATF3 type promote survival of ABC DLBCL cell lines. Constitutive B-cell receptor signaling alone or in combination with activating mutations in Toll-like receptor signaling results in nuclear accumulation of c-Jun/ATF3 complexes. Short hairpin RNA–mediated silencing of signaling molecules, such as CARMA1, MALT1, MyD88, or IRAK1, results in depletion of ATF3 in cells of the ABC subtype.
AP-1 complexes of the c-Jun/ATF3 type promote survival of ABC DLBCL cell lines. Constitutive B-cell receptor signaling alone or in combination with activating mutations in Toll-like receptor signaling results in nuclear accumulation of c-Jun/ATF3 complexes. Short hairpin RNA–mediated silencing of signaling molecules, such as CARMA1, MALT1, MyD88, or IRAK1, results in depletion of ATF3 in cells of the ABC subtype.
In adults, DLBCL is the most common lymphoid malignancy. It is a heterogeneous disease composed of multiple molecular subtypes that differ in their expression of hundreds of genes, their responsiveness to chemotherapy, and survival rates after chemotherapy.2 The activated B-cell (ABC)–like subtype (ABC DLBCL) is the most aggressive form of DLBCL with the lowest cure rate. Initially, the constitutive activity of the nuclear factor–κB signaling pathway was identified as a major feature of ABC DLBCL.3 However, recently, several independent studies have reported elevated expression levels and activity of Jun transcription factors in ABC DLBCL cell lines and clinical specimens.4-6 Although Jun factors are primarily involved in regulating the cell cycle and apoptosis,7 a large number of inducible genes contain Jun-binding sites in their promoters or enhancers and, therefore, they can be considered as Jun-target genes. But the complexity of this regulation starts with the fact that dimerization of Jun is required prior to its binding to DNA. Different Jun factors (c-Jun, JunB, and JunD) can form homodimers or heterodimers with proteins belonging to the FOS, ATF, and MEF families, creating the activator protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factor.8 The composition of AP-1 complexes determines the genes that are regulated, either positively or negatively.
A report from Juilland and colleagues reveals novel and exciting findings regarding the role and molecular composition of AP-1 in DLBCL.1 Using an unbiased biochemical approach, they identified ATF2, ATF3, and ATF7 as constitutive binding partners of Jun in lymphoma cells. Although Jun/ATF2 and Jun/ATF7 complexes were abundant in the majority of cell lines, ATF3 was exclusively expressed in cell lines derived from the ABC subtype of DLBCL (see figure). The clinical relevance of this observation was evaluated in patient biopsies. In a cohort of 350 DLBCL patients, the ATF3 messenger RNA level was significantly higher in the ABC vs the germinal center B-cell (GCB) subtype. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed strong nuclear ATF3 expression in tumors from ABC DLBCL patients. Altogether, these data raise a question about the role of ATF3 in ABC DLBCL. Interestingly, ATF3 has been shown before to contribute to the malignant growth of Hodgkin lymphoma cells and selective knockdown of ATF3 by RNA interference suppressed proliferation and decreased viability of Hodgkin cells.9 On the other hand, ATF3 overexpression resulted in increased apoptosis of solid tumors, as shown in PC3 human prostate cancer cells, HCT-116 human colorectal cancer cells, and others.10 Therefore, Juilland and colleagues used short hairpin RNA–mediated silencing of individual components of AP-1 complexes, as well as the dominant-negative construct that blocks AP-1 activity, to assess the role of Jun/ATF dimers in ABC DLBCL. They found that depletion of ATF3 reduced the viability of the majority of the ABC-type lymphoma cells but had no effect on GCB DLBCL. Interestingly, knockdown of ATF2 also affected cell survival but it simultaneously decreased the expression of ATF3. This effect is consistent with the fact that the transcription of the atf3 gene is regulated by the c-Jun/ATF2 dimer. Thus, data presented in this study indicate that Jun/ATF complexes are important drivers of survival and proliferation of ABC DLBCL. This finding is an important contribution to our understanding the signaling pathways used by lymphoma cells to survive.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The author declares no competing financial interests.